Ventilation pipes - size matters
As a rule, when independently designing a ventilation system, people do not like to particularly complicate the task and select sizes that are called at random. Usually the diameter with a margin and on the work of ventilation is not particularly affected, but this approach is not for engineers to face. It will not be superfluous to know how to properly select the ventilation pipes.

What should be the ventilation pipe
Ventilation compared with other systems, for example, water supply will not experience significant loads during operation, which means that there is no need for a considerable thickness of the metal. Therefore, the first requirement for a metal duct can be called a small wall thickness.
The second important parameter is considered to be corrosion resistance. Still, the level of humidity of the air passing through the channels is high enough, so that the metal should not be covered with a layer of rust in 6-12 months.
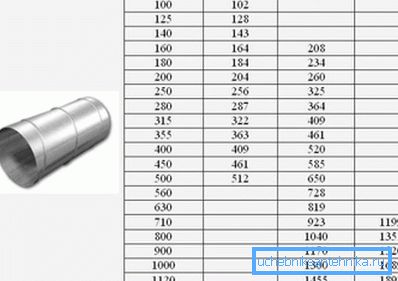
Well, the most important characteristic is the diameter, which directly affects the efficiency of the ventilation system. 120 mm ventilation pipe has a sectional area of 113.04 cm2, diameter, for example, 75 mm - just 44.15 cm2. It is clear that if the cross-sectional areas differ by 2.56 times, then they will be able to skip different volumes of air per unit of time (at an equal flow rate).
Normative base
The main indicator used in the selection of the diameter of the duct can be considered as the air flow per unit of time. In SNiP 41-01-2003, the main requirements for the ventilation system are recorded both in terms of productivity and in terms of geometrical dimensions.
For example, according to this standard for residential premises, the air flow should be (for 1 person):
- for rooms with an area of more than 20 m2 - either 30 m3/ hour, or not less than 0.35 air exchange, calculated on the basis of the total volume of the apartment. Finally, a larger value is assumed in the calculations;
- if the area of the room does not exceed 20 m2, the air exchange can simply be taken on the basis of an average value of 3 m3/ hour at 1 m2 square
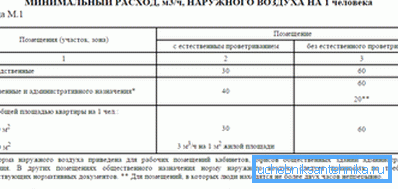
That is, through the medium-sized room (19-20 m2) per hour ventilation should provide circulation of about 60 m3. A small size, for example, a 75 mm ventilation pipe will simply not cope with this task.
Note! Theoretically, it is possible to increase the volume of air supplied even through a small section; it is enough just to install a powerful fan. But this will lead to a large increase in airspeed. It is unlikely that the apartment needs drafts and howling wind in the ventilation.
The same standard (SNiP 41-01-2003) contains some requirements regarding the size of the pipeline.
As for the profile ducts, then you need to navigate on the larger side:
- with a size of up to 250 mm, the wall thickness should be equal to 0.5 mm;
- with increasing sizes up to 1250 - 2000 mm wall thickness increases to 0.9 mm;
- if the size of the larger side exceeds 2000 mm, then an additional calculation is needed to justify the thickness of the metal.

If its limitations and parts of the round ventilation channels:
- for example, round ventilation ducts with a diameter of less than 200 mm are allowed to be used only if the wall thickness does not exceed 0.5 mm. Even if the ventilation pipe of 160 mm will have a wall thickness of 0.6 mm, strictly following the standard, it must be replaced. In private construction, of course, there are no such rigid restrictions;
- but in the case of a large diameter (from 1,800 to 2,000 mm) the thickness of the steel can be increased to 1.4 mm. This is necessary so that the duct does not simply bend under its own weight.
Air duct selection
When determining the dimensions of the cross section, it is necessary to take into account the speed of air movement. The ventilation duct located in the apartment should not be a source of constant noise, and the velocity of the air flow into the apartment (applies to both intake and exhaust ducts) should not cause discomfort.
For this reason, for different parts of the ventilation system, their recommended indicators of air velocity are introduced, which greatly affects the air exchange. For example, a ventilation pipe with a diameter of 200 mm and an air speed of 1.0 m / s can provide air exchange at 113 m.3/hour. With an increase in speed of up to 1.5 m / s, the air exchange will grow 1.5 times to 169.5 m3/hour.
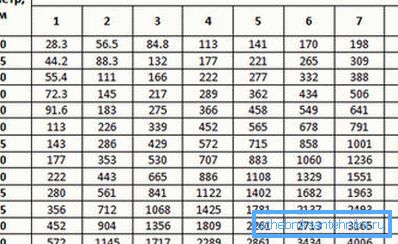
In this case, much depends on the method of air circulation (natural or forced). So, for systems with natural circulation, the maximum air flow rate can reach up to 2 m / s (in mines), in air ducts in apartments the air flow moves at a lower speed.
But if the ventilation pipe in a private house is supplemented with a duct fan, the flow rate increases.
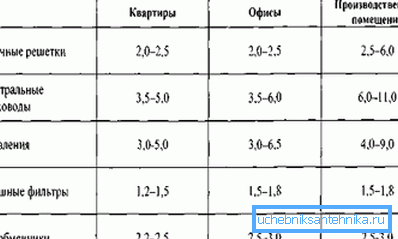
Since the fan power variation is quite large, we have to rely on the recommended values for different parts of the system:
- at the level of the supply grille, the speed should not exceed 1 - 3 m / s;
- exhaust grille - 1.5 - 3.0 m / s;
- air distributor - 1.5 - 2.0 m / s;
- lateral channel - 4.0 - 5.0 m / s;
- trunk ventilation channel - 6.0 - 8.0 m / s.
The procedure for the selection of the duct section
Instructions for self-selection section consists of only a few points:
- first you need to decide on the rate of air in the room;
- then, given a certain air velocity, the area of the ventilation channel is calculated. The calculation is carried out according to the formula
In order to determine the diameter of the ventilation pipe formula is used.
- since the selection of the type size had to round off the result, then you need to check how much the speed of the air flow has changed. Just from the previous formulas you need to display expressions to determine the speed
where a and b - the size of a rectangular section, m
As for air exchange, you can use 2 approaches to determine it, but when the calculations are done with your own hands, they are often simply set by the norm of 30 m3/ hour for 1 person. In general, such options are possible:
- taking into account the frequency of air replacement in the room, in this case, the amount of air exchange is determined by the formula
where V is the volume of the room, m3/hour;
n is the rate of air exchange rate (as a rule, for residential buildings it is assumed in the range of 1-3).
- taking into account the rate of air exchange for the 1st person in the building (the amount of air exchange in this case is considered at the beginning of the article).
Example of duct sizing
Suppose you need to choose the size of the ventilation channel to provide exhaust hoods in a room measuring 4x5x3 m. Only 1 person is planned to be in the room for a long time.
The calculation is carried out in the following sequence:
- air exchange is determined - in our case, you can set the value to 60 m3/ hour (at the rate of 3.0 m3/ hour for every 1.0 m2 square);
- the speed of air movement in the channel is taken - it is possible to stop at a value of 1.0 m / s;
- determined by the cross-sectional area A = 60 / (3600 • 1.0) = 166.67 cm2;
- appropriate size is selected. In our case, you can choose either a circular duct of 140 mm (sectional area of 154 cm2), or a rectangular section 100x200 mm (area 200 cm2);
- speed is checked. For a round channel, it will be v = 60 / (3600 • 0,0154) = 1.08 m / s, and for a rectangular cross section - v = 60 / (3600 • 0.0200) = 0.83 m / s. Both values are within acceptable limits, so the price and method of pipe installation can be a decisive factor in the selection.
What to look for when choosing an air duct
When choosing an air duct, you must take into account not only the design part, but also immediately think about the ease of installation. In the example of the calculation, an air duct was selected with approximately the same capacity, but in the case of a circular cross section, its diameter is 160 mm, and in the case of a rectangular section, only 100 mm in height. When the ventilation pipes will be installed, a saving of 60 mm in height can be very important.

In addition, attention should be paid to such trifles as:
- noise protection and insulation. Sometimes it is better to purchase air ducts with a factory sound and heat insulation layer;
Note! Insulation of the ventilation pipes is necessary because in the winter the air in the non-insulated pipeline will cool down too quickly and there will be problems with the burden.
- if in some places the duct must often bend at large angles, then the use of a flexible pipe may be justified.. Such air ducts can be made semi-rigid (from aluminum foil wound on a steel frame) and PVC. The main advantage of a flexible ventilation pipe is the possibility of a smooth rotation (this has a beneficial effect on aerodynamics) and a reduction in the number of shaped elements to a minimum.

Summarizing
The key to high-quality ventilation can be called a properly designed ventilation system. A significant role is played not only by the location of the air ducts, but also by their calculation (meaning the selection of cross-sectional dimensions). The recommendations proposed in the article will help to avoid the typical mistakes of newcomers, and apartment ventilation will always work stably.
The video in this article shows an example of an already mounted rectangular ventilation system.