Forced-air and exhaust ventilation in residential buildings
For normal human life, inside any room, natural air exchange is necessary, which should ensure a constant inflow of fresh, oxygenated air from the outside, and the removal of exhausted air, saturated with carbon dioxide, from the inside of the room.
In order to ensure normal air circulation inside the building, to preserve the natural microclimate, and at the same time minimize heat loss during the construction of new houses and other buildings, the installation of supply and exhaust ventilation of the required type is immediately performed in all rooms.
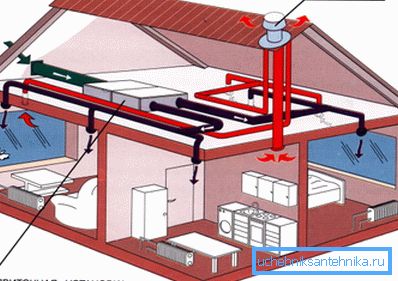
The main features of exhaust ventilation
In order to independently perform the installation of exhaust ventilation in a particular room, first of all, it is necessary to correctly understand all the functions that it must perform, depending on the purpose for which the room will be used.
So that the reader can cope with this simple task without problems, this article will present a brief guide, which describes in detail all the features of ventilation systems used in individual residential construction.
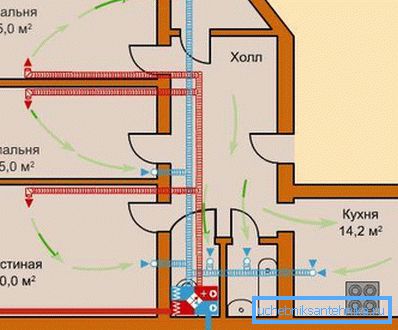
Purpose of the ventilation system
In the design documentation for the construction of buildings, there are special standards of SanPiN for supply and exhaust ventilation designed to normalize air exchange in enclosed spaces, but in addition to ensuring normal human life, they also perform some important functions.
- A constant supply of fresh air contributes to the normal circulation of air inside the room and provides a favorable, stable microclimate.
- Exhaust ventilation in the kitchen, bathroom, toilet, bath, and also in utility rooms contributes to the rapid removal of unpleasant odors, smoke, steam, and other undesirable by-products.
- Ventilation of storage facilities, such as a shed, barn, or storeroom, provides normal humidity and optimum storage conditions indoors.
- The directional movement of air in hidden cavities (thermal insulation layer, underfloor or roofing space) helps to remove water vapor, and prevents the formation of condensate, thereby maintaining the insulating properties of materials.
- The natural circulation of air in the cellars and basements helps to maintain a constant temperature and humidity conditions in the room throughout the year, ensuring long-term preservation of food.
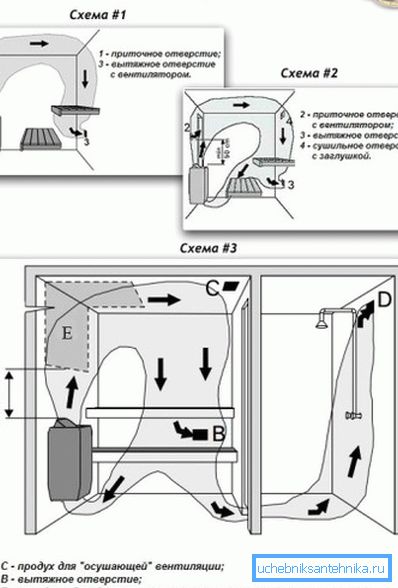
Device ventilation system
Any ventilation system should consist of at least two through holes located in opposite walls of the room. The inlet serves for the inflow of fresh air outside, and the outlet for the exit of exhaust air from the room.
Fresh air from the street enters through the inlet, mixes with the air masses inside the room, and then its surplus, together with the exhaust air is removed to the outside through the outlet.
According to its principle of operation, the device for exhaust ventilation can be of two types - with natural and forced air movement.
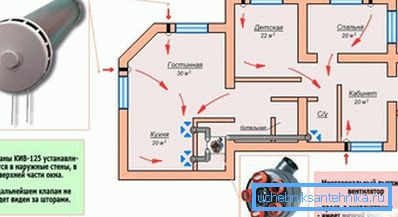
- Natural air circulation occurs due to the difference in atmospheric pressure between the inlet and outlet ports.. To ensure maximum efficiency of such a system, the inlet should be located as close as possible to the floor, and the outlet should be located at the highest point of the room.
- Forced air circulation is more efficient due to the fact that a pressure or exhaust electric fan is used to supply and remove air from a room.. Depending on the installation location of the working mechanism and the direction of movement of the air flow, the forced system can be of three types: inlet, exhaust and intake-exhaust mechanical ventilation of the premises.
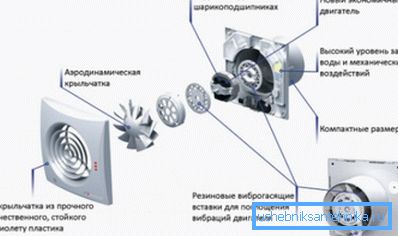
Tip! Forced air circulation is necessary in rooms with high humidity, high dust levels, as well as in those places where large amounts of smoke and water vapor can be generated, for example, above a stove, in the steam room and in the washing compartment of the bath, as well as in the garage, toilet or the cellar.
Structural elements of exhaust ventilation
By itself, the design of the supply and exhaust ventilation system consists of two independent air ducts, one of which serves for the inflow of fresh air, and the second for the removal of the exhausted air mixture.
For efficient and interconnected operation of the entire system, the design of each channel includes several auxiliary devices and mechanisms.
- External air intakes, equipped with grilles, are installed on the inlet path of the system and serve to supply cold atmospheric air to the ducts.
- Air ducts are used to receive, distribute and transport the air flow throughout the ventilation system.
- Mechanical cleaning filters are installed at the inlet of the supply path of the system and serve to clean the air from coarse debris, dust, and other mechanical impurities.

- Dehumidifiers and heat exchangers are also installed at the inlet and serve to prepare the air mixture, namely, to remove excess moisture and give it the necessary temperature due to the heat of the exhaust air.
- Axial and centrifugal fans can be installed both at the inlet and at the outlet of the system, depending on its purpose and design features. Their task is to move the air flow at the right speed in the right direction, as well as to maintain the necessary working pressure in the system.
- Electronic control systems that control the operating parameters of the entire system as a whole, and thereby automatically maintain an optimal indoor climate.
In addition to these devices, each specific system includes various auxiliary mechanisms, such as air valves, distributors, noise suppressors, preheaters, coolers or humidifiers, as well as many elements of mounting and connection fittings, therefore the final cost of inlet-exhaust ventilation is calculated individually, depending on the complexity of installation and technical project.
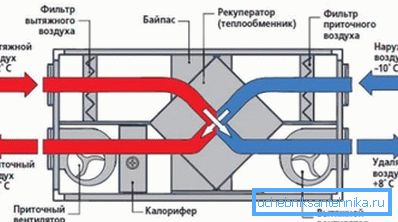
Note! Modern residential ventilation systems include an antibacterial cleaning unit, in which an ultraviolet radiator is installed to disinfect fresh air, as well as an ion exchange filter with silver particles, so the price of such devices can be quite high.
Equipment for ventilation in a residential house
In order to install an effective exhaust ventilation system in your own house, in the bath, in the garage or in the cellar, you must strictly adhere to certain rules and regulations designed to meet the dynamics of air flow and safety requirements.
- The power and performance of electric fans, as well as the length and cross section of air ducts, should be selected using special tables based on the total volume of the ventilated room.
- In case of installation of an exhaust fan, a free flow of air through the ventilation ducts, air vents, mechanical ventilators, and other ventilation devices should be provided.
- All inlets and outlets over their entire area should be covered with grids and nets with small cells that will prevent large debris, small domestic animals, rodents, insects, etc. from entering the system.

- The level of intake of clean atmospheric air should be located at a height not lower than 2 m from the ground level, and the emission of spent air mixture should be slightly higher than the level of the ridge of the roof of a residential house.
- The movement of the air flow inside the apartment building should be directed from the premises towards the corridor, kitchen or bathroom.
- The direction of movement of air masses, both in residential and non-residential premises, including a bath, cellar or bathroom, should pass from the lower part of the entrance door to the upper part of the opposite wall of the room.
- In order to be able to perform routine maintenance of supply and exhaust ventilation, all hidden units and structural elements must be equipped with removable access hatches.

Conclusion
Finally, it should be noted that for the effective use of energy-saving functions, in heated residential premises it is recommended to use supply and exhaust ventilation systems equipped with a heat recovery unit of the spent air mixture.
In order to get more detailed information on this issue, you can watch the video in this article or read similar materials on this topic in other articles on our website.