Polyethylene pipes - all about advanced material
Polyethylene is known to mankind not the first decade. Production of polyethylene pipes is only one of the ways to use them successfully. But ordinary polyethylene is not sufficiently resistant to high temperature, so its area of application has been limited for a long time. And the appearance on the market of such material as polyethylene, stitched, significantly changed the situation in the construction industry.

Scope of the polyethylene pipeline
This material has several important qualities:
- it does not pass water and does not give in to corrosion;
- is a dielectric;
- polyethylene pipe is strong enough and can withstand the pressure that creates in the plumbing and heating system.
The main disadvantage of conventional polyethylene is that it is easily deformed under the simultaneous effects of high temperature and pressure. Therefore, non-sewn material can only be used to supply water whose temperature does not exceed 40? С.

The stitched pipeline does not have these disadvantages and can be used at a coolant temperature of at least 80? С. The upper working limit is declared around 95? С.
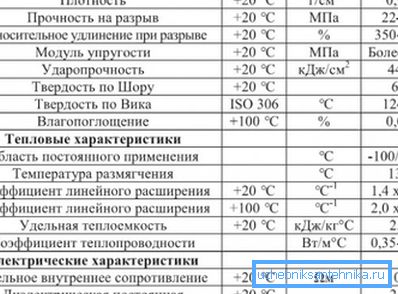
Note! The technical characteristics of the pipeline can be specified limit temperature of about 200? C. At this temperature, the pipe retains its shape if there is no other load than its own weight. In the pressure mode, the pipeline will not be able to work at this temperature.
Another important positive effect of firmware can be called increased elasticity of the material. The pipe from sewed polyethylene perfectly bends even at low temperature.

Normative base
In general, the situation with regulations for plastic pipelines is quite complicated. Considering the fact that such pipes are used for heating systems and plumbing, it can only be noted that GOST 52134-2003. This document is devoted not only to polyethylene, but also to other plastic pipelines operating in the pressure mode.
Of the most important information, the following can be noted:
- sizes vary over a wide range. When selecting a pipeline, it is necessary to take into account the wall thickness, because it is the external diameter that is indicated. The minimum value of the external diameter is 10 mm (wall thickness 1.3 mm), and the maximum 250 mm (wall thickness 34 mm);
- sufficiently strict requirements for geometric dimensions. Thus, only a slight excess of the outer diameter is allowed, but if it is smaller than the declared value, then such a pipeline is rejected, the same applies to the wall thickness;
- pipe marking must necessarily contain information about the method of stitching. For example, the marking PE-Xc says that pipe polyethylene was stitched by the electron-beam method.
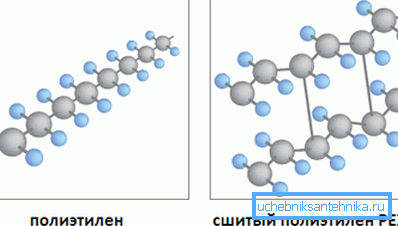
What gives the "firmware" material
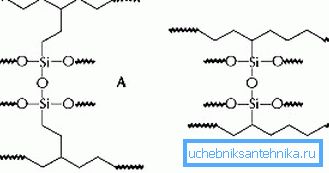
The process of firmware itself implies an impact on the material at the molecular level. If in the usual state the structure of polyethylene can be represented in the form of monomolecular chains, then the stitched material in addition to ties in the longitudinal direction also forms them in the transverse direction. That is, the individual chains are “stitched” into one whole.
The production process uses several methods of stitching:
- type A - peroxide cross-linking, the price of this method is maximum, but the quality of the cross-linking is excellent;
- type B - silanol;
- type C - electron beam method.
The type of cross-linking largely determines the characteristics of the pipeline, so it makes sense to consider this process in more detail.
Peroxide crosslinking
Peroxide is added directly to the melt, and the proportion of the additive is negligible (about 1 - 2 kg per 1000 kg of polyethylene). In order for the stitching process to proceed without problems, it is necessary to provide high pressure (about 20 atm) and a temperature not lower than 300? С.
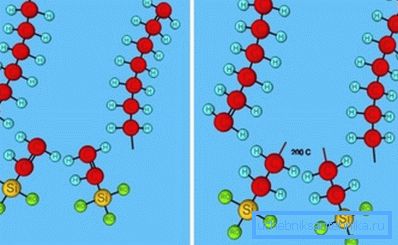
The main advantage of this method is that cross-linking occurs throughout the entire thickness of the material, because peroxide is mixed with the melt. The degree of crosslinking is at least 75%.
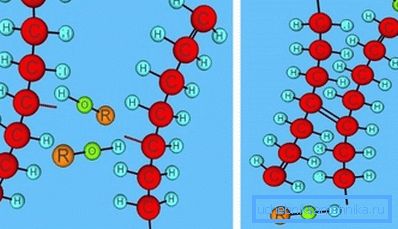
The bonds formed during this process make the material resistant to low temperatures, the density also becomes slightly lower. Also, the PEXa polyethylene pipe has a pronounced “memory” effect, that is, with slight deformations, the material returns to its original form after removal of the load.
Silanol crosslinking
In this case, a substance such as silane and a catalyst that accelerates the crosslinking process is used. As with peroxide, liquid polyethylene is mixed with silane. Then a pipeline is made from this mixture. For the chemical reaction to take place, it is enough to place the finished pipe in hot water.
The main advantages of this method include:
- high impact resistance;
- increased resistance to pressure and high temperature;
- resistance to chemically aggressive substances.
As for the shortcomings, it is possible to note a lower degree of crosslinking (about 65%). In addition, reduced elasticity imposes certain restrictions on the method of installation, for example, it is not recommended to use fittings with a sliding sleeve.
Note! When using fittings with a sliding sleeve, pipes made of stitched polyethylene expand slightly. Due to the low elasticity of the material, cracks may soon appear on its surface, so it is better to use regular compression fittings for pipes.
Sometimes, PEX-d pipe marking can also occur, which means that it was nitrogen, not silane, that was used. The nitrogen efficiency is much lower than that of silane, so PEX-d pipes cannot be recommended for heating and plumbing.
Electron beam method
X-ray radiation affects polyethylene, due to this the degree of crosslinking can reach 60%. But in this case, the probability of uneven cross-linking is high, so that individual sections of the pipe may be less resistant to high temperature and pressure.
It is not recommended to use such a pipeline for water supply, the temperature of which exceeds 70? С. Otherwise, the probability of leakage and destruction of the pipeline.
Installation Features
With the installation of a conventional plastic pipe with their own hands any. The laying of the pipeline from the stitched polyethylene is a little more difficult, but in this case you can do it yourself.
You can use the usual crimp fittings for the connection device. But most often used for this fitting fittings.
Instructions for arranging such a joint looks like this:
- the clamping sleeve must be put on the pipe;
- then the end of the expander is inserted into the pipe and for a few seconds its handles come down, the end of the pipeline expands;
- the expander is removed, and the pipe is put on the fitting;
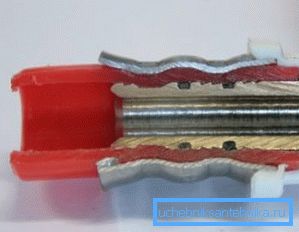
- due to the effect of "memory" polyethylene tightly compresses the metal;
- To fix the achieved effect on the polyethylene, a sleeve is slid (using a press). Due to this tightness of the joint is guaranteed.
Note! There are pipes with fittings already installed on them. This will greatly simplify the process of docking the pipeline.

Summarizing
Polyethylene stitched - a material that is almost devoid of flaws. It withstands the combined effects of high temperature and pressure, is quite elastic and can last up to half a century without the need for replacement.
When choosing a pipeline from this material, you need to take into account a number of nuances, in particular, the method of stitching. The information in this article will not make a mistake when choosing, thanks to this, the durability of the heating or water supply is guaranteed.
The video in this article shows the features of the joining of the stitched polyethylene pipeline.