Plumbing pipes: materials, dimensions and methods of
The topic of this article is the types of plumbing pipes and connections. We have to figure out which metal and plastic plumbing pipes are currently used, how they are connected to each other and plumbing fixtures. In addition, we will find out which diameters are typical for certain communications.

Materials and scope
First, find out which pipes for plumbing can be used and for what purposes.
Pressure water pipes and heating systems
- Black steel is still not losing ground in central heating systems. Its strength is a definite plus; limited corrosion resistance is compensated by the absence of air in the year-round system.
Note! Alas, but the fact that the heating pipes should not be dumped for the summer - only in theory. In practice, the warm time of the years - it's time to repair, and the inevitable leaks between the sections of the cast-iron radiators sometimes force the system to drain.
- Galvanization is devoid of the main disadvantage of black steel. However, there is a nuance here: the zinc layer is broken on the welds. Corrosion-resistant heating or water supply will be only if it is fully assembled on the threads.
- The corrugated stainless steel has the highest tensile strength, is resistant to corrosion, aggressive media and is devoid of the main drawback of previous solutions - the complexity of installation with thread cutting or welding. Flexible corrugated pipes bend with a radius equal to their diameter. The only drawback is the relatively high price (for 15 mm - from 170 rubles per meter).
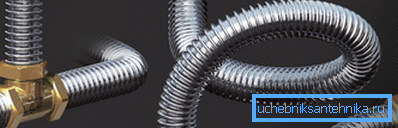
- Metal-plastic used in floor heating systems, autonomous heating and water supply (hot and cold). In the DH it can also be used; However, this material has been severely (and undeservedly) damaged by the reputation of compression fittings for pipes, which, with certain errors in installation, begin to flow through several heating and cooling cycles. The pipe consists of two layers of cross-linked polyethylene with an aluminum tube between them.
- Copper plumbing pipe can be used in all types of heating and water supply systems. This is not a cheap, but extremely durable solution.

- Polypropylene, by contrast, is attractive for its low cost.. Polypropylene plumbing is at least half a century and does not suffer from overgrowth of mineral sediments; The erosion of the internal surface by suspended hard plastic is also not terrible.
Important: in the systems of hot water supply and heating, polypropylene reinforced with aluminum foil or chopped fiberglass (fiber) is used. Reinforcement increases tensile strength and significantly reduces the elongation of the polymer pipeline during heating.
- Polyethylene is used only and exclusively for cold water.. The working temperature of this plastic is limited to 40 degrees.
- Cross-linked polyethylene, however, is fundamentally different from it by increased strength and heat resistance.. Cross-links between polymer molecules change its physical characteristics, allowing it to be used in any heating systems and hot water circuits. The flexibility of the tubes makes them very popular with collector wiring.
Sewage
The list of materials used for sewer systems is noticeably smaller.
- Cast iron has by now lost its former popularity. The reasons - the high cost, large mass and extremely time-consuming installation with embossing sockets. The only argument in favor of cast iron is its acoustic qualities: massive walls absorb any noise, which is very useful in the case of a riser in an apartment building.
- Plumbing PVC pipe, on the contrary, at the peak of popularity. Low weight, simple installation and ease of cutting allowed it to press competing solutions on the current market.
- Polypropylene is used here. It is even lighter than polyvinyl chloride, has greater hardness and, most importantly, heat resistance. The operating temperature of the polypropylene sewage system is up to 90 degrees versus 60 for PVC.

- Polyethylene is used much less frequently - precisely because of the low operating temperature. Its advantage is noiselessness: thick and extremely elastic walls extinguish sounds slightly worse than cast iron.
Installation
How does the installation of plumbing pipes do it yourself in each of the listed cases?
Plumbing, heating
| Material | Mounting methods |
| Steel (black and galvanized) | Gas welding, electric welding, threaded connections, compression fittings, flanges |
| Corrugated Stainless Steel | Compression Fittings with Silicone Seals |
| Metal plastic | Compression Fittings, Press Fittings, Push Fittings |
| Copper | Brazing, compression fittings |
| Polypropylene | Low temperature welding by means of socket fittings |
| Polyethylene | Compression fittings with rubber seals, electrofusion fittings |
| Crosslinked polyethylene | Fittings with sleeves - clamps |

Sewage
| Cast iron | Cabing of sockets with a cabol, pouring gray, less often - annular rubber seals |
| PVC | Rubber seals, in pressure sewage - adhesive joints |
| Polypropylene | Rubber seals |
| Polyethylene | In the free-flow sewage system there is a fashonina with rubber seals, in the pressure one it is low-temperature butt-welding |
Terminology
Some terms are likely to be unusual for readers far from plumbing and therefore need to be commented upon.
- The compression fitting either presses the pipe with a rubber or silicone seal when tightening a cap nut with a conical internal cross section, or presses the pipe itself at the nozzle using a split ring (in the case of soft copper and metal-plastic).
- The press-fitting reliably fixes the metal-plastic pipe on the fitting with a pair of rubber rings when crimping the stainless steel liner with special tongs.
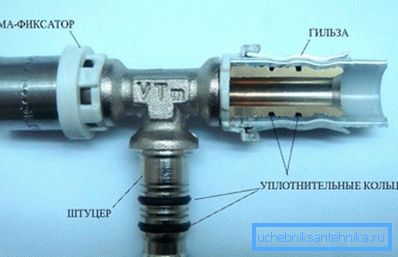
- Push-fitting (from the English-language push - push) is fixed when pressed. Tightness is also provided here with rubber rings, while the fixer is a stainless steel spring ring with feet pointing inwards.
When welding polypropylene, a low-temperature soldering iron melts the inner surface of the coupling fitting and the outer surface of the pipe; then the parts are combined and after cooling they become one.
Butt welding of polyethylene pipelines looks similar.
- The electrofusion fitting contains a heating coil. By feeding it, you can force it to heat the polyethylene to the melting point and to achieve reliable welding of the parts.
- Cross-linked polyethylene has a mechanical memory and after stretching the pipe end with a special tool, it quickly returns to its original diameter, compressing the fitting inserted into it. A sleeve worn over the top provides additional fixation.
- The threaded connections of steel pipelines are made using cast iron and brass fittings; threads are sealed with flax (often with dye) or polymeric materials.
Important: it is on the threads that various plumbing crafts are usually assembled from plumbing pipes - table lamps, floor lamps, tables, etc. After painting, these funny designs look quite presentable.

Dimensions
Let us cite a few interesting facts, one way or another relating to the diameters of pipelines for various purposes.
- Both salespeople and technical writers often indicate the plumbing dimensions of pipes in inches. It is in some way a tribute to tradition: it is in English inches that the diameters of pipe threads are measured. Instructions for converting to the measurement system we are used to are simple: just multiply the size by 25.4 - and we will get the size in millimeters.
- The confusion does not end there. For steel pipes, the main parameter is not the external or internal diameter, but the conditional passage (DU). As a rule, it is close to the internal diameter, but not equal to it, and indicates only the possibility of using the appropriate size of pipe threads to connect the elements of this pipeline.
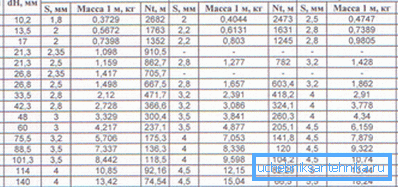
- The dimensions of plastic plumbing pipes of all types are indicated in the metric system. As a rule, they are denoted by the outer diameter; to calculate the internal cross section, you need to know the wall thickness.
What sizes are relevant for heating and water supply systems?
- Cold-water and hot-water supply liners have a diameter of 15-20 mm.
- Leads to the radiator - 20 - 25 mm.
- Water and heating risers - 25 - 32 mm.
- 40 - 65 mm - the diameter of the bottling of heating and water.
- A plumbing pipe of 75 mm and above is used for the installation of elevator assemblies and water meters providing heating, hot water supply and cold-water supply to apartment buildings.
The dimensions of plumbing pipes - PVC, polypropylene, polyethylene and cast iron - for sewage are selected taking into account the possibility of salvo discharge.
- Plumbing pipe 50 mm is used to connect all appliances, except the toilet.
- 110 mm - a typical section of the drain from the toilet and sewer riser.

- 150 and above - the sizes of release on a well and sites of the sewerage between wells.
Conclusion
We hope that our somewhat superficial review of existing solutions will be useful to the reader. As always, the video in this article contains additional thematic information. Successes!