Technical characteristics of the polyethylene pipe: the pros
In the arrangement of water supply systems and pressure sewage systems, almost all diameters of polyethylene pipes are used. At the same time, most experts note the high performance of this material, allowing to design reliable and durable communications.
In this article we will try to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the technical properties of products made of polyethylene, drawing attention to their pros and cons, especially in the aspect of installing pipelines with their own hands, without the use of sophisticated equipment.

Material characteristics
To understand how to maximize the use of polyethylene products in the design and installation of communications, it is necessary first to study the polymer itself.
This substance has the following operational properties:
- The material is resistant to mechanical loads, chemical reagents, as well as to the effects of ultraviolet radiation. This set of advantages provides pipelines with a margin of safety and a long service life (up to 50 years).
- Pipes made of this polymer have a low density - up to 0.96 g / cm3. Due to this, the weight of polyethylene pipes is quite acceptable, and communications exert a relatively low load on the supporting structures.
- As for the grades, in the production of tubular products, the most commonly used types are denser PE80 and PE100. The use of PE32 and PE63 is somewhat limited by their low mechanical characteristics.

- Subject to the observance of production technology, the material is notable for its considerable heat resistance, as well as for an insignificant coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Another plus is high elasticity. The possibility of bending even a rather short segment makes installation easier.
Note! The elasticity of the PE-pipe has disadvantages. The main one is that, after bending, it, unlike metal-plastic varieties, rather quickly regains its shape, therefore, for the installation of piping, it is necessary to turn the fittings.
The price of the material is also quite affordable. In principle, if necessary, the market can find cheaper and more expensive options, so that from a financial point of view, polyethylene acts as a kind of "golden mean".
Pipe properties
Dimensions, weight and marking

One of the advantages of the described product is a fairly extensive size sect.
The range of parts includes varieties with a diameter from 10 to 1200 mm:
- The thinnest models are used for arranging water pipes.. For example, a 32 mm polyethylene pipe may well be used for laying the main water supply system in a private house, but it is more convenient to make the wiring to the water intake points of elements with a cross section of about 20 mm.
- Thicker pipes (up to 100 - 150 mm) are used for the installation of sewer systems. In this case, most often such communications are designed according to pressure type, since cheaper polypropylene or polyvinyl chloride models with a shaped connection can be used for free-flow sewage.
- Polyethylene pipe 300 - 1200 mm - an excellent choice for laying water-carrying communications. The main difficulty in this case will be the arrangement of the joints, because usually professional equipment is used to solve this problem.

Another parameter that needs to be taken into account in addition to the cross section is the SDR. This value shows the ratio of the diameter of the product to the thickness of its wall. The smaller the SDR, the higher the strength of the pipeline, but at the same time, the higher the load on the supporting base.
The weight of a polyethylene pipe of 1 m largely depends on this parameter. We will give some examples in the table below:
| SDR -11, pressure up to 1MPa | SDR - 21, pressure up to 0.5 MPa | ||||
| Diameter, mm | Wall thickness mm | Weight, kg | Diameter, mm | Wall thickness mm | Weight, kg |
| 20 | 2 | 0.12 | 40 | 2 | 0.23 |
| 32 | 3 | 0.28 | 50 | 2.4 | 0.42 |
| 40 | 3.7 | 0.43 | 75 | 3.6 | 0.81 |
| 50 | 4.6 | 0.67 | 90 | 4.3 | 1.19 |
| 75 | 6.8 | 1.49 | 160 | 7.7 | 3.79 |
| 90 | 8.2 | 2.15 | 280 | 13.4 | 11.52 |
| 160 | 14.6 | 6.79 | 400 | 19.1 | 23.38 |
| 280 | 25.4 | 20.7 | 500 | 23.9 | 36.5 |
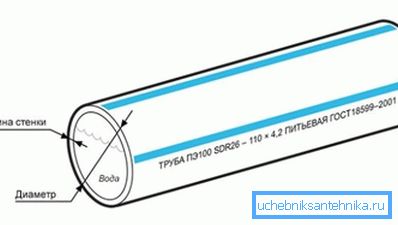
Marking of polyethylene pipes, which is applied to the outer surface of products, necessarily includes the following designations:
- Mark used polyethylene.
- SDR value.
- Outside diameter.
- Wall thickness
- It may also indicate the standard by which the pipe was manufactured, and its purpose.

For example, the product with the marking "PE80 - SDR11 - 45.4 drinking GOST 18599-2001" is a pipe for drinking water supply, made of polyethylene PE80. The outer diameter is 500 mm with a wall thickness of 45.4 mm and the corresponding SDR.
Temperature and pressure
The most important parameters, to which plumbing experts recommend to pay the closest attention, are temperature indicators and the value of withstand pressure.
As for the temperature, it all depends on what kind of material was used:
- Low-pressure polyethylene, from which most products are produced, can be applied in the range from 0 to +400C. When cooled to -100C material becomes brittle, and overheating causes deformation.

- Cross-linked polyethylene is more durable, so pipes made of this material can withstand operating temperatures up to + 90-950WITH.
Note! Melting at 130 is typical for most brands.0C, but you shouldn’t use products at such extreme temperatures: connection nodes will be the first to suffer.
- With regard to pressure, here as the main parameter comes the above-mentioned ratio SDR. As a rule, mass models are capable of operating in the range from 0.25 MPa (SDR - 41) to 2 MPa (SDR-6).
Other options
Choosing products for the arrangement of water supply or sewage, you need to consider other parameters.
The most important in this case are the following:
- The roughness coefficient of polyethylene pipes is usually not more than 0.005 mm. Such a smooth inner surface allows to achieve the necessary throughput with a much smaller diameter. That is why when replacing steel pipes with PE products, sections are usually used a step smaller (for example, 32 mm is used instead of 40 mm).

- For underground sewer networks and water mains, the ring stiffness of polyethylene pipes is of key importance. This value determines how effectively the product resists the compressive load of the soil. This parameter is denoted by the SN index and in our case it can be in the range from 2 to 8. The pipes with SN8 fully withstand the pressure in 6 meters of soil, because they can be used in the most difficult conditions, for example, under highways.
Conclusion
Of course, this is not a step-by-step instruction on the selection of products, but only a description of the most important parameters. On the other hand, having understood the operational characteristics of the pipes, you can easily find a variant that most closely matches the task set before you. For a more detailed study of the material we recommend to familiarize yourself with the video in this article.