How is well depth determined
The need for water on the land plot is not discussed, it should be everywhere where there is life, especially if the cottage is used for planting vegetables and fruits. That is why it is very important to host not just a tap that will supply water on a schedule, under which you will have to adjust, but a full-fledged well with a pump. In our article you will learn what the depth of the well is required without permission and by law.
Where do we start
So, you have acquired a very nice piece of land with beautiful views of the surroundings and excellent soil for planting crops and fruit trees. The only drawback of your purchase was the perceptible distance from the central water supply.
No one would dispute the significance of water for the life of everything on earth:
- Human
- Plants.
- Animals
In principle, nothing is impossible.
However, on the way of water supply to the section from the central water supply you will find many obstacles:
- Connecting to the water supply with the laying of kilometer pipelines becomes a very time-consuming and very slow process.
- The total price for the whole complex of works and materials plus the project and design will quite significantly affect your finances.
Drilling and determining the required depth of the well
In this case, landowners make the only right decision - drilling a well directly on the site or in the area of easy and unhindered access. If you are not ready to perform this task with your own hands, then you will have to contact specialists.
In any case, in the matter of drilling, regardless of the method of work, the very first and, of course, pricing factor is the question of how deep a well is to be driven.
There are several points worth paying attention to.
Here, in fact, two of them that will answer the question - how to determine the depth of the well:
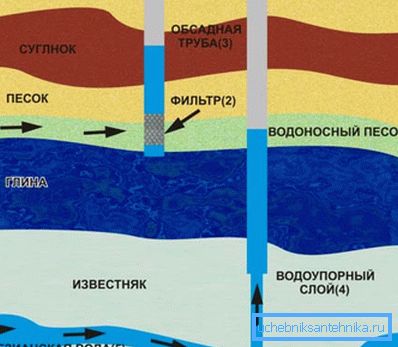
- Geology of your site.

- Type and depth of groundwater.
The groundwater
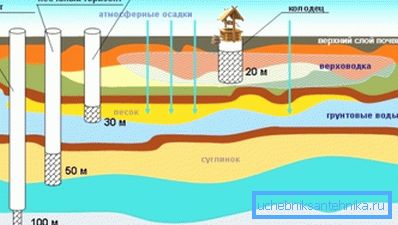
Consider the four main types of groundwater:
- The first - heading, occurs at a shallow depth to 3.5-4 m.
This upper aquifer is filled by rain and melt waters, and in this connection it is characteristic:
- High degree of pollution, as it actually washes away all the dirt from the soil surface and, seeping through the upper layers of the soil, is more likely to be further polluted than cleaned by filtration.
- Almost complete extinction in the dry season and in the cold. Without constant filling, a part of the water from the upper layer seeps deeper, and a part dries out.
- Second - groundwater, as a rule, is located at a depth of about 10 m. A distinctive feature of groundwater is the presence of a powerful hydro-resistant formation under a layer of water. Its role can be played by clayey or stony layers that prevent water infiltration into the underlying layers, which ensures the filling of the groundwater layer even during periods of drought.
The groundwater, which lies at a depth of 8–10 m, is already fairly clean, filtered in transit through layers of diverse soils.
Note! Between upper water and groundwater, like other types of groundwater, there can be several intermediate layers of water. The layer of groundwater may not be continuous, with gaps, and in this case inevitably seepage into the water layers located below.
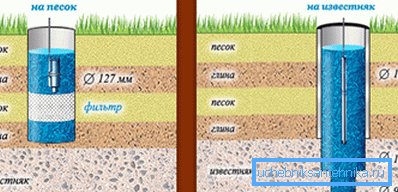
- Third - interstitial waters, are located, as a rule, at a depth in the interval from 10 to 100 m. The name itself of this type of water suggests that they lie between two waterproof layers of soil. The upper impermeable layer may have a low degree of permeability, which provides additional replenishment of interstitial waters due to infiltration from the two upper water layers.
- Fourth - artesian water, lie just below 100 m from the surface of the earth. However, in some cases they can also occur at a depth of 50 meters. For the extraction of artesian water beats deep well. Naturally, this is the purest water.
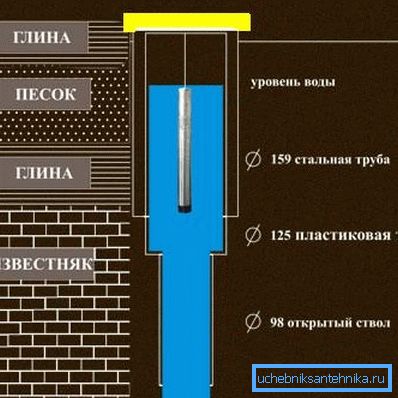
The instruction on how to find out the depth of the well to be drilled is simple - what quality water do you want to get at the output to such an interlayer and drill.
Tip! The quality and continuity of the water supply is influenced by the depth of the pump into the well. Two rules are obligatory here: first, water must flow into the pump by gravity, i.e. the pump is immersed at least 1 meter from the dynamic level of groundwater in the well. Secondly, the pump must be constantly in the water for uninterrupted cooling.
Exploration drilling
Now how to check the depth of a well at a specific site. To clarify this value, reconnaissance works are performed, i.e. test drilling
The most win-win way to measure the depth of a well is to keep a detailed log of the drilling that states:
- Occurrence of soils of different groups.
- The depth of the aquifers.
- The degree of absorption of recycled water.
- Depth of soil washout.
Permissive issues
Another issue to be faced is the need for a permit for drilling. According to the law on subsoil in relation to the extraction of water, land owners, without special approval, have the right to drill and operate a well within the site to the depth of the first aquifer.
And, if this applies to you, then feel free to proceed to work. If the location of a water source outside your land is assumed, then you will have to negotiate and look for those who are responsible for the plot adjacent to you.
Conclusion
There is nothing difficult in the "analysis" of the soil and drilling, this issue can be resolved in two ways. The first is with special equipment when a well with a depth of more than 15 meters is required. The second is independent, when with your own, with a rented drill, you make a well to the level of groundwater, so to speak, for irrigation (see also Cementing wells: goals and methods).

In the presented video in this article you will find additional information on this topic.