Design of ventilation in the house: regulatory requirements
The topic of this article is the design of ventilation in a private house. There are no abstract theoretical studies and recommendations: the proposed material is a summary of the author’s practical experience in designing a ventilation system in his own home.
Foreword
A few years ago, the author of these lines entered a new house. The building attracted a beautiful view from the windows and excellent repair; First impressions, of course, were enthusiastic.
However, the very first winter (it should be noted, rather mild: for the winter Crimea, even -5 is considered a rare frost) revealed a number of problems.
- Glasses of metal-plastic windows were constantly misted. The condensate was going to drops and puddles on the windowsill.
- After some time, the air in the house became heavy and musty. There were unpleasant odors.
- The corners began to dampen; the walls were wet to the touch. Literally a month later, a fungus appeared.

Note: mold is not only ugly. The fungus accelerates the destruction of capital structures; in addition, the products of its vital activity are considered extremely harmful to the health of the inhabitants of the contaminated housing.
- With a seemingly quite comfortable temperature of + 18C at home, it was subjectively very cold.
Last played a decisive role. After several decades in the Far East, the idea of freezing in the Crimea seemed so unnatural that it was decided to devote all the time and effort to solve the problem. It (the cause) was easy to find: the house was completely absent ventilation system.
At that time, the project of house ventilation seemed to the author to be something extremely prohibitive and requiring highly specialized knowledge: there was a catastrophic lack of experience and knowledge. Further actions were committed by the national method of trial and error. This article is an attempt to share good ideas.
Regulatory requirements
The design and calculation of ventilation in a private house was quite logical to begin with the research of regulatory documentation. The search was short-lived: the instruction was found in the domestic SNiP 31-02-2001 Single-family residential houses.

To begin with, it turned out that the temperature maintained in the house did not meet current standards.
| Type of room | Minimum temperature |
| Living rooms, bedrooms, offices and other rooms with a permanent stay of people | 20С |
| Kitchens, restrooms | 18С |
| Baths, showers | 24С |
Changing the air conditioners that heated the house increased the power consumption, but predictably did not change the sad picture in any way: it was still damp and very, very cold in all the rooms. Yes, despite the appropriate temperature.

A section directly related to ventilation provided new food for thought.
| The room | Air Exchange Requirements |
| Any with a permanent stay of people | Complete air renewal once per hour |
| Kitchen while cooking and eating | Not less than 60 m3 / h |
| Bath, bathroom | Not less than 25 m3 / hour |
| Other rooms with a periodic stay of people | Full air update every five hours |
It was easy to calculate the volume of the heated floor in the winter: it was 240 cubic meters. However, due to the specific layout, lack of gas equipment and the presence of only two permanent inhabitants, the calculation of house ventilation was adjusted for heat saving reasons: instead of an hourly air exchange in a volume of 240m3, it was decided to stop at half the ventilation capacity.
Boil work.
Implementation
Schema selection
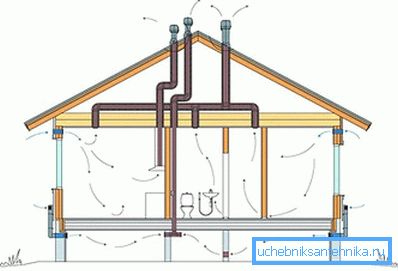
In the already mentioned SNiP 31-02-2001 there are three concepts of ventilation:
- Natural - when exhaust air is forced into the ventilation duct due to natural circulation. Heated, he rushes up and is at the air intake; the inflow is provided by ventilation grilles in the lower part of the walls or by suction through unconsolidated doors and windows.
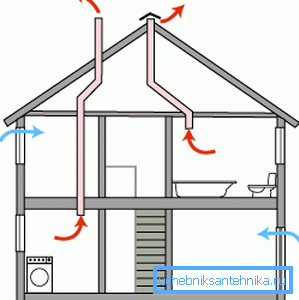
- Forced - with pumping out the exhaust and forcing fresh air fans.
- Combined - when only air is forced out. The supply is again organized by leaky windows and doors.
It was decided to stop on the third variant.
There were several reasons.
- To organize the exhaust from the kitchen, bathroom and rooms, it was possible to use the channel immured by the builders between the bolt on which the floor slabs relied on and the wall. But the intake channel would have to lay, spoiling the walls.
- Natural ventilation would work with unpredictable performance: strong winds are characteristic of the Crimean coast in winter. Forced exhaust is limited by the exhaust fan; winds affect her performance slightly.

- The forced ventilation duct may have a smaller diameter than the duct for natural air circulation.
- Finally, it attracted the low price of the components required for the project. In general, a pipe with a deflector, several ventilation grills, a plastic hatch, a fan with a wire and a switch for it were required.
Installation
It was easy to assemble a few equipment with your own hands.
- The channel between the crossbar and the wall was opened from the side of the street with a punch. A pipe with a deflector nestled in the hole; the groove was zapen and puttied.
- From the inside of the wall a plastic hatch was installed in the duct to install, repair and replace the fan. Through it, the fan itself was installed in the pipe; the switch is brought to a convenient height.
- Ventilation grilles were installed along the canal in each room.

Subtotals
During the first day of the work of forced ventilation, the air in the house ceased to be musty; the unpleasant odors disappeared. The feeling of constant cold at 20 degrees of heat was forgotten, like a bad dream.
Note: with increasing humidity, the heat capacity and thermal conductivity of air is rapidly increasing. That is why, near large water bodies, the temperature slightly above zero is tolerated worse than -10 in regions with low humidity.
The fungus was destroyed by Belize; she also helped to get rid of traces of the life of the mold - untidy black spots.

The only problem was the cool floor: leaking cold air through the unpressurized front door made itself felt.
Inflow from the basement
Finally get rid of the last misfortune helped air supply from the basement. Due to the deepening below the ground level, the temperature around + 14 ° C kept year-round without any heating, despite the ventilation window that was constantly open to the street.
Holes for suction of heated air were drilled in the slabs; on top of them covered with ventilation grilles.

The result was beyond praise:
- With a floor area of 75m2, the average heat output necessary to maintain a comfortable 20C is only 2-4 kW, depending on the outdoor temperature.
- With the heating completely turned off, the temperature does not fall below + 12 ° C even with a negative temperature outside the window.
Conclusion
The author sincerely hopes that his experience will be useful to the reader. Additional information on how to design ventilation in your home can be found by viewing the video in this article.
Successes!