Preventive maintenance of ventilation systems
According to the fact that there is an instruction manual for the operation of ventilation systems, on the basis of which, the units and ducts require preventive repair and maintenance, there are certain deadlines for the performance of certain types of work.
It should also take into account the type of ventilation, which can be:
- exhaust,
- fresh air,
- forced-air and exhaust.

These species, in turn, are also divided by type, such as:
- total,
- local,
- natural,
- mechanical (with electric drive).
We will tell you about the terms, methods, types and types, and in addition there is a video for you in this article.
Much about ventilation
Note. The type and type of ventilation device directly affects the degree of contamination of the air ducts, as well as whether maintenance of the mechanical part is necessary (for extracts and blowing).

Supply ventilation option indicates that clean (cold, warm) air only enters the room through the pipeline, and its outflow occurs naturally through open windows, doors and various leaks in the abutments of the same windows and doors.
In such cases, overpressure does not threaten - this can occur only in specialized tightly closed rooms, but there are diversion channels for this purpose. The air flow can be carried out in a general manner to the entire area of a room or a workshop, but can also be directed to a specific place, as in the photo above, which is more economical in terms of energy consumption.

In terms of appearance, the exhaust and blowing systems for local use are very similar to each other - the same pipes and the same umbrellas, except that the movement of the air flow there takes place in opposite directions.
Suction devices, however, as well as a blower, as a rule, have an electric drive that encourages the circulation of air flow. Local exhaust is mainly used in manufacturing plants to collect harmful gases and unpleasant odors.
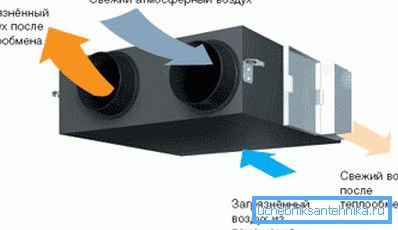
Supply and exhaust ventilation can be mechanical (with electric drive) and natural - the last option is familiar to everyone, since it is used in high-rise residential buildings, offices, shops, medical institutions and enterprises. Natural air exchange through the system of mines and canals can also be diluted with local type exhaust fans, for example, you can find such in bathrooms of residential buildings.
Terms of prevention and types of work performed
What to do every year

- It is necessary to check the bearings of the motor rotating the blades (impeller), which is located in the air heat exchanger.
- Checking the technical condition of the impeller.
- Prevention of siphon drainage.
- Inspection of the water pump located on the heat exchanger.
- Revision supports for vibration isolation.
- Testing of all instrumentation.
- Blinds cleaning grilles.
- Inspection of all wiring.
- Audit vozduhoprovodyaschego pipeline for leakage.
- Heat exchanger treatment with chemical detergents.
- With the help of the same chemical agents clean the internal cavity of the duct.
- Checking the tightness and (if necessary) sealing the joints of the pipeline.
What to do every six months
- Check the filters for ventilation systems for contamination.
- Clean condensate drainage by chemical means.
What to do every quarter

- Check the fasteners for strength and flexibility, as well as their broach.
- Inspect mounted springs in motor-blowers.
- Examine the belt guard for correct position and try to tension them.
- Remove the plaque from the impeller and center it on the shaft.
- It may be necessary to adjust the shafts of the engines and impellers.
- Inspection of parallelism, and, if necessary, adjustment of the position of the shaft and the impeller.
- Prevention of water pump nozzles.
- Check the equipment chain (power, control) and tighten the threaded assemblies if necessary.
- Testing of the three-way valve for air heating and cooling.
- Lubrication of all bearings.
- Adjust the drive belts.
- Debugging on compliance of drive pulley fan pulleys when needed
What to do every month

- Visual inspection of all equipment.
- Revision fasteners for strength and flexibility, as well as their prevention.
- Examine the belt guard for correct position and try to tension them.
- Remove the plaque from the impeller and center it on the shaft.
- It may be necessary to adjust the shafts of the engines and impellers.
- Phase Testing - Voltage and Current Imbalance.
- Prevention of electric actuators of valves and control valves.
- Record indications of instrumentation.
- Cleaning and, if necessary, replacement of air filters.
- Checking the condition of anti-vibration supports.
- Prevention of moisturizing nozzles, pump filter, storage tank and irrigation chambers
- Control of the heat exchanger, drainage and cleaning if necessary.
- Visual inspection and, if necessary, replacement of drive belts.
Mechanical ventilation
Note. Below we will look at the main types of mechanical ventilation, which, unlike the installations of natural air exchange, need maintenance most of all. Forced air circulation is carried out either with the help of an impeller rotated by an electric motor or with an ejector (the final effect is almost the same, although the price is different).
Inlet
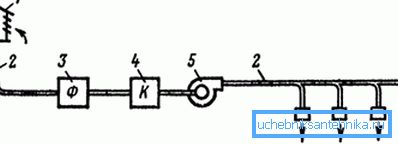
The ventilation system in most cases from the air intake device, which is also called the air intake (1), is installed outside the building (usually on the roof), but at the same time they are looking for a place for it where the cleanest air is.
Air is transported to the premises by the air duct indicated in the diagram by the number 2 - they are made of brick, concrete, a mixture of slag and alabaster, as well as metal and plastic. The air stream is cleaned from dust using a filter (3).
So that in the winter season the strongly cooled air does not get into the room, it is passed through the heaters (4), where hot water and steam are usually used as the heat carrier, but also the use of electric air heaters is practiced. The air flow causes the centrifugal fan to move (5).
Number 6 denotes a nozzle with an air inlet through which air enters the room - this can be local or deployed flow (local or general ventilation), which is regulated by means of valves or choke valves located on the branch duct in the air receiver.
For fans, heaters and filters, as a rule, the working chamber is equipped - they must be in the same room, as required by the rules of operation of ventilation systems.
The transported air is supplied to the working space in a zone no more than two meters high - this corresponds to human growth, therefore, it allows you to breathe clean air. At the outlet, a silencer of ventilation units is installed so that the output stream does not irritate the hearing with extraneous sounds.
Exhaust
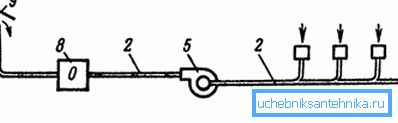
For an exhaust device, nozzles with exhaust holes are necessary (in the figure they are marked with the number 7) through which air is drawn from the room, impellers rotated by an electric motor (5) and channels for transporting air (2).
The figure 8 in the diagram indicates a filtering device for clearing the flow of gases and dust, but filters are installed only in those cases if the concentration of pollution in the air emitted into the atmosphere exceeds the norms for a certain area (residential area, countryside, mountains). The discharge devices themselves (9) should be installed 1-1.5m above the ridge or the top of the ramp.
When exhaust ventilation is activated, clean air enters the room through doors, window vents or specially equipped openings and through leaky connections of the structure (the same windows and doors). In some situations, the system of such air exchange can be a significant drawback in the arrangement of the object - there can be drafts in the room, which, in turn, affects human health.
Supply and exhaust
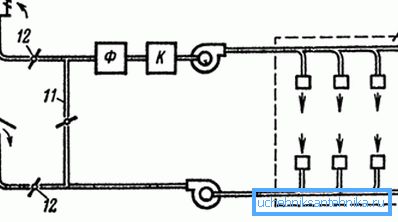
The most functional can be called supply and exhaust ventilation, the schematic diagram of which you see in the upper image. Here are collected together two types of equipment that provide uniform air circulation in the room, regardless of the outside air temperature.
The location of the umbrellas / slits for blowing and exhaust is determined in accordance with the production needs of a particular workshop or public building.
From the outside of the building, it is necessary to determine the place for air intake and the main factor in choosing it is the wind direction - it is mounted on the windward side of the nozzles for discharge with a minimum distance of 8m, as well as away from third-party pollution sources.
If the supply and exhaust equipment is equipped with recirculation, the air that is sucked off by the exhaust (10) from the room is fully or partially returned to the same room through the intake system.
The recirculation system is provided by connecting the inflow and exhaust air with a special duct marked with 11 in the image. But the secondary flow does not flow arbitrarily - it can be adjusted using the valve, which is indicated by 12.
Note. The use of exhaust ventilation with recirculation in various buildings allows saving on heating in winter and on its conditioning in summer.
But for recycling, it is permissible to use secondary air not in each case, but only when there are no harmful substances there, in any case, they should be no more than 4th hazard class and not exceed a concentration of 0.3 qfdc. Also, the use of the recycling system is unacceptable if there are unpleasant odors in the room, and moreover, pathogenic microbes and viruses that cannot be filtered.
Fans
Note. For the forced movement of air through the channels with a pressure loss of not more than 1500kgs / m2 Air-inflating machines or fans are used.

The simplest is an axial fan, which is an impeller located directly in the duct - the air entering there moves with inclined blades along the channel axis. In the domestic sphere, you can see them on the kitchen hoods.
For large volumes of air pumping axial structures are not used due to low power - here you can already find more complex systems with rectifier units. Aluminum profile for ventilation systems of this type, used for installation greatly facilitates the entire structure, which, in turn, makes the installation of equipment cheaper.
Conclusion
If you want to make preventive maintenance of the ventilation system with your own hands, then, first of all, you should pay attention to the recommendations of the company that was engaged in the installation. You can also coordinate the work in accordance with the instructions for the fan, which is issued by the manufacturer.