Ventilation deflector: device, principle of operation,
Ventilation deflector is a simple device that allows to increase the efficiency of the system within 20%. We want to talk about the principle of operation, the features and types of these devices, as well as to focus on how to mount the ventilation deflector with your own hands.

Deflectors of ventilation systems
Device and principle of operation

First of all, it is necessary to figure out what a deflector is in ventilation, since the scope strongly affects the design of the device. In the supply and exhaust systems of natural ventilation, the deflector is installed on the top of the exhaust channel to increase the thrust due to the creation of a reduced pressure area.
The principle of operation of the device is based on the Bernoulli law, one of the consequences of which is the effect of air dilution in a stream with a varying cross section. The higher the flow rate, the more noticeable the pressure drop.
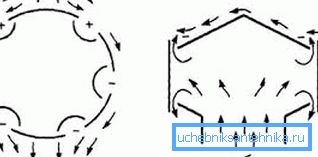
Note! Thus, we see that due to the wind energy blowing the pipe, a relative vacuum is created in the area of its tip, which causes the air masses inside the pipe to be directed upwards, creating additional thrust.
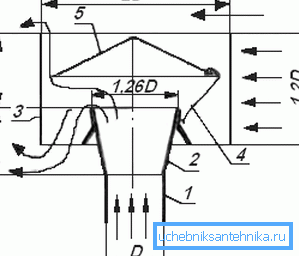
If we consider the ventilation deflector device, we will see several main parts (TsAGI variant):
- Diffuser. It is a piece of pipe in the shape of a truncated cone, which is worn by a narrow side on the pipe. Increases pressure in the pipe at the tip, thus, increases the pressure difference and the activity of ejection of exhaust air by the wind flows;
- Umbrella or cap. It serves to protect the channel from precipitation, debris and other foreign objects;
- Outer cylinder or housing. Cuts through the flow of wind, creating inside the area of low pressure.
In the version of the construction of Grigorovich we will see a slightly different picture.
The structure of the device includes the following nodes:
- Diffuser. Here we see the same truncated cone, but worn on the pipe with a wide side, and the section of this side exceeds the section of the tip. This detail is also called "glass", in which case the tube head will be the "bottom glass";
- Umbrella or cap. Performs a protective function, as in the previous example;
- Reverse cone. It is installed under the hood with its top down and serves to prevent the accumulation of air under the umbrella, as well as to create, together with the diffuser, a tapering wind flow over the end cap.
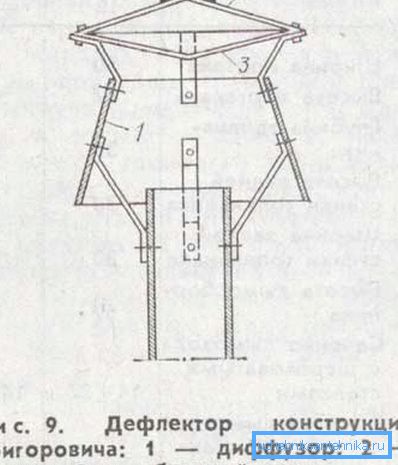
Note! In the Grigorovich variant, we see that the ejection occurs in two directions: in the direction of the inverse cone and in the direction of the wide side of the diffuser. The flow rate under a reverse cone increases due to the narrowing of the channel, which leads to an increase in the pressure difference.
Species

The selection of a vent for ventilation should be based on the freely available varieties and the weather conditions in your area.
Consider the most common models:
- The design of the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute (TsAGI) is one of the most popular varieties. The design features we discussed above;
- Model Grigorovich. This is perhaps the most common type of deflector in our country and abroad. The design is also discussed in the previous chapter;
- Astato open plate design. Also very common and popular due to the simple device and efficient work;
- Rotary models. They are complex devices with a rotating part and a special system of blades supporting this rotation. A distinctive feature is higher price and efficiency;
- H-shaped models. They are distinguished by the presence of two deflectors at once on one tip;
- Deflectors, weathervanes. They are rotary nozzles with a keel, which turns the structure in the direction of the wind so that its flows fall into the system of holes and blades, causing the effect of gas ejection from the duct.

Note! As a rule, the exhaust pipe is displayed on the roof. This creates a difference in the gravitational values of air pressure, and also allows the deflector to be installed in a space open to the wind.
In addition to the concept of the apparatus, we will need the dimensions of the cross sections of the channels and cylinders or their ratio. The calculation of the deflector for ventilation is carried out on the basis of these ratios or is carried out from scratch for a specific device.
If we talk about materials, in most cases all models are made of two types of raw materials: metal or plastic. The most commonly used are galvanized steel, tin, stainless steel and aluminum.

Plastic vent vent has a lower cost, a variety of colors, but is afraid of high temperatures and quickly comes into disrepair.
Installation

For those who purchased the deflector, our installation instructions:
- In most models, the device has a lower nozzle, which is worn on the pipe and fixed with clamps, bolts or rivets. Clamp - the easiest way to mount;

- The diffuser to the lower pipe is attached to the brackets with a threaded connection. Usually, these are 3 or 4 brackets, which are fastened to the end of the nozzle with nuts, and the opposite ends of the diverging brackets are inserted into the holes on the diffuser and are also fixed with nuts;

- In the upper part of the diffuser housing mounted rack for the cap. These can be screw brackets or bolted plates. A cap with or without a reverse cone is attached to the posts.

Note! The diameter of the umbrella must exceed the diameter of the outlet of the diffuser, otherwise slanting rain will fall inside the channel.
Conclusion
The use of deflectors allows you to increase draft exhaust ventilation and protect it from wind blockage. It is also possible to increase the overall efficiency of the system and protect it from reverse thrust.
The video in this article will help you better understand the rules of device and installation of this design.