Pipes for gas pipelines: materials, installation rules,
In which cases steel or polyethylene pipes for gas pipelines are more preferable? Are there any rules governing the laying of gas within the garden plot? According to what regulatory documents are pipes manufactured that can be used? Let's try to find the answers together.

Features of materials
To begin with, let's formulate the key features of both possible solutions.
Steel
The defining property that makes steel the main material for laying gas pipelines is strength. Collision with the car, vandalism, seismic activity (of course, within reasonable limits) with the minimum probability will lead to a violation of the tightness of the pipe and gas leakage.
For reference: during earthquakes, more than half of the victims and destructions fall not on the impact of the earthquake itself, but on the fires that follow them. The main reason is the destruction of gas mains, coupled with damage to the electrical wiring.
What other qualities have become worth noting?
- Widest operating temperature range. Steel pipes slightly change their mechanical properties in the range from -40 to + 100C and above. At lower temperatures, however, many steel grades become brittle.
- Low corrosion resistance. If a dry environment with no oxygen inside the pipeline eliminates corrosion, then the outside of the pipe has to be periodically repainted with stripping the old paintwork, and not from aesthetic considerations.

- Steel pipes are a great conductor. During their operation, it is necessary to solve the problems of grounding and cathodic protection: stray currents and the occurrence of various electrochemical processes can not only lead to an accident on a gas pipeline, but also sharply accelerates corrosion.
- Finally, the price per meter of a steel pipe is somewhat higher than that of a polyethylene equivalent. We give some wholesale prices.
| Nominal diameter, mm (size ranges do not match, so the closest diameters are taken) | Cost per meter, rub. | |
| Steel Pipe VGP | Polyethylene pipe PE100 SDR 17.6 | |
| 65/63 | 269 | 110 |
| 90/80 | 311 | 226 |
| 100/110 | 452 | 335 |
Note: for a steel gas pipeline, the maximum allowable pressure is 16 kgf / cm2, for a polyethylene pipeline - only 3. However, in most cases, the strength of polyethylene is excessive.
Polyethylene
How is a plastic pipe for a gas pipeline fundamentally different from a steel one?
- Weight per meter less than 3-7 times. From here - more simple transportation and installation.
- Polyethylene is not afraid of corrosion and contact with aggressive media. It is one of the most chemically resistant polymers: it is not without reason that it is used for the production of containers in which concentrated acids are stored. Practical consequence: no maintenance of the pipeline after installation is required; periodic painting can be forgotten, like a bad dream.

- Like all plastics, polyethylene is a dielectric. If so, it is possible not to be afraid of stray currents; grounding and cathodic protection are not required.
- In the entire range of operating temperatures, the mechanical properties of the gas pipeline remain virtually unchanged: the plastic retains its viscosity, which is able to extinguish an arbitrarily strong blow, and elasticity, which promotes reversible deformation under loads. Simply put, if a truck passes through a polyethylene pipe, it will return to its original form.
- In contrast to steel, butt welding of pipes is fully automated, which eliminates the human factor and, accordingly, the quality variation of joints.

- The upper bar of the operating temperature is limited to only 40-45 degrees.
Problem of choice
So steel or plastic?
The choice of the reader can make their own, based on the above descriptions. However, it is necessary to take into account some legislative restrictions.
The use of polyethylene is not allowed:
- In regions where the temperature of the coldest five-day winter is below -45 degrees. The elasticity of plastic at low temperatures has its limits.

- In zones with seismicity above 6 points. Despite the aforementioned elasticity, the tensile strength of steel is still noticeably higher.
- In the urban zone of high pressure of the first and second categories. There probably needs a little explanation. To different categories of gas pipelines refer to the working pressure:
| Category | Working overpressure, MPa |
| one | 0.6 - 1.2 for natural gas, 0.6 - 1.6 for liquefied gas (gas holders) |
| 2 | 0.3 - 0.6 |
| 3 | 0,005 - 03 |
| four | Less than 0,005 |
- Polyethylene can be laid only in the ground. Ground and surface laying, installation of polyethylene pipelines in tunnels and collectors, as well as inside buildings for any purpose is prohibited. This manual is related to the low mechanical strength and flammability of the material.
Thus, when installing a gas pipeline within the site, one can be guided by an uncomplicated rule: polyethylene can be laid in the ground along the site; from entering the house gas is only diluted with steel. The transition between polyethylene and steel should be located outside the house above the ground level.

Nuance: alas, to save money and perform gas installation from the point of connection to the house with your own hands will not work. All work must be performed by a licensed construction and repair organization.
Payment
Immediately distress the reader: a simple calculation of the diameter of a gas pipeline is impossible. The reason - too many defining factors.
Rate their list:
- Type of gas. Methane, propane and propane-butane mixture have different densities and in terms of hydrodynamics behave differently.
- Pipe material. Steel and polyethylene have different resistance to flow.
- Mass flow rate of gas. It, in turn, is determined by the thermal power of the gas equipment and its efficiency.
- The length of the pipeline. The more it is - the greater the loss of pressure.
- Every turn, every element of the valves also affects the pressure drop.

- The temperature of the gas also greatly affects its hydrodynamic characteristics.
- Finally, for different types of boilers, stoves, etc. let's say a different range of working pressure; accordingly, the allowable pressure drop across the pipeline will also vary.
What should the potential owner of a gas boiler do? The simplest solution is to use one of the online calculators that allow you to enter all of the above data and get a turnkey solution. Taking into account the pitch of pipe diameters, minor errors due to unaccounted for minor factors will not lead to catastrophic consequences.
Let's use a calculator, kindly laid out on its website by the Moscow office of the company Antonio Merloni Group, selling gas-holders.
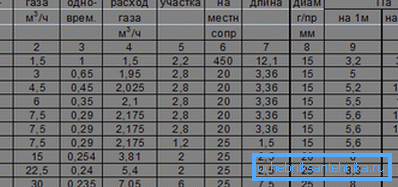
The use of a propane-butane mixture with a peak flow rate corresponding to a thermal power of 36 kW, with a 20-meter-long polyethylene inlet and a gas temperature of +2 C, will force us to use an input with a minimum inner diameter of 11 mm.
Regulations
It is obvious that the design and construction of gas pipelines made of polyethylene pipes and steel must be based on certain regulatory documents on which these pipes are produced. Which ones?
Polyethylene
Polyethylene gas pipes are manufactured according to the requirements of GOST R 50838-2009.
We study the main points of the document.
- The maximum working pressure of a polyethylene gas pipeline cannot exceed 1.2 MPa. The maximum gas temperature is only 40 C.
- The nominal outer diameter of pipes varies from 16 to 630 millimeters. The wall thickness is tied to the SDR parameter (the so-called ratio of diameter to wall, which characterizes the strength of the pipe at break) and can be from 2.5 to 52.7 mm.
- With a diameter of up to 200 mm, a pipe can be supplied in the form of a coil or a coil, with a larger section, only in straight sections. In this case, the length of a straight line can be from 5 to 24 meters.

Steel
For steel pipes, there are several documents in parallel.
- Steel water gas welded pipes are manufactured according to GOST 3262-75.
- Welded products for long-distance gas pipelines - longitudinal and spiral-seam - are made according to GOST R 52079-2003.
- According to GOST R 52568-2006, they produce seamless, longitudinal and spiral-welded pipes for gas mains, equipped with protective coatings.
What information can be found in these standards?
GOST 3262-75
VGP pipes are longitudinal welded pipes, that is, they are made by rolling a straight billet in a straight mill and then boiling a longitudinal seam.
They are delivered in straight sections from 4 to 12 meters. The length can be unmeasured, measured or multiple measured with an allowance for each cut equal to 5 mm.
The diameter range is from 6 to 150 mm. Pipes are divided into light, ordinary and reinforced; these categories are quite predictably different wall thicknesses.

As part of the standard, products are made from both black steel and a protective zinc layer.
Useful: for reasons of the most effective corrosion protection, galvanized pipes are assembled on threads. For their sealing on gas pipelines, FUM tape is used. On welds, the zinc layer is inevitably disrupted.
GOST R 52079-2003
Under this standard, pipes for highways are manufactured with a huge overpressure. The reason is clear: pumping stations must overcome the tremendous loss of pressure resulting from the considerable length of the lines.

Products can be made in three ways:
| Diameter range, mm | Preparation method |
| 114 - 530 | Welding a flat workpiece with one straight seam using high-frequency welding |
| 159 - 1420 | Welding a flat billet with a spiral seam using arc welding using flux (DSF) |
| 530-1420 | Welding of a flat billet using DPF with one or two straight seams. |
The wall thickness can vary from 8.21 to 40 mm, the working pressure reaches 9.8 MPa (100 kgf / cm2). The working ambient temperature can drop to -60 C.
In general, pipes are supplied in lengths of unmeasured length from 10.5 to 12 meters; in agreement with the customer, however, it is possible to supply segments of measured length.
GOST R 52568-2006
The diameter range is fully consistent with that in the above document - from 114 to 1420 mm. The manufacturing methods have already been mentioned: seamless, longitudinal and spiral welded.

The key difference between these pipes and those produced according to GOST R 52079-2003 is the presence of a protective coating. One or another of its type is applied depending on the conditions of use.
| room | Design | View | Application area | Diameters, mm | Operating temperature range, С |
| one | Three-layer polyethylene (3PE) | Normal | Underground pipelines in temperate and cold climates | 114 - 1420 | -40 - +60 |
| 2 | 3PE | Heat resistant | Underground pipelines in hot climates | 114 - 1420 | -50 - +80 |
| 3 | 3PE | Special | Horizontal drilling pipelines | 114 - 1420 | -60 - +60 |
| four | Two-layer polyethylene (2PE) | Normal | Non-Responsible Piping | 114 - 820 | -50 - +60 |
| five | Three-layer polypropylene (3PP) | Normal | Underwater, underground laying | 114 - 1420 | -10 - +80 |
| 6 | 3pp | Frost resistant | Districts of the Far North | 114 - 1420 | -20 - +80 |
| 7 | 3pp | Special | Horizontal drilling, pulling | 114 - 1420 | -20 - +110 |
| eight | Two-layer polypropylene | Normal | Increased product temperature | 114 - 820 | -10 - +110 |
| 9 | Single layer epoxy coating | Normal | Underground gasket | 114 - 820 | -20 - +80 |

Conclusion
We hope that our material will help the reader to decide on the choice of a solution. Additional information, as usual, can be found in the video in this article. Successes in construction!