Pipeline welding: materials and technologies
What materials are welded pipes made of? How does the technology of making welded joints in each case look like? How should pipeline welding be performed according to GOST? In the article we will try to answer these questions.

List of materials
First, find out which pipes allow you to make the connection by welding.
- Steel is a traditional material, somewhat lost its former popularity against the background of the spread of polymers. In, so to speak, field conditions it is cooked by electric and gas welding.
Nuance: galvanized pipes are preferably connected by threads. Welding breaks the protective zinc layer in the area of the seam.
- Polyethylene pipes are connected by low-temperature butt welding.
- Polypropylene pipelines are also welded, but in this case the joints are made not by butt joints, but are bell-shaped..

In this order, we will become acquainted with the technology of welding.
Steel
As already mentioned, electricity and gas are used for welding.
Gas welding
The welding machine consists of two cylinders (oxygen and acetylene), a pair of high pressure hoses and a torch with a pair of valves regulating the gas flow.
Consider how the welding itself is carried out:
- The hoses with the burner are connected to the cylinders, after which their valves open. To seal the connection between the cylinders and the hoses, a fluoroplastic washer is placed under the coupling nut.
- The acetylene supply valve opens slightly on the burner, after which it ignites.
- The oxygen supply is regulated to obtain a steady blue flame with a bright glow in the center. Red color of a torch means incomplete combustion of acetylene, dim blue flame - an excess of oxygen.
- The welded edges of the pipes are heated until the surface melts; as the steel begins to melt, the welding wire is inserted into the flame of the torch. Melt droplets are moved from it to the weld field, gradually connecting the pipes.

Attention: welding works are performed in transparent glasses and a dense suit of fireproof material. The instruction is connected with the fact that during heating and undercutting of edges, red-hot dross and metal splashes often fly.
When performing welding with their own hands, a novice gas welder will inevitably have a number of problems.
We will try to describe the decisions of some of them.
- For cutting, the desired section of the pipe is first heated to a white glow and the beginning of the surface melting; then, when the distance from the burner nozzle to the pipe is about 1 cm, the oxygen supply increases with a valve. The jet blows melt. By the way, this work is more convenient to perform, replacing the burner with a torch: in addition to a more powerful torch, it allows you to adjust the flow of the cutting stream of oxygen by a separate valve.
Useful: not only acetylene can be used for cutting, but also more available propane. The relatively low flame temperature is compensated by the greater power of the torch.
- Fixed seams (for example, when replacing a section of a riser against a wall) are performed with a mirror. At the same time, it is necessary to constantly adjust their actions taking into account the mirror image of visible movements.
- An alternative way to perform a non-folding seam is to cut a window in a pipe. On its frontal side a U-shaped incision is made; then the cut tongue folds out. After the seam is welded from the inside, the tongue is bent back into place and brewed.

- Thick-walled pipes (with walls from 3-4 millimeters thick) do not boil with gas in principle. Metal of such thickness can only heat the cutter, which, you understand, is useless for our purposes.
Electric welding
The tool kit includes a welding transformer, a pair of cables and a holder for electrodes. The welding electrode is a thin steel bar coated with a dielectric material, which at the temperature of an electric arc turns into molten slag.

Why do we need electrode coating?
There are two reasons.
- The thickness of the coating allows, when the holder is approached at an oblique angle to the pipe, to ignite and maintain an electric arc. Without it, the welder would have to keep the continuously melting electrode at a constant distance of 0.5-2 millimeters from the seam, which, you see, would be a little more than tedious.
- In addition, the coating melt (slag) protects the steel melt from contact with atmospheric oxygen and the complete burning of carbon, which would affect the mechanical properties of the weld.
The process of welding the ends of the pipes requires a certain skill: to keep the arc burning, avoiding sticking the electrode and burning the walls of the pipes, is more difficult than it might seem.
Thick-walled pipes need preliminary chamfering.
After the seam has cooled, it is cleaned of slag and visually inspected for possible defects.
Safety
Both gas and electricity are potentially dangerous to the health and life of a welder.
Labor protection rules were literally written in blood, and the cost of non-compliance may be very high.
- When loading cylinders, remove the wedding ring and other jewelry from your hands if you wear them. The accidental fall of the cylinder more than once and not two led to the fact that a person caught the ring by the valve lost a finger.
- The room where gas is boiled should be actively ventilated. In addition to the fact that when painted or galvanized pipes are heated, many extremely harmful substances are released, it is worth remembering about the possibility of leakage of highly explosive acetylene.
- Welding hoses must not be spliced. Each connection is a potential leak or disconnect point from a random jerk.
- The burner nozzle needs periodic cleaning. If it is clogged with fumes, scale, or metal splashes, a reverse blow is possible - an explosion of an acetylene-oxygen mixture in the burner itself or in the hoses.

- Welding mask is necessary even for tacking, not to mention welding seams. Cook vpriglyadku - it means to doom yourself to a sleepless night with severe pain in the eyes. The skin on the face also burns like a sunburn: the spectrum of the radiation of the arc includes ultraviolet light.

By the way: if you burn your eyes with a welding arc, wash them with soap. The procedure is unpleasant and painful; however, the pain from the burn will remove the soap solution.
- It is necessary to cook by electric welding only in dense and dry mittens. They will save you from burns with splashes of metal and slag. In addition, the mitten will not allow you to close the holder and grounded pipe with your hand.
- Welding work should be carried out on a dry dielectric base. If this is not possible, at least high rubber boots are required.
Polyethylene
The technology of welding pipelines made of polyethylene is very different from welding works on metal.
In short - the following operations are performed:
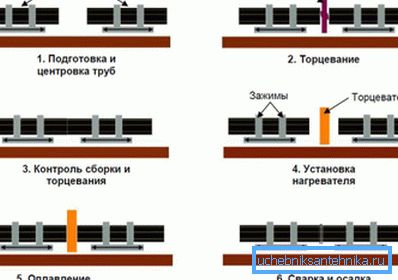
- The edges of a socketless pipe or pipe and fitting fit strictly at right angles to the longitudinal axis and are cleaned of chips, debris and dirt.
- Then they are pressed against a flat heating element (mirror) with a non-adhesive coating heated to 200 - 220 degrees.
- After the polyethylene begins to melt, the mirror is removed, and the ends are pressed together with a force of about 1.5 kgf / cm2. Molecular diffusion takes the further fate of the seam: the melt of polyethylene turns into a single whole, and after cooling, the seam has little strength from a monolithic pipe.
How long the joint heats up and cools down depends on the wall thickness of the pipes being welded.
| Wall thickness mm | Duration of heating, s | The duration of the cooling joint under pressure, s |
| 4.5 | 45 | 6 |
| 4.5 - 7 | 45 - 70 | 6 - 10 |
| 7 - 12 | 70 - 120 | 10 - 16 |
| 12 - 19 | 120 - 190 | 16 - 24 |
| 19 - 26 | 190 - 260 | 24 - 32 |
| 26 - 37 | 260 - 370 | 32 - 45 |
| 37 - 50 | 370 - 500 | 45 - 60 |
| 50 - 70 | 500 - 700 | 60 - 80 |
Hint: in case the reader misses a clear pattern - the duration of the heating is equal to the wall thickness multiplied by 10 in millimeters.
On the welding of polyethylene is useful to know a few things.
- When the wall thickness is less than 4 mm, pipes are connected by compression or electrofusion fittings for pipes. The exception is low-responsible low-pressure pipelines (for example, dacha water supply system).

- Mechanical devices are used for centering and clamping pipes, and for pipes with a diameter of 250 mm or more, they are hydraulic.
- In windy weather, the free ends of the pipes are usually jammed. Draft can affect the duration and quality of the weld reflow.
Polypropylene
Equipment for welding of polypropylene is all the same low-temperature soldering iron. Not only that: many devices are universal and allow you to weld both polypropylene and polyethylene.

The mode and technology of welding, however, are somewhat different:
- The heating element for propylene should be heated to 240 - 260 degrees.
- It is supplied with nozzles that allow to melt not the ends, but the outer surface of the pipe and the inner surface of the fitting.
How is the flare connection of the polypropylene pipe being brewed?
- The pipe is inserted into the socket of the soldering iron; at the same time, a pipe connection fitting is put on the second side of the nozzle.
- After the surfaces have melted, the parts are combined with a smooth translational motion, and for some time they are held still.

Heating and cooling time is determined by the diameter of the pipeline.
| Outer diameter of pipe, mm | Duration of heating, s | Connection duration, sec | Duration of cooling, min |
| sixteen | five | four | 2 |
| 20 | 7 | four | 2 |
| 25 | 7 | four | 2 |
| 32 | eight | 6 | four |
| 40 | 12 | 6 | four |
| 50 | 18 | 6 | four |
| 63 | 24 | eight | 6 |
| 75 | thirty | ten | eight |
Of course, there are a number of subtleties.
- The twists of the parts when connecting is not allowed. They form a wave on the melted surfaces, which can lead to depressurization of the compound under pressure.
- Aluminum-reinforced pipes require pre-stripping. Depending on the location of the reinforcing layer, a shaver is used to clean the outer surface of the pipe, or a flat-cutter that selects a layer of aluminum foil located in the middle of the wall.

Standard
Manual arc welding of steel pipelines and other structures is regulated by GOST 5264-80. Most of the regulatory document is a schematic of seams of different types with comments and recommendations.
Let us highlight a few common points.
- When performing a double-sided seam (this technology, in particular, is practiced in the construction of large-diameter pipelines designed for significant operating pressure), before boiling from the reverse side, the root of the seam is scraped from slag to a pure metal.
- The welded ends of the pipes can be washed offset from each other by no more than 0.5 mm with a wall thickness of up to 4 mm, 1 mm with a thickness of 4-10 mm and 10% of the wall thickness, but no more than 3 mm with a greater thickness.
- When the difference in the thickness of the walls of the pipes being connected is more than 1 mm, for the walls of a thinner pipe are 1-4 mm, more than 2 for walls of 4-20 mm and more than 3 for walls of 20-30 mm, the thicker pipe is preliminarily grinded from the outside to align the seam.

Conclusion
We hope that the material offered to the reader will be useful. Additional information on how pipelines can be welded can be found in the video in this article. Successes!