Device well under the water: the main elements and tips on
What is a well? The answer seems to be obvious: a hole in the ground from which water is being pumped out. Obvious and erroneous. We have before us a whole range of equipment - from the filter with a settling tank to the system of automatic pump start The topic of this article is the installation of water wells.
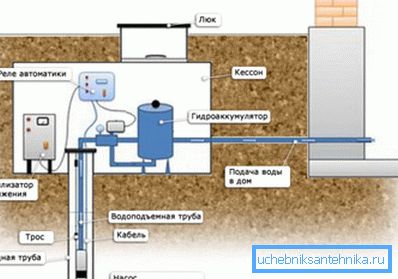
Components
So what does a well consist of? We will immediately stipulate: we are discussing the construction of a well of relatively small depth (up to 70-100 meters) with a flow rate sufficient to provide water for residents of one or two or three private houses. Industrial wells capable of delivering tens of cubic meters of water per hour and taking water from the lower horizons are more complicated.
Move down the wellbore.
- Sump This is a pipe with blind walls, recessed into a waterproof layer below the filter.
- Actually a filter that ensures the purification of water coming to the pump from sand and soil particles.
- Casing pipe, ensuring the stability of the borehole walls. It is thanks to her that the narrow vertical well does not crumble in the very first days of operation.
- Pit or caisson located at the wellhead. The purpose of the construction of this shallow well is twofold: it protects the pipe through which water is supplied from freezing and prevents the soil from shedding over the casing.
Curiously: in warm regions, wells often do without this element. In particular, in the Crimea, with its positive temperature of the coldest winter month, one can observe casing sticking directly out of the ground; water enters the house through non-buried input.

- A pump that lifts water from a depth.
- Pressure pipe through which water flows from the well to the house.
- Non-return valve preventing backflow of water when the pump is stopped.
- Automatic pump control.
- Hydroaccumulator or accumulative capacity, allowing the pump to stand idle.
In this order, we analyze the device wells for water in more detail.
Underground part of the well
Casing Column
The filter and the sump are part of the casing and lowered into the well drilled with their own hands or with the involvement of technology well as a whole. The column, as a rule, is assembled on the spot from pipe sections supplied with locks (most often threaded).
The diameter of the casing is usually slightly larger than the diameter of the pump; for the most common 4-inch pumps, a 125 mm tube is used.
What materials can be used and what are their key features?
- The traditional casing material is black steel. Despite the susceptibility to corrosion, its service life reaches 50 years or more due to the solid wall thickness - 5-6 millimeters. The thick-walled pipe is not afraid of any ground movement and ensures the well is working under any conditions; the only disadvantage of this material is the high price.

- Asbestos cement pipes are much cheaper; much lower and their strength. The material is suitable only for stable soils with a small depth of the well (drilling on the sand).
- Low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE) is an even more economical material. It has a practically unlimited service life - with one reservation: soft plastic cannot withstand mechanical stresses.
It is useful: only casing pipes are used as casing, which are distinguished by their strength and wall thickness.
- Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (NPVH) - a compromise between the strength of steel and low cost polyethylene. Pipes somewhat stiffer made of HDPE; threaded connections make it easy to combine them into a column.

What is the filter that eliminates pollution?
- Steel casing strings are usually completed with a stainless steel braided filter.
- The plastic filter is a perforation zone. Small holes with a small interval are located over a length of 1-3 meters of the pipe after about a meter long section of the sump.
Priyamok, caisson
The pit is a well, open slightly below the level of freezing. The walls are concreted or laid out of red brick (silicate does not tolerate prolonged contact with water). A clay lock is formed around the casing rising in the middle of the pit of the casing, protecting the well bore from water ingress from the surface.
From above, the pit is covered with a concrete slab or thick boards and is insulated in any way possible.
The caisson is a turnkey solution, a plastic, steel or concrete bell, often supplied with a hatch. Caissons are in great demand because of the significant time savings at the well equipment stage.

Pump
What could be the device that raises the water to the surface?
In the shops you can find three types of well pumps.
- Surface is located in the pit or caisson and raises the water, creating a vacuum in the down pipe. It is clear that from a great depth in such a way the water does not lift: this type of pumps is used exclusively when equipping wells with sand at a water depth of no more than 10 meters.
- Diaphragm Submersible Pump provides head due to cyclic oscillations of a solenoid with a pair of membranes. A set of ball valves provides the movement of water in the right direction on both phases of the cycle.
These devices provide good pressure for compact size and low cost; however, for deep wells they should not be used. The instruction is associated with a relatively small (no more than 2 years) resource between repairs: the membranes in the process of work are continuously deformed, accumulating the so-called material fatigue, and require periodic replacement.

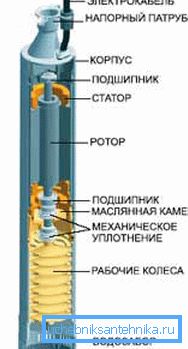
- Finally, at the heart of the most popular scheme is the centrifugal pump. - The usual centrifugal impeller lies. The centrifugal pump differs from its close cousin, the vortex pump, by the large distance between the impeller and the casing (thus, manufacturers avoid accelerated erosion with inevitable abrasive particles) and the presence of several steps to compensate for the inevitable drop in pressure with increasing clearance.
Each stage consists of a separate impeller and diffuser; at the same time, the impellers are mounted on the shaft common to all electric motors. One stage increases the pressure at the pump outlet by 5-10 meters.
Overhead equipment
What does a well device for water look like above ground level?
Buffer
The hydroaccumulator or accumulative capacity acts in this role.
Each solution has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- The accumulator is able to create more pressure in the water supply system, it can be placed at any point of the water supply system. However, accumulators have a relatively small volume and are quite expensive.
- Accumulative capacity, on the contrary, at a moderate cost can have a very significant amount, which will allow you to transfer power outages or repair the pump without discomfort. However, it will have to be located at the top of the building.
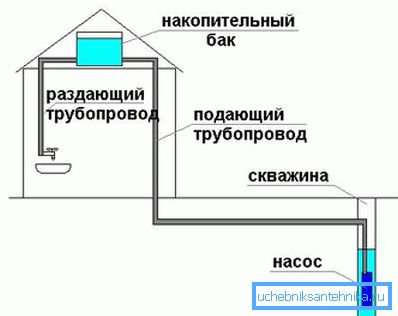
Reference: in order to ensure an acceptable pressure of 1 kgf / cm2 in the water supply system, the capacity will have to be raised to a height of 10 meters, which roughly corresponds to three floors.
Automation
It is a sensor, at the command of which the relay turns on and off the pump.
The type of sensor depends on the type of buffer capacity:
- In the case of a hydroaccumulator, the pump is turned on when the pressure in the water pipe falls below the threshold value.
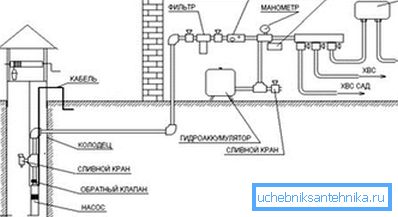
- In accumulative capacity the float-operated sensor of level of water is placed.
Conclusion
If the reader has not received an answer to any questions - perhaps he will find them in the video in this article. Successes!