Exhaust ventilation at home what kind of her to choose and
Many of us, building our own homes, pay great attention to the weatherization of the house. Carefully isolate it, seal even the slightest crevices, put plastic windows, etc. As a result, then it is discovered that the air in the rooms is stale, there are constantly unpleasant odors and dampness.
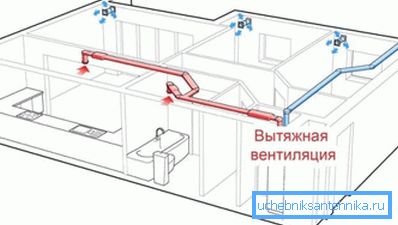
Note! We should not forget that in the rooms we not only live, but also breathe. Comfortable life you will provide only the right exhaust ventilation device in a private house or high-rise.
All types of ventilation
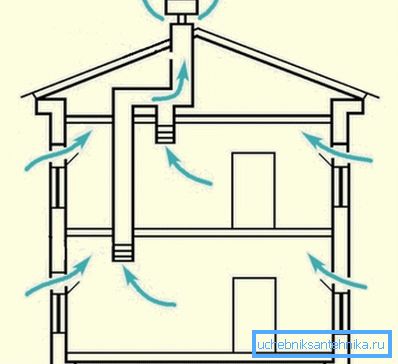
Ventilation systems are classified into three groups:
- purpose;
- the type of movement of air flow;
- method of moving air.
Based on the functions, ventilation can be:
- intake;
- exhaust;
- recirculation (recoupment) - in this case, when pure air is supplied, a certain amount of heated exhaust stream is mixed into it.
By way of moving streams, the systems are:
- channelless - air enters through doors and windows;
- channel - flows move on a network of air ducts.
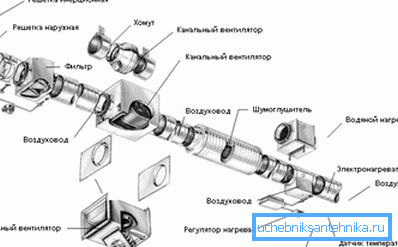
By the motive power of the system is divided into:
- natural;
- mechanical.
In the first case, the air moves due to the laws of nature. In the second - only after the start of the fan.
By design features, the instruction divides ventilation into three types:
- natural;
- forced-air (forced);
- mixed, (natural with forced stretching).
Optimal choice
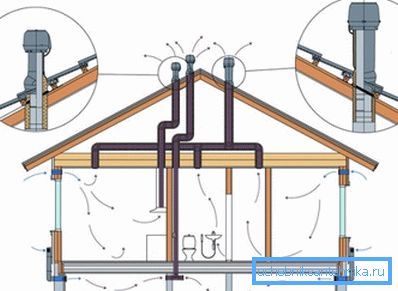
To determine the optimality of the application of a system, the following conditions are taken into account: the size of the structure, its material and the degree of purity of the atmosphere.
- Natural ventilation is perfect for a small house built in an area with a clean atmosphere.. It is best suited for buildings made of adobe, brick, logs, lumber, foam, gas and cinder block, claydite-concrete.
- Mechanical forced-air ventilation in a private house is optimal if it is large or located in an area with atmospheric pollution.. This system will provide rooms with a sufficient volume of air and purify it with the addition of built-in filtration.
Such ventilation is best suited for buildings made from 3D panels, SOTA, SIP, MDM, polystyrene concrete, “Canadian” frame houses.
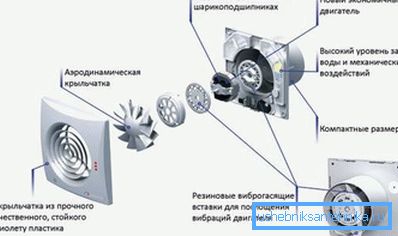
- When a natural type of ventilation cannot cope completely with its task, the installation of a mixed analog will help.. Its installation is carried out only in rooms with highly polluted air or where condensate accumulates. These are toilets, bathrooms, kitchens, basements, cellars, boiler rooms.
System planning
The ventilation device can be divided into several stages.
Stages arrangement
- Calculate the volume of air exchange. In its course it is necessary to calculate how much supply air, according to sanitary requirements, is required by the building.
- Determination of the diameter / cross section of the channels. From this will depend on the effectiveness of the system.
- The choice of the type of ventilation.
- Determination of points for air intake / intake and places for equipment installation.
- Further, a scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation of the house.
- Arrangement of ventilation.
It should be remembered that the comfort of living in the house depends on the constant inflow of outdoor air, at the optimum speed of movement of the streams.
Note! Some homeowners, wanting to air it to the maximum, put too powerful ventilation with a fan, not taking into account the size of the rooms. Such an air exchange takes too much heat from the building and supercools it.
Any of the ventilation systems has its own standard volumetric flow rate. If they are natural, is the value equal to 1 m? per hour, if forced - 3/5 m ?. Often you can not do without the use of a forced construction.
For example, when in premises a small speed of movement of air flows, and it is no longer possible to make a section of the air ducts.
- When the system is natural to let the air volume in 300 m? for an hour, ventilation channels with a cross section of 250 × 400 or a diameter of 350 mm are necessary.
- When using a mechanical analogue, you can confine yourself to a duct with sides of 160 × 200 or a diameter of 200 mm.
Calculation of house ventilation
The most important data affecting the calculation of ventilation:
- the number of permanent residents in the house;
- building area;
- amount of air in all rooms.
In addition, it must be remembered that many household appliances, such as stoves, gas stoves, burn oxygen in the air. When calculating it is necessary to take into account the fact in which rooms you need the fastest air renewal.
Designed ventilation systems, according to the state sanitary and engineering standards, voiced in SNiP, GoST, SanPiN, DBNah. The most common calculations for the area, sanitary requirements or air exchange rate.
The simplest calculations are based on the floor space.
- They are used to calculate the volume of air in residential buildings.
- It takes into account the fact that, according to sanitary standards in living rooms, it is necessary to supply 3 meters per 1 square meter? in the hour of outdoor air.
- This calculation does not take into account the number of permanent residents. For its implementation, it is necessary to multiply the total area of the rooms in the house by the sanitary rate of air exchange.
The multiplicity calculations are much more complicated than the first method.
Note! This method uses several data types and is applied only by professionals. The result of the calculations is the rate of air exchange, which indicates how many times in an hour the exhaust air is replaced by a completely street one. When calculating for different purpose rooms, different standards apply.
When designing for sanitary requirements, in addition to the rate of air exchange, the norms (in meters per hour) per permanent resident are also used. This calculation is also divided for different types of premises. As a result, all calculated figures are summed up, the result is the value of the required air exchange.
Selection of the duct section

After calculating the air exchange, you should choose the system scheme yourself and calculate its channels.
- Manufacturers produce two types of ducts: rectangular and round.
- The first of them are made taking into account the aspect ratio of the channel, which should be 3: 1.
- For mechanical systems, the air velocity in the main pipe should be 5 m / s., In the branches - 3 m / s. For natural counterparts, the value is 1 m / s.
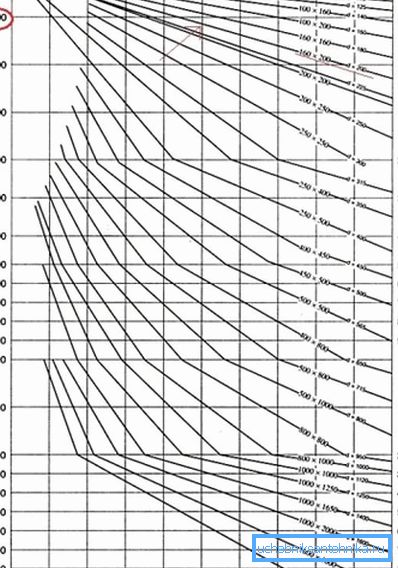
- To find the size of the channels there is a regulatory chart that takes into account the speed and cost of air.
- So, with a standardized air exchange of 360 m? per hour and forced ventilation, it is necessary to elect pipes with a section of 160? 200 mm or with a diameter of 200 mm.
Ventilation requirements
The main conditions for proper arrangement of the ventilation system are given below.
- Exhaust air from the channel is removed on the roof, 1/2 meter above its level.
- If the system is mechanical, the air enters the premises with the help of an intake grille located 2/3 m from the ground level.
- The movement of air should be arranged so that the air from the hall, nursery, bedrooms and other living rooms go to the most contaminated areas: toilet, bathroom, kitchen. Due to this, the least clean air will not be able to get into the residential sections.
- Separate exhaust ventilation ducts must be placed in the kitchen for gas stoves and gas water heaters (if available). In this room, only the mechanical system will be effective.
- Ventilation should be installed in all areas of the house, without exception.
If you want to put plastic windows

Now sealed plastic windows that completely block the flow of outside air into the room are in great demand.
Note! When choosing a product model, make sure that it has a supply valve. It will provide an opportunity to organize the flow of fresh air into the room.
- If there is no such fixture in the purchased windows, you can install the valve yourself in one of the walls.
- It is a round-shaped nozzle passing through the entire thickness of the wall.
- From the inlet and outlet, such a tube is closed by gratings.
- If the supply valve is made behind a heating radiator, then the outside air will immediately warm up in winter. Such a device can be equipped with a filter and a temperature sensor.
Air recovery
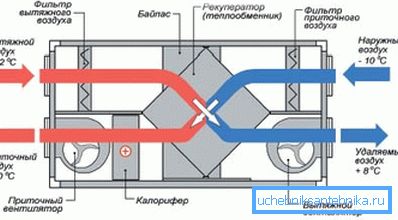
- At the moment, ventilation supply and exhaust systems with heat energy recuperators are becoming more and more common.
- Such devices heat incoming outside air in winter.
- Installations have good economy, although the price of the design itself is more expensive than conventional mechanical analogs.
- However, during operation, it makes it possible to save up to 40% of the heat in the building. The principle of operation of the heat exchanger is based on the partial heating of cold supply air with a warm exhaust stream.
- If there are severe frosts, you can connect the heater, which is built into the recuperator. So the outside air will be warmed up more efficiently.
- In such systems, the air enters / is vented by means of a fan. In most cases, additional equipment is quite voluminous. Based on this, it is best to place it in the attic.
Conclusion
Competently equipped exhaust ventilation system in your own home and not only will give you the opportunity to constantly breathe fresh air and prolong its service life (see also Ceiling ventilation: features and benefits).
The video in this article will help you understand this issue.