Residential ventilation: schemes and regulatory requirements
How can ventilation in a residential building - apartment or private be implemented? What do the current building codes say about this? What standards of air flow should be followed when self-designing?
How to implement air exchange in a private house? Let's try to figure it out.

Regulatory requirements
Let's start with a study of existing regulations. Actual SNiP for ventilation of residential buildings - 2.04.05-91 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning and 2.08.01-89 Residential buildings.
For the convenience of the reader, we bring the key requirements of the documents together.
Temperature
For a living room, it is determined by the temperature of the coldest five days a year.
- With its value above -31С in the rooms it is necessary to support at least + 18С.
- When the temperature of the coldest five-day week is below -31C, the requirements are somewhat higher: the rooms should be at least + 20C.
For corner rooms with at least two common walls with a street, the rates are 2 degrees higher - +20 and + 22С, respectively.
Useful: the variability of requirements is due to the fact that at low temperatures and increasing heat loss, the dew point (the point in the thickness of the enclosing structure, where the condensation of water vapor begins) shifts towards the inner surface. The indicated temperatures exclude freezing of the wall.

For bathrooms, the minimum temperature is + 18C, for bathrooms and showers - +24.
Air exchange
What are the ventilation norms of residential premises (more precisely, the rate of air exchange in them)?
| The room | Minimal air exchange |
| Living room | 3 m3 / hour per 1 m2 area |
| Kitchen | 60 m3 / hour for electric stoves and 90 m3 / hour for gas stoves |
| Bathroom, toilet room | 25 m3 / hour |
| Combined bathroom | 50 m3 / hour |
Additional requirements
What other requirements and recommendations can be found in the SNiP on heating and ventilation of residential buildings?
- The ventilation scheme may provide for air exchange between separate rooms. Simply put, you can arrange the hood in the kitchen, and the air flow - in the bedroom. Actually, the document specifies the recommendation: exhaust ventilation should be provided in kitchens, bathrooms, bathrooms, toilets and drying cabinets.

- Ventilation of the apartment should be connected to the general ventilation channel not less than 2 meters from the ceiling level. The instruction is designed to minimize the likelihood of tipping over in windy weather.
- When using separate rooms in a residential house for public use, they are supplied with their own ventilation system, not connected with the house.
- At the coldest five-day temperatures below -40 ° C for three-storey and higher buildings, the equipment of forced ventilation with heating systems is allowed.
- Gas boilers and columns with the discharge of combustion products into the general ventilation may be installed only in buildings no higher than five floors. Solid fuel boilers and water heaters can be installed only in one- and two-storey buildings.
- Supply air is recommended to be supplied to the premises with a permanent stay of people. Which, in fact, again leads us to the already mentioned scheme: the flow of air through the living rooms and the exhaust through the kitchen and bathroom.
How it works
So, we studied the basic requirements for ventilation of residential premises. And how is the ventilation in apartment buildings and private houses?
Apartment buildings
Traditions
The scheme traditional for Russia and the entire post-Soviet space is natural ventilation, which uses the difference in density between warm and cold air for air exchange. Warm is forced out to the upper part of the room and from there to the ventilation channel; the influx of cold in the houses of Soviet construction was provided by vents for ventilation and loose fitting wooden frames.

Exhaust ventilation was equipped according to the already mentioned scheme: in bathrooms, toilets and in kitchens. The rooms were ventilated with fresh air.
Since the own vertical ventilation channel for each apartment is a luxury that is not allowed in high-rise buildings, the ventilation systems of individual apartments began to be combined by vertical shafts.
The mines were united by a horizontal canal, which is led to the roof and equipped with an umbrella to protect it from precipitation; the outlet to each apartment was supplied with a short vertical channel — a satellite that prevented air exchange between apartments.
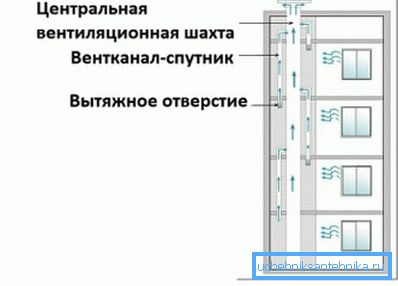
What are the advantages of such a scheme:
- Simplicity of construction and, as a result, minimal investment costs.
- Minimum operating costs. In essence, they are reduced only to a rare cleaning of clogged ventilation channels. The cause of clogging is soot from gas stoves and, rarely, violations during construction work.

- The flow of fresh air into the room directly from the street, without the need for any intermediate processing.
Of course, it was not without flaws.
- On the upper floors, the pressure that ensures the work of ventilation is minimal. From here - frequent cases of notorious overturning of thrust in windy weather.
- A long channel with rough walls (traditional materials of the mine and branches in the apartment - brick and concrete) provides high aerodynamic resistance, reducing the efficiency of ventilation.
- Channels are often leaking: cement mortar is used to connect their elements. Air leaks further reduce traction.
Modernity
Recently, with the construction of new buildings, a scheme with a warm attic has been increasingly implemented. How she looks like?
The horizontal channels connecting several mines are a thing of the past. Instead, the entire attic turned into a static pressure chamber.
Important: due to the stabilization of the high temperature in the attic, one of the main problems of the upper floor is solved - the cold ceiling. As a result, heating requirements are reduced.
Mines combined with horizontal taps into a single unit of industrial manufacturing. This minimizes the number of potentially leaking compounds.
Release from the attic is installed in each section of the house. Its combination with the elevator machine room allows, without disturbing the architectural appearance of the house, to increase the height of the issue up to 2 meters from the roof level, thereby further increasing the traction.
Umbrellas, protecting the mine from rain and snow, are gone: they caused a drop in thrust. Instead, at the base of the mine, a pallet is installed with a drain into the sewer.

The mine opening onto the roof acquired a square cross section, which improved traction in windy weather regardless of the direction of the wind.
The attic, assembled from reinforced concrete slabs, began to be divided into sections.
Thereby solved two problems:
- Air flows from different entrances cannot be mixed. Their mixing under certain conditions could lead to the fact that the thrust in one channel would increase at the expense of another channel.
- The relevant fire safety regulations were observed: a fireproof partition can prevent the spread of hot combustion products during a fire.

What is the result?
- The work of ventilation in general has become more stable, independent of the strength and direction of the wind.
- The aerodynamic resistance of the satellite channel increased from 1–1.5 to 6–9 Pa, which made the air exchange in the apartments less dependent on the floor.
Nuance: on the top two floors, the traction may still be insufficient, since the channels — satellites of the required height — simply cannot be accommodated. The problem is completely solved by installing exhaust fans in the apartments: in this scheme, their work can no longer lead to the fact that the exhaust air from one apartment will get into the other.

Forced exhaust
The main problem of any natural ventilation scheme is its dependence on the strength of the wind.
The solution to this problem is quite obvious:
- The aerodynamic resistance of the mine is artificially underestimated (for example, by installing adjustable valves).
- The shaft is supplied with a radial fan with noise reduction system.
The price of increased efficiency is a slight increase in operating costs and the investment value of the project.
Foreign experience
A rather interesting ventilation scheme is implemented in multi-apartment buildings by German builders.
- Exhaust ventilation is organized through the kitchen and combined bathroom.
- The air intake is a common channel that opens into the room with several small openings around its perimeter and a central valve fitted with a solenoid and a return spring. The air duct has a high aerodynamic drag and a camera for silencing sound.

How it works:
- In standby mode, the hood is carried out in a limited amount.
- When you turn on the light in the bathroom or forcibly supply power to the kitchen valve, the capacity of the air intake increases dramatically; In addition, forced ventilation is activated.
Private house construction
It is clear that for single-family houses there is no general ventilation scheme: the project is made up for a specific structure. The author will allow himself to share his own thoughts, supported by the experience of installing ventilation in his house.
Schema selection
The choice focused on exhaust ventilation with forced inducement and natural air inflow through the basement.
There were several motives.
- Exhaust ventilation involves laying a single channel.. Supply and exhaust - two, which means a much larger amount of work and damage to repairs already done.

It should be clarified: in this case, the channel for air exhaust has already been. In this role, the groove disguised by the builders between the girder, on which the floor slabs relied, and the outer wall, appeared. It was necessary only to punch holes for the air intake and organize the exhaust on the street.
- The calculation of the natural ventilation of residential buildings is extremely complex; for this purpose, either complex formulas that take into account many variables are used, or online calculators, often giving unreliable results. In forced exhaust, the performance with the minimum error is equal to the performance of the exhaust fan.
- The air intake from the basement (dry and located below the ground level) made it possible to make the supply air temperature stable regardless of the weather.. The temperature of the soil below the freezing point is kept at +10 - +14 degrees.

- Operating costs negligible. We give a table of the dependence of the power consumed by the fan on its performance.
| Productivity, m3 / hour | Power consumption, W |
| 110 | 13 |
| 200 | 25 |
| 300 | 35 |
Implementation
The implementation of the scheme with their own hands required a minimum expenditure of time and money.
- Air flow is organized in the living rooms. The holes in the floor are covered with grids with nets to protect against insects.

- Exhaust grates installed in plasterboard, closing the channel between the bolt and the wall.
- From the channel to the street a hole was punched into which a exhaust pipe with a duct fan and an umbrella was installed to protect it from rain and snow. The pipe is sealed and caulked; the fan is equipped with a remote switch.
Total expenses amounted to about 1,500 rubles. The level of humidity in the house has stabilized at a comfortable level; The temperature in winter with the heating turned off is at least + 12C.
Conclusion
We hope that our miniature review of how to organize ventilation will be useful to the reader.
As usual, the video in this article contains additional thematic materials. Successes!