House ventilation scheme: features of choice and
In this article we will talk about which ventilation schemes in an apartment building or a country cottage are relevant today. In addition, we consider what requirements are imposed on these schemes and how certain modifications of ventilation systems are made by hand.
Until recently, the construction of efficient ventilation systems was in demand mainly in the industrial construction of multi-storey buildings. Currently, similar schemes at the professional level are used in the design of low-rise individual housing facilities. And this is not surprising, since it is not enough to build a new house, it is necessary to ensure in it the freshness of the air and the optimal microclimate.

The need for air exchange in the room
Professionally designed ventilation is not a whim, but a necessity. After all, excessive or insufficient air humidity, combined with a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide, can cause drowsiness, headaches and even exacerbation of chronic diseases.
The situation is even worse when heating or heating devices are operated in the house, which to a large extent consume oxygen. An unacceptable level of moisture content is also unacceptable, as excessively dry air provokes poor health, while too humid air causes dampness and the appearance of pathogens, such as mold.
The lack of effective air exchange in the room threatens the emergence of a number of pollution that have a negative impact on human well-being and health.
What can threaten health in the absence of ventilation:
- Carbon dioxide is a natural product of human metabolism. In low concentrations, such impurities in the air are safe, and in high concentrations they can lead to discomfort and fainting.
- Carbon monoxide in small quantities is safe, but at elevated concentrations causes nausea dizziness. Excessive gas concentration can be fatal.
The concentration of carbon monoxide can be caused by the operation of heating equipment with an open flame and with an insufficiently effective smoke removal system.
- Nitric oxide - penetrates the premises from nearby roads during ventilation through open windows. Excessive concentration adversely affects the condition of the respiratory tract and the general well-being of a person.
- Formaldehyde fumes are a toxic impurity that appears in the air when used indoors for new low-cost furniture made of chipboard. In addition, such evaporation in some cases can be released from the surface of some building materials.
- Radon is a toxic, odorless gas, well soluble in water. Radon accumulates in poorly ventilated basements and basements and can cause a number of diseases.
- The smoke of cigarettes is dangerous both for the smoker and for the people around him; it can only be removed with the help of effective ventilation.
- Dust is the most problematic type of air pollution, as there are many ways of its penetration into the room. High-quality ventilation with inlet filters does not allow dust from outside, making living in the house more comfortable.
As we could see, the need for home ventilation is obvious. It remains to consider the currently relevant schemes and choose the best option.
Current varieties
All types of ventilation of a building site can be divided into natural type schemes and schemes based on forced action.
- Natural (passive) ventilation - This is the most common type when it comes to construction sites built twenty or more years ago.
As a rule, natural-type systems operate according to the supply and exhaust circuit, when through one pipe the exhaust air is taken out from the inside, which is replaced by the same amount of air coming through the air inlet.
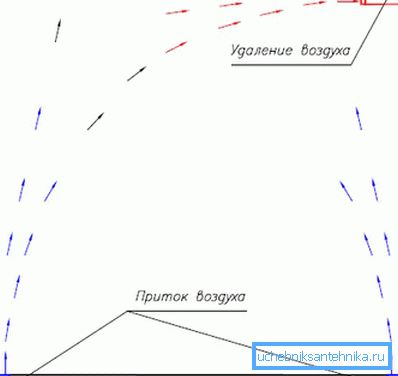
A properly designed system is theoretically efficient and is characterized by high performance. But in reality, natural-type systems have more drawbacks than advantages.
Since air exchange is based on the difference in pressures and temperatures outside and inside the building, with warming and cooling the performance of the system varies, and this process is very difficult to control.
- Forced ventilation It is devoid of the previously described drawbacks, since due to the use of blade fans with adjustable speed, it is possible to control the intensity of air exchange, regardless of weather conditions.
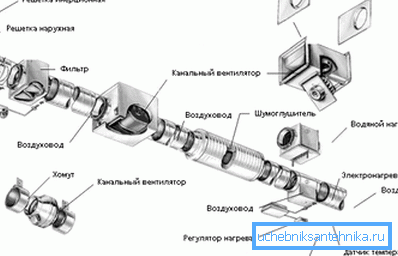
Important: Of course, the price of forced action systems is higher, since special mechanized equipment is used. Again, such systems are technically sophisticated, and therefore they require skilled maintenance.
Another advantage of forced ventilation is the possibility of combining it with heating equipment or air conditioning installations.
The device of natural ventilation in a country house
Instructions for the device of passive ventilation systems are largely determined by such features of a construction object as the area and configuration of the premises. In addition, the design should take into account the presence of the basement and basement, which also require intensive air exchange.
The best option is to plan passive ventilation simultaneously with the design of the construction site. However, if air exchange is to be normalized in an already operated building (and this is often the case) there are effective methods to achieve successful results.
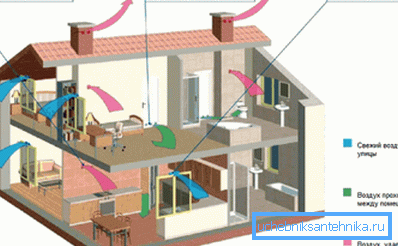
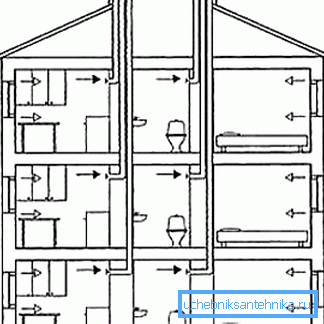
For example, in the diagram attached to the text, we can see how passive ventilation is implemented in an already operated house with minimal changes in the layout. Changes made are limited to the installation of exhaust ducts, as well as the installation of door grilles, hoods and air intakes.
All alterations of the construction object in this case are limited to the installation of technological holes in the walls and ceilings. Therefore, such work may well be done by hand without the involvement of qualified professionals.
You can learn how to punch holes of large diameter in the brick walls from the relevant articles presented on our portal.
Important: If you need technological holes made under the diameter of the pipe, you can use the service of diamond cutting. Despite the high cost, such holes will exactly repeat the outlines of the ducts, and therefore do not have to spend time on plastering.
Particular attention in the development of ventilation schemes in residential areas should be paid to the parameters of the duct.
There are many formulas and algorithms by which these quantities are calculated. In order not to focus your attention on this topic, we note that for rooms with an area of up to 50 m? there will be enough air ducts made of pipes with a diameter of up to 100 mm.
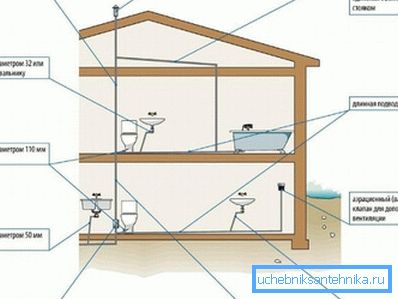
What materials to use for the manufacture of air ducts? This question is asked by many builders who master the ventilation for the first time. Unlike forced systems, in passive circuits there are no special requirements for the type of materials used to construct air ducts.
The easiest way to use sewer PVC pipes bell-shaped type of gray or orange. Such materials are simple in terms of processing, as they are easy to cut with a regular hacksaw. In addition, the socket connection, despite its simplicity, demonstrates a high degree of tightness.
And, most importantly, unlike metal pipes, polymer analogs are less prone to condensation.
Important: In order to achieve optimum comfort of living, the supply and exhaust air duct system must be supplemented by an effective sewage ventilation scheme in a private house. Such an approach to the organization of air exchange in a construction site will allow to combine all the channels into a single system and thus reduce the cost of the work carried out and materials consumed during installation.
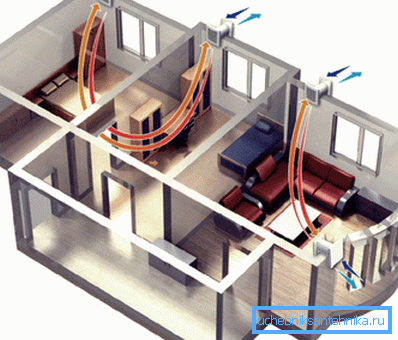
The device of forced ventilation in a country house

Instructions for the installation of such systems are in many ways similar to the construction of passive action schemes. But, there is a significant difference: the forced circuits are built using mechanized blowers - blade fans.
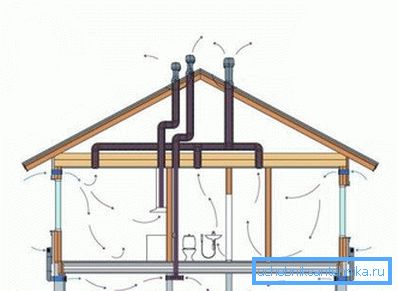
Current forced ventilation schemes can be divided into the following types:
- Systems developed at the design stage of a construction object are equipped with full-fledged air ducts and a common fan unit.
- Systems implemented in an already operated house are based on the use of low-power motorized hoods, which are installed in each individual room. Air flow in this case is based on the passive method.
Conclusion
So, now that we have outlined in general terms the features of the implementation of popular air exchange systems in a residential building, you can decide which scheme corresponds to your building project.
Are there any questions that need clarification? More useful information can be found by watching the video in this article.