Polyethylene water pipe: regulatory documentation,
How practical are polyethylene pressure pipes? What standards govern their production? What ways can you install the plumbing from polyethylene pipes - with your own hands and using industrial equipment? Let's try to answer these questions.

First meeting
What do we know about polyethylene? It is the cheapest and most widely used plastic in the world, produced by the polymerization of ethylene gas. It is resistant to acids, alkalis and low temperatures, it easily transfers considerable mechanical loads and strong impacts due to its viscosity and damping properties.
Note: the elasticity of the polymer is maintained at low temperatures, so the water pipes made of polyethylene can tolerate the freezing of water in them without destruction. The pipe is stretched, and after defrosting returns to its original size.
Depending on the conditions of polymerization distinguish polyethylene of low (PND), medium (PSD) and high (LDPE) pressure:
| Designation | Polymerization conditions | Mechanical strength |
| LDPE | 200 - 260С, 150 - 300 MPa | + |
| DED | 100 - 120С, 3 - 4 MPa | ++ |
| HDPE | 120 - 150С, 0.1 - 2 MPa | +++ |
From the mechanical properties of plastic depends on the strength of the polymer water pipe produced from it. The most durable products from HDPE.

The working temperature of the pipes is limited to 40 - 60 ° C: at higher temperatures, the polymer begins to soften.
Normative documents
Requirements for the quality of pipes are set out in GOST 18599-2001. Let us highlight some points that have practical value in their selection and operation.
The main operational parameters of the pipe are:
- Nominal diameter. It can take values from 10 to 1200 mm.
- Nominal wall thickness. Its value varies from 2 to 59.3 mm.
- MOP - maximum nominal pressure. Measured in megapascals. To convert to more usual kgf / cm2, it is enough to multiply the MOP by 10.2.
- SDR - standard dimensional ratio, the ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness. The smaller the SDR, the larger the calculated working pressure.
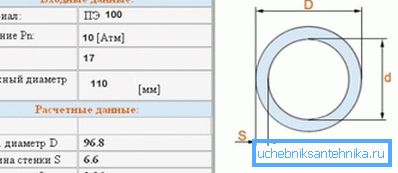
- Mrs - the so-called long-term strength of the material, measured in megapascals. This parameter with a somewhat vague description is always displayed in the pipe name.
How to read the designations provided for by the standard?
They include:
- An indication of the strength of the material. PE 32 means polyethylene with MRS = 3.2 MPa, PE 63 - with MRS 6.3 MPa, etc.
- SDR option.
- Nominal diameter and wall thickness.
- Purpose pipe (drinking or technical).
- Reference to GOST 18599-2001.
For example, under the name PE 100 SDR 11 - 32 x 3 drinking GOST 18599-2001 hides a polyethylene water pipe of 32 mm with a 3-mm wall, made from a material with MRS = 10 MPa for drinking needs.
Besides:
- The color of the pipe is black (alternatively, black with blue stripes) or blue.
However: 32 products made from PE must be exclusively black.

- With a diameter up to 180 mm pipes can be supplied in coils, on coils and in straight lengths. With a larger diameter - only in straight sections.
- Products must have smooth surfaces - external and internal. Only slight waviness is allowed.
Installation
How to assemble plumbing from polyethylene pipes supplied in straight pieces? Connection methods depend primarily on the diameter and thickness of the wall.
Walls over 4 mm
Here, butt welding is the main method of installation. To melt the ends of the pipes, a flat, anti-adhesive coated electric heating element (mirror) is used; centering and subsequent clamping of pipes are provided by manual, mechanical or (with a large diameter) hydraulic device.

The clamping force is 1.5 kg / cm2; the time of heating and fixation is determined by the wall thickness of the pipeline:
| Wall, mm | Heating, s | The output of the heating mirror of the lumen, s | End compression, sec | Pressure joint cooling, sec |
| 4.5 | 45 | five | five | 6 |
| 7 | 70 | 6 | 6 | ten |
| 12 | 120 | eight | eight | sixteen |
| nineteen | 190 | ten | eleven | 24 |
| 26 | 260 | 12 | 14 | 32 |
Despite the low thermal conductivity of the polymer, it does not provide complete protection against freezing at a low flow rate of water through the pipeline. External plumbing pipes of polyethylene pipes are always laid below the level of soil freezing; accordingly, the estimate for laying water pipe from polyethylene pipes will, willy-nilly, include earthworks, and in winter time - also thawing of the top layer of soil.
It is curious that butt-welded whips are often used to reconstruct old steel and cast-iron water lines, and not always these works require excavation.
Ways of pulling a polyethylene pipe into an old water supply can be attributed to two main categories:
- Pass through the old trunk pipe of a smaller diameter. The smaller roughness of polyethylene compared with metals compensates for the reduced clearance; however, deposits on the walls of old pipes can make the broach problematic. Even despite the preliminary mechanical cleaning: sometimes the ruff is unable to cope with perennial layers of lime and rust.

- Pass pipe of the same diameter with the preliminary destruction of the old pipeline. In this case, a hydraulic calibrator is preliminarily pulled through the old pipe by a cable, which cyclically increases and decreases its outer diameter, destroying the old line and pressing its fragments into the soil.

Walls less than 4 mm
With a small thickness of the walls, the assembly of the plumbing from polyethylene pipes can be carried out with the help of electric-welded or compression fittings.
- In the first case, the socket fittings are put on the ends of the pipes, after which a voltage of 12 volts is applied to their contact terminals. Reheating the spiral heater built into the fitting causes it to fuse reliably with the pipe.

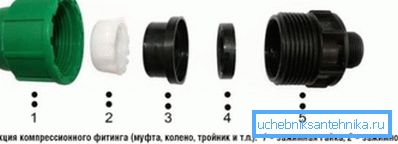
- Compression fitting crimps the pipe with a rubber O-ring when tightening the union nut. This method of connection does not require the use of any tool other than scissors for cutting pipes. The simplest instructions can help avoid leakage during assembly: be careful when positioning the rubber sealing ring and avoid it past the groove between the pipe and the body of the fitting.
Conclusion
Hopefully, we managed to answer all the questions of interest to the reader. As always, additional thematic information will be offered to him by the video in this article. Successes!