Fans for ventilation: an overview of the basic structures
Selection of the fan for the ventilation system is one of the most important moments when designing air exchange circuits. It is extremely important that the selected device provides the necessary performance, and the air intake / removal is carried out in the right amount.
Below we consider what types of fans for ventilation are used in different situations, and also give a number of tips for installing units for domestic needs.

Varieties of models
Radial
Radial structures are called devices, in which the working parts - the blades - are located on the rim. The rim itself rotates around an axis, creating a stream of high pressure air.
Note! In most cases, such systems are installed outside the premises - on the roof or on remote wall consoles. Internal installation of radial fans is justified only on the technical floor.
The efficiency of such a device, as well as other parameters, is determined by the shape of the air intake vanes.
- Models with backward curved blades in relation to the direction of rotation of the rim, demonstrate good efficiency only when working with clean air. Quite often, this design has a fan for ventilation. With regard to the advantages of this model, the most important should be considered a low noise level when working even at the power limit.
- Straight blades (radial and deflected back) are often used in the construction of systems for removal of polluted air. The impeller configuration prevents the ingress of contaminants to the rotating parts of the axle and the rim, which significantly reduces wear on parts and facilitates preventive maintenance.
- Forward-curved blades provide high air exchange efficiency even at relatively low pressure. The shape of the wing part allows to achieve good performance in terms of the relatively small size of the device, because such designs are preferred in the design of domestic air exchange systems.
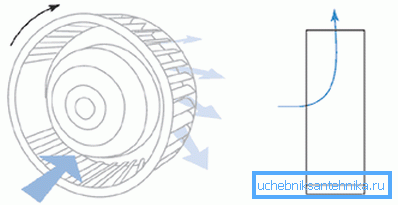
The general advantages of this type of device include good air injection, which ensures its excessive inflow, which means that conditions are created for the smooth operation of the exhaust.
Axial
Axial (axial) fan - the most common model that is used in most exhaust devices. These devices are equipped with exhaust hoods, forced flow systems, ceiling, floor fans, etc.

The design of this type of device is quite simple:
- The torque, as in the previous case, is transmitted to the axis of the mechanism.
- Immediately attached to the axis of the blade (the so-called propeller type of attachment). The volume of transported air depends on the shape and size of the blades, which explains the variety of models on the market.
- On the other hand, mounting the blades directly on the axis leads to significant performance losses, because most often the axial ventilation fan is mounted in a cylindrical housing or duct with minimal gaps between the walls and blades.

Note! In order to increase productivity, guide blades are often installed behind the propeller part. Mounting the air exchange system in the kitchen or bathroom can be done with your own hands, taking the plates from galvanized steel as parts.
Diagonal
A diagonal fan is the result of combining the principles by which axial and radial models are constructed:
- Blades fixed at a large angle are mounted on the impeller.
- When the wheel rotates, the pressure increases due to an increase in centrifugal force.
- Moreover, the greater the speed of rotation of the fan, the higher the injected pressure.

As for the scope of these devices, it is very limited. As a rule, centrifugal fans for ventilation systems in systems of forced air cooling, as well as in large-volume inlet circuits.
Diametral
Diametric devices are very different in appearance from other devices that are used to provide inflow and exhaust:
- The impeller is a rod or cylinder of relatively small diameter.
- Air intake vanes are mounted on the rod or the outer wall of the cylinder. They may have a very different profile, but the most commonly used models are with blades curved in the direction of the air flow.
- The air passes from the outside of the fan, because to increase the pressure moving parts are usually placed in special housings.

This design allows you to move large enough volumes of air. For this reason, diametrical fans are used where it is necessary to install relatively compact devices, for example, when organizing air curtains, etc.
Note! The key disadvantage of the diagonal and diametric models is the high complexity, due to which the price of the devices also turns out rather big. Most often they are used in industrial air exchange networks, as well as in arranging the ventilation circuits of modern apartment buildings.
Tips for choosing
Installation recommendations
Most often, residential premises (private houses and apartments) are not completed with forced ventilation. This is due to the fact that during the design process, the so-called slotted ventilation, diffusion of air through leaks in window and door frames, is put into account.
However, the installation of modern sealed windows, as well as exterior doors with sealing circuits minimizes the amount of incoming air, and the flow stops almost completely. As a result, air exchange standards are not fulfilled even approximately, which affects our health.
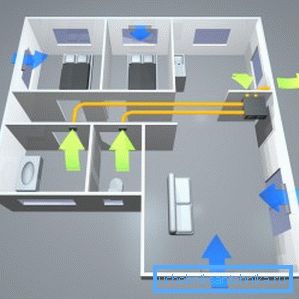
On the other hand, after several years of operation of exhaust ducts without proper maintenance, their throughput is significantly reduced. As a result, neither the inflow nor the extractor effectively work, and the air in the living quarters becomes stagnant and practically unsuitable for breathing.
The output will be to ensure the flow of air (ventilation or installation of special valves) and the installation of special exhaust devices.
As a rule, such devices are mounted:
- In the kitchens. First of all, these are exhaust hoods that remove smoke and steam from the space above the stove, as well as special fans in the kitchen windows.

- In the bathrooms. Here, most often, a ventilation grid with a fan is fixed under the ceiling, which allows you to quickly get rid of unpleasant odors.
Note! Also forced ventilation of the bathroom normalizes the humidity regime, which allows you to protect the room from infection by fungi. Naturally, the high humidity of the exhaust air must also be taken into account, because the instruction recommends installing devices with good waterproofing here.
- In workshops and other rooms, which need an operational hood.
In addition to the above-mentioned installations, complex wall valves with ventilating mechanisms have recently become popular. The most modern models of such valves can operate both in the inflow mode and in the exhaust air removal mode.

Parameter Definition
The question of how to calculate the fan power for ventilation is most relevant in the design of industrial premises and public buildings: this is where a large number of people are constantly located, and oxygen consumption per unit of time will be significant.
For ordinary living quarters, the calculation will be quite simple, since the possibilities for natural adjustment are much greater here.
Instructions for determining the parameters involves the use of the following formula:
L = Lnorm * N, where:
- L is the required volume of air, m3/ h
- Lnorm - the rate of air consumption by one person per unit of time (according to SNiP 41 - 01-2003, this value is 60 m3/ h)
- N - the maximum number of people that can be in the room.
In addition, to improve the efficiency, you can use the multiplier of air exchange rate (for living rooms - 1-2, for offices - 2-3, for production areas - 4 and more).
Multiplying the figure obtained in the previous case by the corresponding factor, we get the recommended performance of the ventilation unit. Then we will only have to compare the result of the calculation with the technical parameters of the models available on the market and choose the appropriate one.
Conclusion
Information on how to choose a fan for ventilation, and what type to use in a given situation, will be useful, first of all, for those who are planning to design all communications of their home.
For a more detailed acquaintance with the range of air exchange equipment, as well as with the intricacies of the arrangement of ventilation networks, we recommend watching the video in this article.