Hot-rolled pipe: production technology and current standards
How does the production of seamless pipes method of hot deformation? What GOST on steel seamless hot-rolled pipes are currently in effect? Let's try to answer these questions.

Production technology
Let's start with the study of production technology.
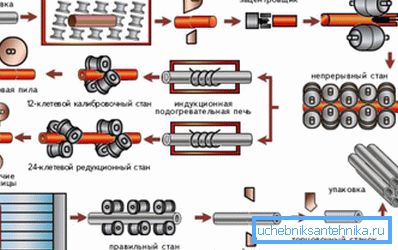
- Cylindrical billets (rods) are loaded into the furnace using an electric bridge crane. The loading is controlled by the operator and is performed individually as the already heated rods are processed. Unloading - also piece, roller conveyor.
- The rods are cut into blanks of measured length.
Curiously: the design of scissors provides for the presence of heat-resistant screens that protect the hydraulics from overheating by infrared radiation. The temperature of the workpiece at the exit of the furnace significantly exceeds 1000 degrees.
- At the piercing mill, the monolithic cylinder turns into a hollow: the rollers feed the workpiece towards the piercing rod.
- A mandrel is inserted into the former rod (now called a sleeve), on which rolling will be performed. Then the sleeve passes the rollers, which turn it into a pipe slightly thicker than the required diameter.
- The mandrel is removed, and then sent to the bath for cooling and lubrication.
- The rear end of the pipe is cut with a saw: when removing the mandrel, it is partially deformed.
- The pipe is heated by an induction heater and enters the reducing rollers, calibrating it to the target size. The rollers are continuously cooled with water during operation.
- After cooling and re-straightening with rollers, a cold-cutting stage begins: a single-layer package of pipes is pressed and cut into lengths.
- After passing the Quality Control Department, finished products are tied up in packages and sent to the warehouse.
Regulations
What should be seamless hot-rolled pipes according to GOST? First, let's look at the numbers governing the standards of production.
There are two of them:
- GOST 8732-78 for seamless steel hot-deformed pipes determines their assortment and maximum tolerances;
- GOST 8731-74 contains technical requirements for products and describes quality control methods.
Curiously: the standard number 8731-78 is mentioned on the official websites of a number of suppliers. There is an obvious confusion: the document was adopted in 1974 and put into effect on January 1, 1976. It can be assumed that the non-existent GOST 8731-78 for steel seamless hot-rolled pipes are 8731-74 and 8731-87 mixed in someone's wild imagination, adopted during the restructuring and later canceled.
Let's get acquainted with the requirements of documents.
GOST 8732-78
A complete list of sizes with which seamless pipe can be produced according to GOST 8732-78 is too large to be transferred; we mention only the ranges.
- Diameter - from 20 to 550 mm.
- Wall thickness - from 2.5 to 75 millimeters.

- The mass of the running meter varies from 1.08 to 878.57 kg.
By the way: manufacturers and dealers usually indicate the price of any steel not per unit of length, but per ton. If you are going to make some metalwork with your own hands, you will have to convert the moldings into weight when purchasing.
- The length of pipes of unmeasured length provided for by the standard is from 4 to 12.5 meters. However, in agreement with the customer it is allowed to manufacture large or smaller segments.

- Maximum deviations in length are +10 mm with a length of up to 6 meters and up to +15 mm with a length of more than 6 m or a diameter of more than 152 mm.
The tolerances for the outer diameter for the convenience of the reader are summarized in the table.
| Outer diameter, mm | Maximum deviations | |
| Increased manufacturing accuracy | Normal manufacturing accuracy | |
| Up to 50 | 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm |
| 50 - 219 | 0.8% | one % |
| Over 219 | one % | 1.25% |
Similarly, we will do with permissible deviations in wall thickness.
| Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness mm | Maximum deviations,% | |
| Increased manufacturing accuracy | Normal manufacturing accuracy | ||
| Up to 219 | 15 and less | 12.5 | +12.5; -15 |
| 15 - 30 | +ten; -12,5 | 12.5 | |
| 30 and more | ten | +ten; -12,5 | |
| Over 219 | 15 and less | +12.5; -15 | |
| 15 - 30 | 12.5 | ||
| 30 and more | +ten; -12,5 |
In coordination with the customer the pipes can be delivered:
- By wall thickness and internal diameter;
- By varying thickness and by outer and inner diameter.

GOST 8731-74
We turn to the study of the second document.
Products of interest to us are made:
- With the rationing of mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength and relative elongation) of steel grades St6sp, St5sp, St4sp and ST2sp. With a wall thickness of more than 10 mm, hardness is also standardized.
- With standardization of chemical composition.
- With rationing and composition, and mechanical properties.
- With rationing of composition and selective control of images after heat treatment.
- Without rationing, but with obligatory hydraulic tests.
On the surface of the products are not allowed the presence of cracks, sunsets and flaws. Minor defects and dross, however, may be present if they do not remove the walls beyond the tolerance limits.
The ends of the pipes are cut at right angles. However, the standard also allows steel seamless hot-rolled pipes with a bevelled weld. Chamfer angle - at least 70 degrees to the longitudinal axis. (See also the article Butt-Weld Pipe: Features.)

When cutting pipes with a wall thickness of more than 20 mm, not only miter saws, but also gas cutters can be used; in this case, the allowance for the cut should be not less than the same 20 mm.
Acceptance of pipes by the customer is carried out in lots. The text of GOST contains detailed instructions on the formation of batches: the products in them are selected according to diameter, wall thickness, steel grade, type of heat treatment and are supplied with a single document certifying quality. (See also the article Cast Iron Sewage Pipes: Features.)

The number of products in one batch is also agreed: for a diameter up to 76 mm - no more than 400 pieces, with a larger diameter - no more than 200.
However: with a diameter of less than 76 mm and a wall thickness of 2.5 mm, the batch can be increased to 600 units.
Regulatory document lists possible test methods. However, without technical details: for them, he sends the reader to the relevant standards.
The following types of tests are provided:
- Control macrostructure;
- Visual inspection with grading of detected defects;
- Determination of chemical composition;
- Tensile test;
- Hardness tests;
- Flattening;
- On the bend;
- On boarding;
- For distribution;
- Hydraulic test.

Conclusion
We hope that the information offered to the reader will be useful. As usual, you can familiarize yourself with additional thematic materials by viewing the video in this article. Successes!