How to measure water pipes: everything you need to know
The range of water pipes includes products of various sizes. In order not to get into an unpleasant situation, when the purchased parts do not fit the section or other parameters to those already installed, it is important for each plumber not only to know the most common pipe diameters, but also to be able to measure them correctly. Our article will be devoted to these questions.

Dimensions of sanitary equipment
Main settings
Before analyzing the size range of water and gas products, which is given in the corresponding State Standards and SNiPs, you need to understand what parameters we will operate on.
When measuring these parts, we will need the following values:
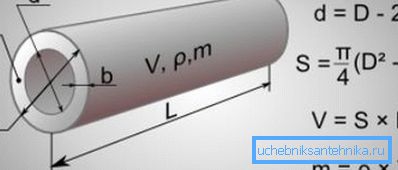
- D - diameter. It represents the distance between the points farthest from each other on the outer surface.
- Doo - conditional pass. The magnitude of the conditional passage is equal to the diameter of the inner channel of the pipe, rounded to a standard value with a certain degree of accuracy.
Note! In international marking, the symbols D and Dn, respectively, are used to denote the outer diameter and conditional passage.
- s - wall thickness. The higher this value, the more durable the structure will be, and the more pressure the pipe will withstand.
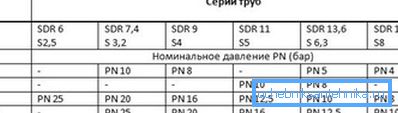
In addition, in order to fully appreciate the capabilities of a particular model, the so-called standard aspect ratio (SDR) is used. This value is calculated by the formula:
SDR = D / s
As a rule, the SDR value is rounded to tabular values, which allows you to easily select a material with the desired resistance to internal pressure.
Inches or millimeters?

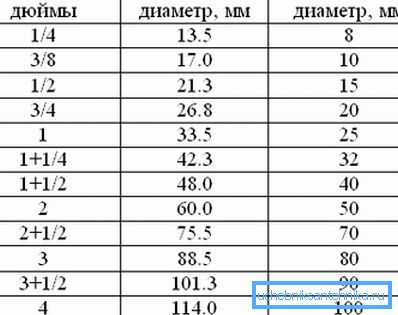
Another important point is to determine the ratio between the metric and inch pipe sizes. It would seem that there is nothing simpler - just multiply the diameter of the pipe in inches by the size of one inch (about 25.4 mm) and we get the desired result, but in practice everything is somewhat more complicated.
The fact is that the inches characterize the pipe thread, which is cut to the outer diameter, and when selecting pipes (especially when replacing metal products with plastic), the inner diameter is important.
So professional plumbers use standard ratios:
- Water pipe 1 2 inches - conditional passage 15 mm, outer diameter from 20 to 22 mm.
- Water pipe 3 4 –pipe in 20 mm, external section from 25 to 27 mm.
- Inch product - 25 and 32 mm, respectively.
- Water pipe 1 1 2 - conditional passage of 40 mm, depending on the wall thickness may have a diameter of 45 to 50 mm.
Also in our article tables of ratios of inch and metric dimensions of the pipes most often used in work are given.
Bandwidth
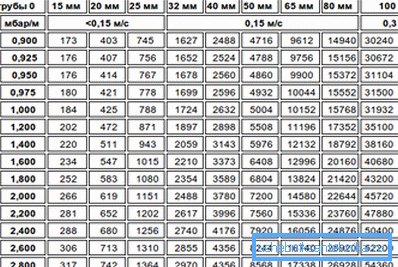
Sometimes for the selection of parts used in the construction of communications, it is required to find out the capacity of a pipe of a certain diameter.
This value indicates how much liquid can pass through the internal channel per unit of time, and depends on the following factors:
- Material of which the pipe is made.
- Product shape (round / profile).
- The diameter of the conditional passage.
- The total length of the contour.
- The presence of the slope and its degree.
- System pressure
For the calculation of this value, cumbersome formulas are usually used, because plumbers usually either use standard, time-tested solutions, or use table values. Thus, according to such a table, the throughput of a water pipe is 100 mm with a speed of movement of liquid at 0.3 m / s and a pressure of 90 Pa / m will be about 30 thousand kg / h.
Note! In order not to do your own calculations, you can download a special calculator program.
Methods of measurement at home
You can measure the pipe with your own hands in several ways:
- If the product has a sufficiently large diameter, then the easiest way is to use a flexible measuring tape (a tailor meter is perfect). Wrap the tape around the pipe and measure the circumference in the widest part. Then we calculate the diameter, dividing the circumference by the number "Pi", approximately equal to 3.1416.
Note! Since standardized parts are used in everyday life, the instruction recommends simply dividing the circumference by 3: the accuracy will be quite sufficient.
- To work with small-diameter pipes, you can use a caliper or micrometer. If you are confronted with similar tasks on an ongoing basis, it is better to purchase a model with an electronic display: its price is slightly higher than that of standard gauges, but it is incomparably more convenient to use it.
- Using a caliper you can also determine the internal diameter of the product. To do this, at a slice in several places, we measure the wall thickness, calculate the average value of this parameter and subtract it twice from the set value of the outer diameter.

- Finally, to solve the problem, you can use graphical programs. To a pipe that needs to be measured, we apply either a ruler or an object with previously known dimensions (for example, a matchbox). We photograph the product, and then with the help of computer programs we correlate the dimensions of the standard with the dimensions of the pipe.

Note! Most often, this technique is used for large-scale objects, as well as for pipes, access to which is very difficult to obtain.
Conclusion
Find out what product in front of us - a water pipe 50 mm, 60 mm or 1 1/2 inches - in several ways. And the more accurately we measure, the higher the likelihood that a suitable part will be selected for the connection or replacement. You can learn more about the principles of measuring pipe products in the video in this article.