Ceiling ventilation: features and benefits
The development of building technologies has given us a lot of new materials and structural solutions, among which are suspended ceilings. A feature of such ceilings is the presence of a gap between the floor slab and a decorative surface in which you can hide the ventilation channels or organize a channel-free system. We will talk about the features and advantages of the ventilation in the ceiling.

General information

Under the ceiling ventilation understand such a system in which the ducts or ducts are located above the ceiling. This allows you to remove the pipes and ducts from the functional areas of the room and win in terms of the effective use of its area.
Note! This arrangement allows you to deliver air anywhere in the apartment or house. Another advantage is also noted: mining is performed at the highest point, and it is there that the dirtiest and hottest air accumulates.
Fastening of ventilation to the ceiling is carried out in various ways: clamps, anchors, self-tapping screws to the L- or Z-profile, traverses, punched tape or metal beams. To enhance the decorative qualities of the room, the network of air channels is hidden behind the hinged structure.

Ceiling systems are channel and channelless. We want to tell about the differences and features of these solutions in more detail.
Ceiling ventilation systems
Ducts

Despite the development of channelless VAV-systems, good old channel ventilation remains the undisputed market leader. The overwhelming majority of all modern climate systems are built precisely in the duct design.
If the location and appearance of the air ducts in production and utility rooms are not critical, then in residential buildings and apartments it becomes decisive: not everyone has an industrial interior with metal pipes overhead.

Due to decorative restrictions, builders did not use a system of canals with an extensive network and targeted air supply, but were limited to several vents in the kitchen area, bathroom, and sanitary facilities. This led to a noticeable stratification of air masses and the appearance of multiple stagnant zones.
Today, it has become possible to use ceiling ducts: suspended ceilings mask air ducts well, which allows supplying air masses and removing exhaust air pointwise.
Note! Here the ventilation ceiling ceiling diffuser plays an important role, which allows to increase the flow rate and its range, which leads to high-quality mixing of air masses and equalization of temperatures.

Advantages of channel systems:
- Address point supply of fresh air allows the most efficiently distribute the incoming mass of fresh, clean and cooled gas among its consumers;
- Channel performance allows you to effectively monitor the ventilation in real time and make adjustment and adjustment of modes by means of automation;
- Under channel duct conditions, it is easier to organize effective air treatment systems: filtration, cooling, heating, etc .;
- It should also be noted the possibility of installing fire dampers and other protection systems with separate channels.
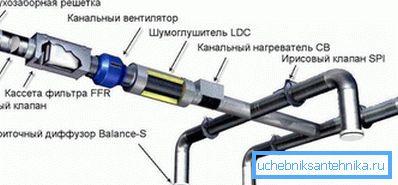
The disadvantages of channel performance are its qualities:
- The duct system is mounted as a fixed network, which is laid before the finishing works. As a result, any redevelopment or interior change faces the problem of inconsistencies between the new layout and the old ventilation network. This is especially true in office and rental premises;
- When switching to reduced performance modes, there is a drop in the air supply speed and the range of diffusers with a fixed area, which leads to stagnation in the zones between the diffusers (this problem is partially solved by the ceiling fan-chandelier);
- Complicated branched networks differ in the high cost of equipment, maintenance and repair;
- Compared with channelless systems, energy consumption increased by 30%;
- The microclimate inside the channels contributes to the development of mold, which is not observed in channelless performance.
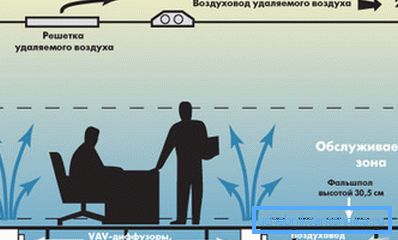
Channelless

As the name suggests, these systems do not contain pipes or ducts for transporting air masses. Instead, they use the space between decorative and structural ceilings or floors as an air duct.
This solution allows us to win not only from the point of view of design and ergonomic space, but also has much more significant economic and technological points of view.
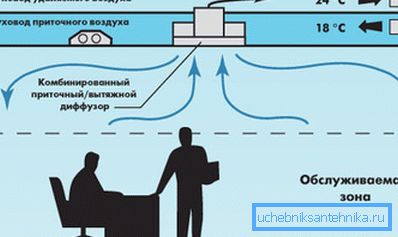
The latest ceiling systems operate on the principle of variable air volume (VAV), or variable air flow. At the same time, the working pressure in the underground and ceiling ducts is 12.5 Pa, which, in comparison with the standard 373 Pa in the channels, is in itself worthy of attention.
Consider the main advantages of channelless HVAC systems:
- Flexibility. In contrast to the network of channels, a common duct allows you to place diffusers anywhere, moreover, no problems are caused by their transfer to other places. At the same time, complicated recalculation and redesign is not required;
- Energy saving. As already mentioned, the power consumption of the ceiling ceiling ventilation systems is reduced compared to the channel by 30%;
- No mold. The temperature and relative humidity of the air passing through the ducts is equalized by recirculation and heating to such values at which the development of fungal organisms is impeded;
- Reduced capital investment. Potentially, duct-free systems should become noticeably cheaper than others, because the price of pipes alone, fixtures, installation work and design is still high.
Note! It’s too early to speak about the shortcomings of this solution, since there are no reliable data on the practice of using channelless systems.
At this stage, we can note the shortage of craftsmen with sufficient experience in the construction of such facilities. In addition, there is no clearly developed instruction for their installation, which makes the work with your own hands a risky occupation.
Conclusion
Ceiling ventilation system has a number of advantages in comparison with wall or other form of networking. The most progressive solution today is channelless VAV ventilation, located in the underground and inter-ceiling spaces (see also the article Chimneys and ventilation: danger, operation and prevention).
Additional visual information is contained in the video in this article.