Gost on the crane: we study the existing normative documents
The purpose of this article is to find out which state standards regulate the production of valves. We will get acquainted with several current GOST and study their basic requirements. So go.
Scroll
Let's start with a short list of documents with which we have to make contact.
- GOST 25809-96 It is dedicated to the types and sizes of mixers and taps produced.
Curiously, imported plumbing also mostly fits within the size limits given by the standard - simply because its recommendations derive from the characteristics of human anatomy.
- GOST 21345-2005 describes general technical conditions for the production of ball and cork cranes. With some reservations: they are designed for pipelines with a pressure of up to 250 atmospheres and can not be used in special conditions (in nuclear energy, during transportation of corrosive liquids, etc.).
- GOST 9544-2005 contains the norms of tightness for valves and classifies it according to the class of tightness.
- GOST 10944-97 contains technical conditions for the production of regulating cranes (chokes, three-pass, etc.).

GOST 25809-96
Marking
The standard, among other things, sets the standards for the designation of faucets and mixers. In their labeling should use the following notation:
| Designation | Decryption |
| Cm | Mixer |
| Cr | Crane |
| Mind | Washbasin device |
| M | Washing device |
| AT | Bathtub device |
| WU | Common for washbasin and bath (usually with a long swivel gander) |
| Dsh | Shower |
| Bd | For bidet |
| TO | For water heating column |
| D | Two-hand (separate cold and hot water taps) |
| ABOUT | Single lever |
| L | Elbow |
| R | Leads go through a sink or sink through different holes |
| C | Central (eyeliners pass through a sink or sink through a single hole) |
| B | Onboard installation |
| H | Wall mounting |
| H | Wall mounting |
| Shl | With shower on a flexible hose |
| PC | With shower on the rod |
| Tr | With shower on stationary pipe |
| Schb | With brush for on-board installation |
| Schn | With brush for wall mounting |
| BUT | With a goose aerator |
| Ive | With pull-out spout (gander) |
| St | Gander with jet straightener |
| R | Gander with flaring |

Instructions for reading the label is simple and straightforward.
Designation includes:
- Type of sanitary appliance (Cm or Cr).
- The sequence of letters.
- Reference to the standard.
So, SM-MDTSBA GOST 25908-96 is a classic kitchen faucet: it is designed for washing, equipped with two taps, pipes are inserted through one central hole, the faucet body is attached to the sink itself, the spout is equipped with an aerator.

Requirements
We will not give all the options for the manufacture of faucets and mixers with their basic dimensions provided by the standard: those who are interested can familiarize themselves with its full text independently.
Select only the key points.
- The shape of the hull, thumb, gander and switches is not regulated by the standard and is determined by the working drawings.
- Wall-mounted mixers should have a center distance on the liner, equal to 100 or 150 mm.
However: in practice, all domestic products that can be found on the market are produced with a center distance of 150 mm.
- The gander should be supplied with an aerator, a straightener (a short vertical section preventing water splashing in the direction of the edge of the sink) or flared.

- Central mixers can be made with a cast tee or flexible liner.
Author's note: now there are almost no cast tees on sale, which is good news. Replacing a tee mixer - a Christmas tree with your own hands is associated with a partial disassembly of steel water supply, is very tiring and takes at least an hour. For comparison - the mixer on the hoses is changed in 15 minutes with two smoke breaks.
- The threads for connecting the shower hose to the faucet body and the watering can must be G1 / 2 (half-inch) in size, for the gus - G3 / 4 (three-quarters of an inch).
- On-board faucets should be able to be mounted on openings in sinks and washbasins 34 mm in size.
- Delayers (eccentrics for wall-mounted faucet installation) must have an eccentricity of 3 mm. It compensates for the deviations of the installation of the pipes from the standard center distance. In addition, the shape of the scythes should allow their twisting: they are provided with protrusions inside or facets outside.

- Mixers must be supplied complete, with a full set of hoses and gaskets.
GOST 21345-2005
The standard has the status of international: it is adopted on the territory of 12 states of the former USSR. The need to replace the previously existing GOST 21345-78 arose due to reasons rather organizational than technological: the ball valve according to GOST 21345-78 does not have any serious structural differences from its modern counterparts; the design of cork valves has not undergone any fundamental changes over the past half century.
What should be a cork or ball valve according to GOST 21345-2005?
- In a full bore crane, the effective diameter cannot be less than 95% of the diameter of the inlet nozzle with the size up to DN350 and not less than 92% with the size DN400 and more. The effective diameter of the valve with narrowed passage is coordinated with the consumer.
Important: modern ball valves attract, among other things, minimal hydraulic resistance. The narrowed passage reduces this advantage over cork and screw valves to a minimum.

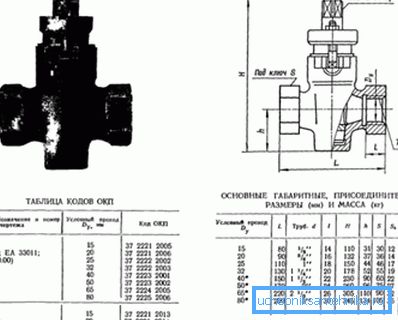
- The nominal size of the valve in accordance with GOST should correspond to the following table:
| Conditional pass | Size in inches |
| ten | 3/8 |
| 15 | 1/2 |
| 20 | 3/4 |
| 25 | one |
| 32 | 1 1/4 |
| 40 | 1 1/2 |
| 50 | 2 |
| 65 | 2 1/2 |
| 80 | 3 |
| 100 | four |
| 150 | 6 |
| 200 | eight |
| 250 | ten |
| 300 | 12 |
| 350 | 14 |
| 400 | sixteen |
| 450 | 18 |
| 500 | 20 |
- Before assembling the crane, all its parts must be cleaned of dirt.
- The rubbing surfaces of the plug and casing of the plug valve must be coated with acid-free lubricant.
- The tightened gland can enter a groove with a maximum of 30% of its own height (not less than 2 mm).
- When assembling the body on the studs, which is typical for large diameters, the GOST on the ball valve requires that the ends of the studs protrude from the nuts at least one turn of the thread. Studs are wrapped in the case until it stops.
- For the extreme positions of the handle should be provided limiters.

By the way: cork taps without handles do not and cannot have one in principle.
- The crane can be supplied partially disassembled, with the handle removed or the gearbox (for products of large diameter). Removed parts are packed in the same container.
GOST 9544-2005
How is the ball valve classified according to GOST 9544-2005? What are the requirements for the tightness of its gate?
Let's start with the test method. They are carried out in a simple and transparent way: the valve element is hermetically attached to a pipeline of the appropriate diameter, after which a working pressure is created in it. Gas valves are tested with compressed air; To control leakage, the valve is placed in water.
The holding time with tightness control must comply with the following table:
| Conditional pass | Holding time, sec | |
| Water | Air | |
| DN50 and less | 120 | 60 |
| Over DU50 | 180 | 120 |
Curiously, the cork or ball valve according to GOST 9544-93, replaced by GOST 9544-2005, was tested depending not only on the diameter, but also on the type of seal. For metal-to-metal and non-metal seals, the test duration varied.
How are hermetic classes assigned? Let us give a table of class assignment depending on the leakage volume at different nominal diameters of the valve element.
Please note: class A is assigned in the absence of visible leaks.
| Nominal diameter | Permissible leakage when the nominal pressure is exceeded by 1.1 times, cm3 / min | |||
| D1 class | Class D | Class C | Class b | |
| 15 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.027 | 0,009 |
| 20 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.012 |
| 25 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.045 | 0.015 |
| 32 | 0.3 | 0.192 | 0.058 | 0.018 |
| 40 | 0.4 | 0.24 | 0.072 | 0.024 |
| 50 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| 65 | 0.9 | 0.39 | 0,117 | 0.04 |
| 80 | 1.1 | 0.48 | 0.144 | 0.048 |
| 100 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.18 | 0.06 |
| 125 | 2.2 | 0.75 | 0.225 | 0.075 |
| 150 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 0.27 | 0.09 |
| 200 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 0.36 | 0.12 |
| 250 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 0.45 | 0.15 |
| 300 | 8.0 | 1.8 | 0.57 | 0.18 |
| 350 | 11.0 | 2.1 | 0.63 | 0.21 |
| 400 | 13.0 | 2.4 | 0.75 | 0.24 |
| 500 | 17.0 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
It is useful: for all types of modern ball valves, a typical tightness class is A. At the same time, their price is approximately equal, and often lower than the cost of cork, screw valves, steel and cast iron valves. The influence of such a set of qualities on customer preferences is quite predictable: other types of valves and fittings are rapidly being forced out of the mass market plumbing.

GOST 10944-97
This GOST for a three-way valve, choke and other control valves for heating also has international status; however, it was adopted only in eight former union republics. Highlight the main provisions of the document.
The standard applies to regulating and blocking the flow of coolant taps, which remain operable at temperatures up to + 150 ° C and a pressure of at least 10 kgf / cm2. It describes all the main types of fittings used in heating - screw, cork, ball valves and chokes (the regulating unit of which is a moving reciprocating needle).
Product marking is determined by:
- Type of crane. Thus, the letter B is marked with a screw valve, the letter P - cork, W - ball and D - choke.
- Functionality Here is a list of symbols:
- КРТ - three-way crane regulating.
- KRP - the gate crane regulating.
- KRD - double adjustment crane regulating.

- KRM - the crane regulating assembly.
- KZ - stopcock.
In the closed position, the control valves should not pass more than 20 cm3 / min for the size of DN15 and 30 cm3 / min for the DN20 at a pressure drop across the valve of 10 kgf / cm2.
If the faucet is not universal and is suitable only for right or left-hand installation, it is additionally marked with the letters P or L.
The minimum test pressure that must be maintained by all standard-compliant valve elements is 15 atmospheres.
The outer surfaces of the cranes are lightened (cleaned of oxides and scale).

- The angle between the axes of the threads should be 90 or 180 degrees with an accuracy of 1 degree angle.
- Time to failure (in particular, without tightening the gland) should not be less than 1000 cycles.
- The material and design of the handle should prevent it from heating above + 40 ° C over the entire range of operating temperatures.
- The device should be supplied with limiters of the movement of the handle in extreme positions. In this case, the design of the limiters should exclude a change in their position in the living conditions.
- By production the use of the following materials is allowed:
- Brass - for body and shutter.
- Fluoroplastic - for sealing joints.
- Handles - from polypropylene, polyamide and polystyrenes with steel core or embedded parts.
The marking on the body should indicate the manufacturer's logo, nominal diameter and maximum working pressure, and in the screw valves and chokes - the direction of flow of the coolant. The case is marked with a convex or depressed font.

Conclusion
We hope that our acquaintance with the current regulatory documents will be useful to the reader. The video in this article traditionally contains additional materials on the topics we are discussing. Successes!