Shiber for ventilation: device, purpose of use, alternatives
What kind of fixture is a vent gate? What is it used for? What does the gate consist of and how does it fit into the ventilation duct?
What can replace it? Let's try to answer these questions.

What it is
Before us is the simplest valve for adjusting and closing the ventilation duct. It is a flat valve with a thickness of about a millimeter, made, as a rule, of galvanized steel sheet.
The latch, depending on the size of the gate, can move along two types of guides:
- With a small size of the duct (up to about 250 mm) - in the slot pocket.

- In channels with a higher capacity, the valve is fixed by a pair of corners. Such guides are easier to clean from dirt; moreover, they create slightly less resistance when opening and closing the valve.
Note: regardless of the type of guides, the valve does not block the duct tightly and does not ensure the complete absence of leaks from it in the open position. As a result, the gate cannot be used as a valve for fire or emergency ventilation.
Classification
What are the gate valves for ventilation systems? By what signs can they be classified?
Duct shape
A typical industrial duct has a round shape. The reason is simple: a round section has a maximum area with a minimum circumference. As a result, at a fixed wall thickness, the price per meter of a channel with a certain throughput is minimal.
Slightly less used rectangular boxes.
What are they needed for?
- In this case, it is much easier to install heaters that provide heated air. Most of them are square or rectangular in shape: the production of water heaters under a circular cross section is simply not technological.
- Rectangular duct is easier to hide behind a false ceiling or false wall. With the same section as the round, it is able to occupy less storage space.
As you might guess, gate valves are manufactured for air ducts of both types. In the first case, they are mounted on the sockets with their subsequent compaction; in the second, flanged connections are used.

The angle to the axis of the duct
A typical gate valve closes the duct, cutting it at an angle of 90 degrees to the longitudinal axis. Even with relatively low air flow rates, a partially closed valve, causing turbulence, becomes a source of strong noise. That is why it is not used to adjust the cross-channel.
In the systems of pneumatic transport, however, often there is a need for a partial restriction of the patency of the duct. In this case, an oblique gate is used, cutting through the flow at an angle of 45 degrees.
Its shape allows you to kill two birds with one stone:
- The noise level is significantly reduced due to less turbulence on the obstacle.
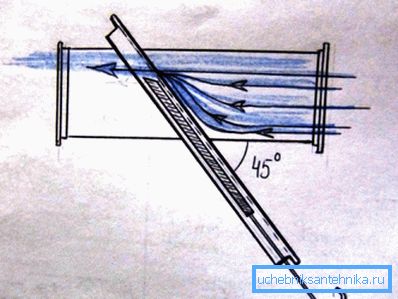
- A more precise adjustment of the channel capacity becomes possible: a shift of the valve by a fixed amount means a smaller percentage change in the living section.
Installation
How to install the gate vent valve with your own hands? More precisely, what to seal the connection? The instruction is quite predictably found in SNiP 3.05.01-85 Internal sanitary and technical systems.
Flangeless connection
| terms of Use | Applicable Materials |
| Temperature up to 40 degrees | Gerlen sealing tape |
| Temperature up to 70 degrees with a round section of the duct | Mastic Buteprol |
| Temperature up to 60 degrees with a round section of the duct | Shrink Cuffs, Heat Shrink Tape |

In addition: sealing of socket joints with silicone sealants is practiced. SNiP does not prohibit their use: after the list of recommended materials, it specifies the possibility of using sealing methods that are not included in this list.
Flange connection
| terms of Use | Applicable Materials |
| Transportation of air with temperatures up to 70 degrees | Foam rubber, polymeric mastic rope, various types of rubber (including porous) |
| Transportation of air with temperatures above 70 degrees | Asbestos cardboard, asbestos cord |
| Acid vapors transportation | Acid resistant rubber |
For flange connections, SNiP specifically stipulates some features of the assembly.
- The suspension or support securing the air duct should not fall on the flange.
- All bolts must be located on one side of the flange.

- If the flange is horizontal, the bolts should be on top of it, nuts should be on the bottom.
Comment: this recommendation is related to commonplace security. A bolt is heavier than a nut and, if dropped from a height, is capable of inflicting more severe injuries.
Alternatives
These include numerous dampers and valves, differing both in the functions performed and in the device.
Fire valves are designed to promptly stop natural or forced ventilation in case of fire, as well as, on the contrary, for a massive supply of air to the evacuation routes of people.
Depending on the initial position, valves are distinguished:
- Normally open;
- Normally closed;
- Double action.
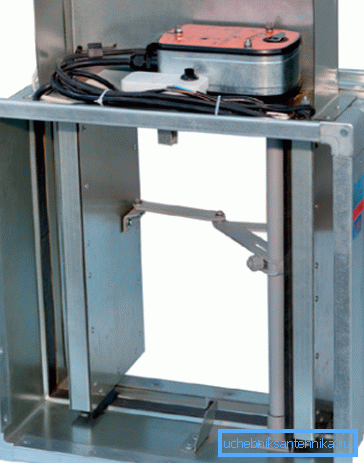
To actuate the valve can be used:
- Solenoid and recoil combinations. The solenoid can open the valve; close it; hold in the open and closed position, counteracting the return spring; responsible for the operation of the lock, release the valve.
- Fusible lock complete with spring. Valves with such a scheme of work are cheap, but they are capable of only a single actuation.
- Servo with motor and gearbox.
In addition, instead of oblique gates, throttling valves with manual or electromechanical actuators are widely used.

Conclusion
We will assume that our acquaintance with the new type of ventilation equipment took place. As usual, the video in this article will offer the reader additional topic information.
Successes!