Pipeline corrosion protection
We all know that protecting the pipeline from corrosion is an essential part of a set of technical measures to create the conditions for its long-term operation. At the same time, it is necessary to clearly realize that not only network designers and builders should take an active part in creating such protection, but also their end users, that is, each of us.
In the most general case, the destruction of metal structures during operation is due to electrochemical reactions that occur when they interact with a wet environment. At the same time, the oxidation rate of metal pipes is largely determined by the chemical composition of the liquid, and also depends on the characteristics of the soil at the site of their installation.

That is why the choice of one or another method of combating corrosion should take into account the specific conditions in which the destructive processes themselves take place. The complex of protective measures to combat them may include the following activities:
- use for arranging pipelines of materials that are slightly susceptible to corrosive destruction (stainless steel or copper, for example);
- special chemical treatment of the fluid in the highways, allowing to correct its anti-corrosion properties;
- combined use of active and passive methods of protecting pipelines from corrosion, including their electrochemical treatment.
If using corrosion-resistant materials for arranging pipeline systems is more or less clear, the implementation of the last two methods of protection requires special explanations.
Chemical water treatment
It is known that the water circulating through the pipeline contains in its composition active impurities, giving it a certain chemical aggressiveness. Such aggressiveness can be associated with the content of chlorine compounds in it, as well as active carbonate (bicarbonate) impurities.
The main task of chemical water treatment is to change its structure by transforming an aggressive and tough medium into a milder form (into the so-called weakly calcified liquid). The lowered rigidity index of the carrier ensures the formation of small salt deposits of calcium [Ca (OH) 2] or soda (NaOH) on the internal surfaces of the pipelines, creating an artificial coating that reliably protects the metal from possible corrosive effects.
In addition, the addition of special inhibiting substances to the water carrier can dramatically slow down the corrosion process, reducing its level from local to minor (local).
In the sections of the underground pipeline, which ensure the distribution of the water carrier at various points of water intake, the most effective method of corrosion protection is the introduction of special “sequestering” additives - the so-called polyphosphates. In galvanized steel pipelines, for example, the addition of polyphosphates (phosphates or silicates) also leads to the formation of a thin protective film on the inner surface of the pipes, protecting the metal from corrosion.
Tip! The use of such reagents in drinking water mains with drinking water is permissible only if the requirements of the current sanitary and epidemiological standards are met.
Active and passive methods of protecting the material pipe
First of all, we note that the known methods of protecting underground metal structures from corrosion damage can be divided into passive and active. The first of them involves the application to the outer surface of pipes of special protective coatings prepared on the basis of such well-known processing products, such as coal tar pitch or bitumen. In some cases, polymer or epoxy resins are used to prepare such coatings.

Since the passive method does not always succeed in ensuring complete protection of the pipeline, at the same time it uses the so-called active corrosion protection based on the effect of cathode polarization of metals by their electrochemical treatment. Such an approach can be implemented in two different ways, one of which, electroplating, leads to the formation of a thin film of corrosion-resistant metal (zinc, for example) on the inner and outer surfaces of pipes.
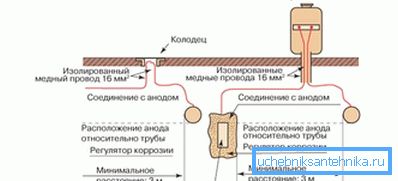
The second of these methods (it is also sometimes called electric) suggests reliable protection of pipelines against corrosion due to the use of the effect of stray induced currents. To implement this technique, you will need a suitable DC source, made in the form of a power supply module, which includes a network transformer and a rectifier.
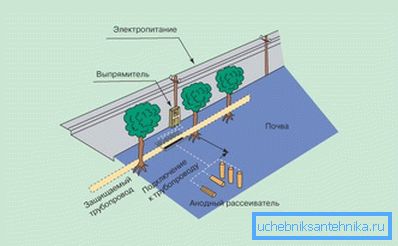
When organizing an electrical protection method, the positive pole of the power supply module is connected to a special anode diffuser, which is a grounded graphite or metal bus, and a negative one - to the pipeline you are protecting. At the same time, the current dissipated by the grounding device forms an artificial electric field around the pipe, which significantly reduces the potential of the metal structure and provides the necessary protective effect.
The magnitude of the protective current in the electrical circuit is ultimately determined by the parameters of the pipeline itself (its dimensions and insulation characteristics), as well as the level of soil aggressiveness at the site of the pipeline.
Tip! Before complex anti-corrosion treatment of metals, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the surface of the pipe from all foreign layers (paint residues, oil or grease stains, as well as dust and rust).
As for the technique of applying passive protection, it is not much different from the traditional methods of painting metal surfaces using a soft brush or spray gun.
Video
This video is about protecting the pipeline from electrochemical corrosion.