Installation of water supply and wastewater systems: from
What materials can perform the installation of plumbing and sanitary in the apartment or private house? What should be the diameter of the pipe? What slope to lay the sewer? In the article we will try to find answers to these and some other questions.

Selection of materials
To begin, let's remember what options the modern market can offer.
For water supply are used:
- Black and galvanized steel.
- Corrugated stainless steel.
- Metal plastic.
- Copper.
- Polyethylene.
To clarify: because of the low heat resistance (not higher than 60-70 degrees), polyethylene is used only on cold water.
- Crosslinked polyethylene. The cross-links between the molecules of the polymer significantly change its physical properties: they can be installed heating and plumbing hot water.
- Polypropylene.
The choice between them is quite ambiguous; however, the author would dare to recommend a corrugated stainless pipe for networks of centralized hot water supply and reinforced polypropylene for a water supply system with its own boiler or column.

Why? You see, in some cases (abruptly open or closed valve, falling of the valve's cheeks, tearing of the valve of the screw valve, etc.) the nominal pressure in the hot water system, which is 3.5 - 6.5 kgf / cm2, can be short-lived increase by 2-3 times. It is the hydraulic shock that causes a significant part of the accidents and flooding of apartments.
For a number of reasons, the probability of a water hammer is much higher in systems with centralized hot water supply; that is why they should be safe and use material with a significant margin of safety.
Reference: for corrugated stainless steel Kofulso declared resistance to hydraulic pressure up to 60 atmospheres.
In the event that only cold water is supplied to a house or apartment, the probability of a water hammer is vanishingly small. If so, you can save on the plumbing: the price of polypropylene is at least three times lower than the cost of stainless steel of the same pogonazh.
What is bad other materials:
- Steel without anticorrosion coating rusts and builds up from the inside with lime deposits.
- Galvanizing involves a very labor-intensive assembly on the threads with adjustment of the sizes of the pipes.
- Copper is much more expensive than other solutions in the absence of any major advantages over the same stainless steel.

- Cross-linked polyethylene is not very aesthetic with open laying and requires the purchase of a very expensive (from 10,000 rubles) expander.
- Metal-plastic significantly inferior to stainless steel strength, and polypropylene - the price.
What kind of valves is better to buy? Here the answer is quite clear: our choice is ball valves.
When buying them you should pay attention to several things:
- Rotate the lever should not require much effort.
- The stem must be equipped with a nut, which allows to tighten the seal.
- It is better to prefer taps without chrome, with a yellow casing. This ensures that the body material is brass, and not silumin, which differs from it in extremely low mechanical strength.

What to use as a material for sewage?
For wiring around the house or apartment - bell-shaped gray PVC pipes with rubber o-rings. They are rather strong and durable at quite reasonable cost.
But when replacing the riser in an apartment building, it is better to prefer cast iron or so-called silent plastic pipes, including a layer of a material of increased density. They will not allow the sound of drained water to disturb your peace at night.
Calculation of water supply
What exactly needs calculations?
- Planned flow through the pipe.
- Its diameter, which is selected by the flow.

- The drop in pressure in it. If at the end of the sanitary device the pressure will be less than five meters, it is worth thinking about increasing the water supply section.
Consumption
Expenditure standards for household sanitary appliances are contained in SNiP 2.04.01-85. We give part of the corresponding table.
| Device type | Total consumption of hot and cold water, l / s |
| Hydrant | 0,100 |
| Washbasin | 0,120 |
| Washing | 0,120 |
| Shower cabin | 0,120 |
| Bath (with water) | 0,250 |
| Toilet bowl | 0,100 |
| Toilet Bowl Faucet | 1,400 |
| Water tap | 0,300 |
Captain Evidence suggests: some devices can be used at the same time (for example, a washstand and a sink). In the calculations used peak total consumption.
Diameter
To calculate it, we need two formulas — the area of a circle and the flow of water through a known section at a known flow rate.
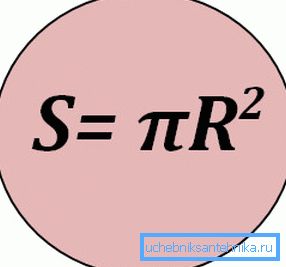
The area of a circle is calculated as S =? R ^ 2, where is the number? is assumed to be 3.1415, and the radius r is half the internal diameter of the pipe.
Water consumption can be calculated by the formula Q = VS. In it, Q is the desired value, V is the water flow rate, and S is the cross-sectional area.
Note: for convenience of calculations, all values for calculations are converted to SI units - meters, square meters and cubic meters per second.
1.5 m / s are taken as the estimated flow velocity, the maximum allowable for the household drinking water supply. Exceeding this limit will mean the appearance of hydraulic noise.
Let us, as an example of your own hands, calculate the size of the water supply system that will supply water to the simultaneously used bathtub, toilet with cistern and sink.
- The total consumption according to the table above will be 0.250 + 0.100 + 0.120 = 0.470 l / s. We recalculate it in SI: 0.47 l / s = 0.00047 m3 / s.
- With a maximum permissible flow rate of 1.5 m / s, the cross-sectional area is calculated using the second formula as 0.00047 / 1.5 = 0.000313 m2.
- Using the first formula, we calculate the radius of the internal section of the pipe. It is equal to 0.0099 meters, or 9.9 mm.
- The diameter, respectively, will be equal to 9.9 * 2 = 19.8 mm.
Do not forget: plastic and metal-plastic pipes are marked with an outer diameter, which, as a rule, is one step larger than the inner diameter. For polypropylene, the required size in our case is 25 mm.
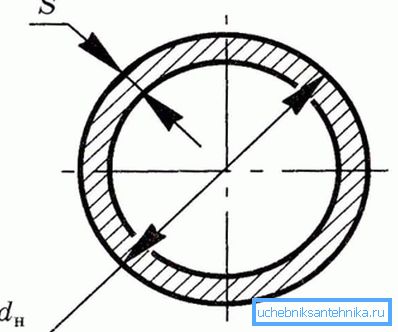
Pressure drop
In this case, the instruction for calculating the drinking water supply is reduced to the use of the formula H = 1,3iL, in which:
- H is the desired drop in meters of water column.
- L is the length of the pipe.
- i is its hydraulic slope.
What is hydraulic slope and where to get its value?
This is the name of the resistance that the pipeline has to the flow through it. It depends on the pipe material, its diameter and flow rate.
Values for all running materials and sizes can be found in the so-called Shevelev tables. They indicate the value of 1000i - hydraulic slope for 1000 meters of pipe. To get the i value substituted into our formula, 1000i should be quite predictably divided by 1000.
Let's calculate the pressure drop in our water supply with an internal diameter of 20 mm, specifying a couple of additional input:
- Pipe material - polypropylene.
- Its length is 12 meters.
For the value of 1000i we will have to refer to the directories. We present the relevant in our case part of the corresponding table:
| Flow rate, m / s | 1000i for plastic pipe with an inner diameter of 20 mm |
| 0.99 | 108.1 |
| 1.24 | 160.5 |
| 1.49 | 221.8 |
| 1.74 | 291.6 |
At a flow rate of 1.49 m / s, closest to the maximum allowable value, 1000i will be equal to 221.8; i, respectively, equal to 221.8 / 1000 = 0.2218.
We substitute this value together with the pipe length into the formula: 0.2218 * 12 * 1.3 = 3.46 meters. The minimum allowable pressure of 5 meters on the end plumbing appliance will be only with a head at the input of 8.46 m (which corresponds to a pressure of 0.846 kgf / cm2). Since the actual pressure in the water supply line is usually not less than 2.5 - 3.5 kgf / cm2, the diameter of the pipe is quite sufficient.

Laying sewage
The choice of the diameter of the sewage system is subject to the simplest rule: outlets to separate washbasins, sinks and showers are laid with a 50-mm pipe; the sections uniting drains from two and more devices, and branches to the toilet bowls are made 110 mm in size.
The slope is 3.5 cm per meter for 50 mm and 2 cm for 110 mm. Counter-slopes are unacceptable: each of them will become a place of constant accumulation of fat and suspensions, and in the long term - a point of blockage.
The maximum distance between the fixation points of the waste pipe is 10 times its diameter.
It is most convenient to cut the pipe in place with a grinder with any cutting disk. It is better to perform work outdoors or having protected the respiratory organs with a gauze bandage: it is definitely not worth breathing in plastic dust.
From the outer side of the pipe cut at the site with a sharp knife the chamfer is removed.

Reduce the need for docking effort will help ordinary soap.
They can rub both the rubber seal and the end of the pipe with the bevelled.
- Ratruby always oriented against the direction of flow of wastewater.
- Turns better to perform not one 90-degree angle, and two 45-degree. In this case, there will be much less problems with cleaning when clogged.
- For the same reason, on long sections and turns, it is worthwhile to provide for revisions or tees with plugs.
Assembly of water supply
Stainless steel
In this case, the installation of water pipes is carried out using the simplest compression fittings with silicone rings - seals. Tool - two open-end or adjustable wrench. The minimum radius of rotation of the pipe is equal to its diameter, so that the number of fittings will be minimal.

For fixing the pipe to the walls using plastic or metal clamps; the distance between the attachment points should be no more than a meter.
Polypropylene
Installation of water pipes made of polypropylene is performed by a low-temperature soldering iron with a set of nozzles for different diameters.

To connect the pipes used cast fittings from the same polypropylene.
The soldering process looks like this:
- The soldering iron is supplied with a nozzle of the appropriate size for the pipe and heats up to 240 - 260 C.
- The pipe and the socket of the fitting are combined with the nozzle for a few seconds, after which the pipe is inserted into the fitting and is held for some time.
The duration of heating, fixation and cooling of pipes to obtain a strong connection depends on their size:
| Diameter, mm | Heating, s | Connection, s | Cooling, min |
| 20 | 6 | four | 2 |
| 25 | 7 | four | 2 |
| 32 | eight | 6 | four |
| 40 | 12 | 6 | four |
| 50 | 18 | 6 | four |
As always, there are a number of subtleties:
- On aluminum-reinforced pipes, the foil must be removed from the field of welding. This work is carried out by a shaker (with external reinforcement) or a flat-cutter (when the reinforcement layer is located in the middle of the wall).
- Pipe and fitting are combined strictly by forward movement, without rotation. Otherwise, the melted plastic wave will weaken the joint.
- Long straight sections of polypropylene on hot water are supplied with expansion joints - U-shaped or ring bends.

- Clamps should not prevent the pipe from lengthening during heating.
Conclusion
We hope that we managed to help the reader in the selection of materials and the implementation of their own projects. In the video in this article, you can, as usual, find more information. Successes!