Classification of ventilation and familiarity with
This article is devoted to what kind of ventilation is and by what criteria it can be classified. In addition to the actual classification of species, we will pay attention to some types of ventilation equipment, learn about their device and functions.

What it is
The origin of the word ventilation from the Latin ventilatio - airing, in general, gives a comprehensive picture of the essence of the process. The term initially means only the removal from the room of polluted, exhaust air and its replacement by external air.
In addition: in the framework of established terminology, the same word often denotes sets of equipment that provide air exchange.
Progress, however, does not stand still: since Latin terms were borrowed by modern European languages, ventilation equipment has learned to perform many additional functions.
- Ventilation is entrusted with the supply and cooling of the supply air to comfortable temperatures.
- She learned to regulate the humidity of the atmosphere in the room, drying the air or, on the contrary, moistening it.
- The ventilation equipment was assigned the function of cleaning the air from dust and other contaminants.

Classification
So, by what signs are modern ventilation systems classified?
Motion of air movement
It can be natural or forced. Natural circulation is ensured primarily by the difference in the density of warm and cold air. Warm air masses rush upward and are forced into the receiving lattice of the ventilation channel, from where they are removed to the street.
Additionally, the rate of circulation can be affected by:
- The pressure drop created by the wind at the location of the supply and exhaust channels on different sides of the building.
- The vacuum created in the ventkanal in windy weather by the deflector is a special shape with a canopy opening onto the street.

The main drawback of natural ventilation is the instability of the flow of air through it, which depends too much on the temperature delta between the room and the street, on the direction and force of the wind.
Forced or mechanical ventilation is provided by the fans. Its performance is very stable and independent of external factors; moreover, it is easy to adjust simply by reducing the speed of the impellers. The price of consistency is energy dependence: when power is interrupted, the fans stand up.
Note: effective filtration, heating and air conditioning are possible only in forced ventilation systems. To a large extent, precisely because the corresponding processes require a stable flow of air through the corresponding equipment.

Air flow direction
The apartments in apartment buildings are familiar to all of us exhaust household ventilation, designed to remove the exhaust air (usually through the bathroom and the kitchen).
Air flow in this case is passive. In the Soviet-built apartments, it was carried out through unconsolidated window frames and doorframes; In modern homes, plastic windows are increasingly equipped with inlet valves.
Such a scheme has a rather unpleasant feature: air is injected into a dwelling, the temperature and humidity of which are determined only by the weather and the season. For the inhabitants of housing, for finishing materials and furniture, sudden changes in temperature and humidity are not so useful.
Inlet, or, as it is sometimes called, reverse ventilation, allows you to carry out the very activities that we have already mentioned above - to dry or moisten the air, change its temperature in one direction or another, and filter out pollution.
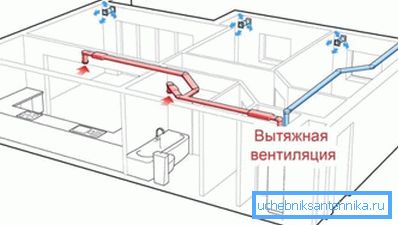
Purpose
What functions can perform ventilation systems?
| Type of system to destination | Functions |
| General ventilation of a workshop, building or section | Creating the same environmental parameters in the entire volume of the room. |
| Local ventilation | Supply clean or remove polluted air directly at the site of any work. A typical example of a local exhaust ventilation device is a kitchen hood. |
| Emergency ventilation in production | Forced air exchange at production sites where a large amount of harmful substances may be released. The so-called gas ventilation, used after the operation of gas extinguishing systems, falls into this category. |
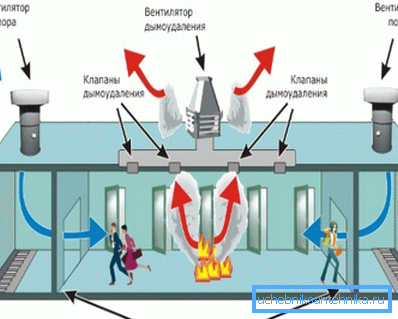
| Fire (smoke) ventilation | Provides accelerated pumping of combustion products in case of fire; at the same time it supplies a large amount of clean air to the evacuation routes (in particular, to elevator shafts and corridors). For obvious reasons, PVC or polypropylene ventilation is not used in this capacity: duct material is steel with a thickness of 1.2 mm. |
Presence of air ducts
Air ducts (ventilation channels) for transportation of clean or exhaust air are called channel ventilation. A ductless ventilation system is a scheme in which air is pumped out or injected directly through a wall or ceiling of a building — by means of a fan or naturally.
Equipment
Now let's get acquainted with some types of devices used in ventilation systems.
Fans
An axial fan is an impeller mounted on a motor shaft that transports air flow along its own axis of rotation. Typical examples of an axial fan are the cooling system of the processor of any modern desktop computer or the exhaust hood in the ventilation duct in the kitchen.

By the way: when installing exhaust ventilation with your own hands, it is better to choose a model of an exhaust or duct fan with a sliding bearing, rather than rolling. The instruction is associated with less noise in this type of bearings.
The advantage of the axial scheme is a relatively high efficiency. The disadvantage is a relatively small pressure created at the outlet.
Radially predictably called a fan, forcing the air flow to move along the radius of the impeller. The impeller rotates in the housing; Most of the losses are due to air friction on the inner wall of the casing of the device. However, due to the minimum gap between the wheel and the cochlea, this scheme provides a much higher output pressure than the previous one.

Muffler
Obviously, comfort ventilation should produce a minimum of sounds. However, productive fans for some reason do not want to spin silently. The logical contradiction is overcome by the installation of a silencer after the inlet fan - containers with developed internal fins, covered with noise-absorbing material (fiberglass, porous rubber, etc.).

Recuperator
This is a common name for devices that carry out heat exchange between exhaust and intake ducts. They allow very significant savings on heating and air conditioning.
There are three concepts of the work of the heat exchangers.
- The plate heat exchanger provides cross-movement of immiscible flows from adjacent channels with a large number of common walls.. The scheme is extremely simple and energy-independent. Its only drawback is the freezing of the heat exchanger at low temperatures; The problem is solved by temporarily opening the bypass for the supply air, after which the warm stream of the exhaust duct quickly melts the ice.
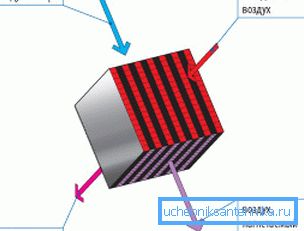
- In a rotary device, a wheel with a developed fins rotates around an axis located on the border of the flows. The advantage of the solution is leveling the humidity of the supply air due to the transfer of condensate on the edges of the rotor. Disadvantages - the complexity of the design, energy dependence and partial mixing of the streams, which leads, in particular, to the transfer of odors between them.
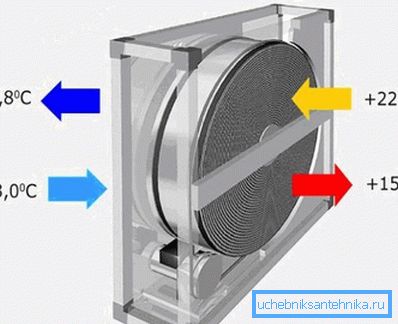
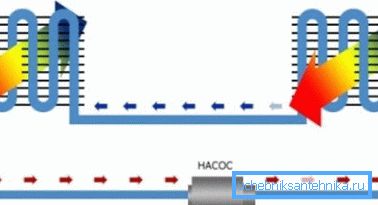
- The unit with an intermediate coolant is, in effect, placed in the ventilation circuit of two convectors and a circulation pump, a kind of miniature heating system without a boiler. The disadvantages of the scheme - the complexity, high cost and low efficiency. Its use is justified only in those cases when the architectural features of the building make it necessary to spread the inflow and extract to a considerable distance.
Heater, air conditioning
As already mentioned, the ventilation device often includes devices for adjusting the temperature of the inlet flow. An air heater is an electric or water heater; in most cases, the cooler is a conventional ducted air conditioner with an external block placed on the roof or facade.

Plenum chamber
This is a simple fixture for the inlet duct, which allows air to be distributed over the entire grid area. It is a box of small volume, in which the turbulent flow turns into laminar.

Fire damper
Their function is to block the spread of flame through general exchange ventilation in case of fire, to ensure effective removal of smoke and the inflow of fresh air to the evacuation routes. By the initial position of the flap, they are divided into normally open, normally closed and double-acting valves.
The valve may be actuated by a spring or a solenoid. A fusible latch, an electromagnetic latch, or the same solenoid that keeps the valve from closing or opening can act as a lock.

Conclusion
We hope that our somewhat superficial insight into the types of ventilation systems and equipment has satisfied the reader’s curiosity.
As usual, the video in this article will offer him additional material. Successes!