Submersible pumps for wells: first acquaintance
How does a well pump work? What are the characteristics and how to choose a submersible pump for a well? What should you pay special attention to when installing it?
In the article we will try to answer these and some other questions.

Working conditions
What are the conditions for domestic well pumps?
Understanding this will give us a clearer idea of which characteristics are most important when evaluating a device.
- Water is pumped by the pump to cool the motor.. The quality of cooling is affected, among other things, by the gap between the device body and the walls of the well: too small a distance is undesirable. Moreover: in this case there is a risk of jamming the product when lowering or removing.
- The pump is suspended at some distance from the bottom of the well; while most of the time the water column above it is a few meters. In this way, the inevitable seasonal variations in the groundwater level are compensated.
- Service, to put it mildly, difficult. Removing the product from a depth of several tens of meters is not a trivial task in itself; deformation of the wellbore may well make it impossible.
Please note: if the installation of a submersible pump into the well with your own hands is quite feasible, then lifting it when the casing is deformed may well require the involvement of drilling equipment.
- The pressure that our unit should create is not limited by the distance to the surface. An excess is needed, which will not only create enough pressure to operate the drain tanks and mixers, but also overcome the hydraulic resistance of the pipes.

Classification
So, what are the devices we are discussing?
Vortex
Its design is quite simple: the impeller creates excessive pressure at a distance from the axis of rotation; along the axis, on the contrary, rarefaction occurs, providing water intake from the well. It would seem that the scheme is simple and fault-tolerant, so that the price of the pump will be minimal, and the service life will be great.

However, as always, the devil is in the details.
Remember what pressure should create this unit. At tens of meters, right? In order to provide an overpressure of 7-9 kgf / cm2 at the outlet, the gap between the impeller and the casing must be calculated in fractions of a millimeter - otherwise the water will simply run around in a circle.
If the ingress of large particles that can wedge the impeller can prevent the coarse filter at the inlet, then what to do with small abrasives? They wear blades and smash the hull; as a result, costly repairs are required, resulting in a complete replacement of the pumping part.
Captain Evidence suggests: vortex pumps are used only for wells with extremely pure water containing no more than 30 grams of impurities per cubic meter of volume.
Screw
Screw downhole pumps - the exact opposite of vortex in terms of fastidiousness with respect to impurities. They cope with lifting liquids containing up to 50 percent of sand and other suspended matter. How is this achieved?
At the heart of the design is the Archimedes screw (or worm), a structural element used by the ancient Greek inventor for lifting water in ancient times. Rotating, it creates dynamically moving areas of high pressure.
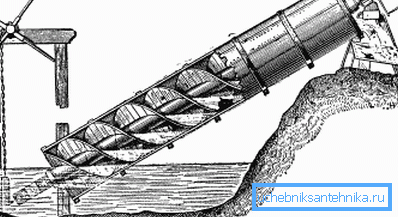
Such a device generates several design features.
- The need for a separate engine, as well as problems with its waterproofing, disappears. The rotating worm itself is the rotor of the electric motor, and the body is its stator.
- The efficiency of devices is only 50-70 percent, which is much worse than that of competing solutions. Part of the energy is spent on useless mixing and heating of water: the pump’s own hydraulic resistance is extremely high.
- Productivity is also noticeably lower than that of competitors.
- Outlet water requires mandatory filtration. However, devices of this type are more often used not for continuous operation in wells, but for their cleaning during silting or during pre-operational preparation.
- From the gap between the worm and the housing (the so-called compression fit) depends on the performance of the pump. The tighter parts fit, the higher the performance and pressure at the outlet.
However: the resource of the stator at the same time repeatedly decreases due to the increasing degree of mechanical wear.
- If the rotors are made as hard and wear-resistant as possible (as a rule, stainless steel is used), elastic materials, including rubber-based compounds, are widely used for the internal shells of the stators.

Membrane
Cheapness of devices of this type is beyond competition. Its reason is in the simplicity of its design: the elastic membrane is driven by a solenoid, to which a high frequency power supply is supplied to the control circuit; ball valves cause water to move in the right direction, blocking its movement during the return stroke of the membrane.

Despite the cheapness, a potential buyer can be advised to keep as far as possible from the diaphragm pumps.
What is the reason for this instruction?
- The membrane resource is limited, regardless of its quality and the material used for the manufacture. It is deformed in the process of work, which inevitably at some point leads to its destruction. Raising the pump for maintenance, as we remember, is a dubious pleasure.
- A ball valve wedged with sand or a small pebble causes an idle pump operation with a very fast failure of the solenoid.
- The pressure and performance of such a product is below any criticism. The typical representative of this class — the domestic Malysh — was widely used several decades ago in country wells and shallow wells; Now all membrane devices are practically superseded by the following type of pumps - centrifugal.

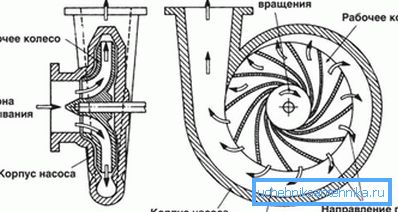
Centrifugal
It is under this scheme that most of the devices currently sold work. Structurally, they strongly resemble vortex; however, the gap between the impeller and the casing is much larger, which makes the design less sensitive to impurities. Particles up to 2 millimeters in size and the amount of suspensions up to 150 grams per cubic meter do not create problems.
How are the pressure and performance provided? After all, it would seem obvious that the main technical characteristics of submersible pumps for wells - head and productivity - should increase catastrophically with increasing clearance between the impeller and the casing, shouldn’t it?
The problem is solved simply and gracefully. On the motor shaft several stages are successively installed, each of which consists of an impeller and a diffuser. Each stage increases the pressure by 5 - 10 meters; As a result, the overpressure at the outlet can be 20 or more atmospheres.
Selection
So, the well is drilled, the casing is installed. We are in the store and we are going to purchase a device that in the next few years will provide us with water - drinking and intended for household needs. What to look for when buying?
Head pressure
Nominal pressure should not be less than necessary; However, a significant excess of it is also undesirable: the result will be not only excessive energy consumption, but also potential problems with flexible connections (they are not very resistant to high working pressures).
How to calculate the need?
- Take the depth of the pump. The minimum distance from the bottom of the well is about one meter; taking into account groundwater level fluctuations, it is recommended to lower the pump approximately 5-10 meters from the water surface. The depth of the empty and water-filled parts of the trunk is easily measured with a lead weight rope - it is enough to measure the dry and wet part of the rope.
- The resulting value is added 30 meters. Excessive pressure should create the pressure necessary for normal operation of the mixers and filling valves in the water supply system.
- 10% is added to the result for unaccounted losses.
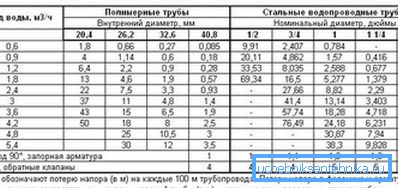
So, for a pump immersed to a depth of 40 meters, the nominal head of (40 + 30) * 1.1 = 77 meters is desirable.
Please note: in practice, the result is rounded up to tens of meters. In our case, it is worth buying a device with a nominal pressure of 80 m.
Performance
Ideally, it should be greater than the peak water demand of the family, but not exceed the flow rate. For a family of 4 people, a device with a capacity of about 50 liters per minute is usually taken; the need for watering the backyard plots this value roughly doubles.
How to determine (even approximately) the flow rate?
- Determine the height of the water column above the pump. Measuring it, as we already know, is not difficult as a sinker on a rope.
- We pump out the well completely.
- Find out how long the water level will recover. To do this, we make periodic measurements with a small interval.
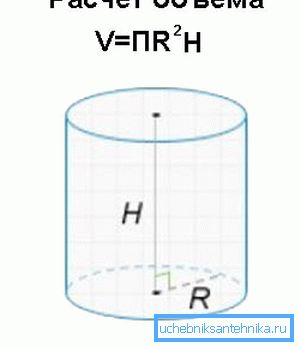
- We divide the volume of pumped out and subsequently entered into the well for the elapsed time. How to calculate the volume of water column of known height? It is equal to the product of this height by the square of the radius of the casing and the number pi. Thus, a pillar with a height of 10 meters and a diameter of 10 cm has a volume of 10 x (0.05 ^ 2x3.1415) = 0.0785 m3, or 78.5 liters.
Diameter
In most cases, it is 4 inches (about 10 centimeters); however, there are 3-inch models in the range of manufacturers.
Note: with equal performance, a pump with a smaller diameter is usually more expensive. The smaller the dimensions of the motor, the harder it is to provide the necessary torque.
Manufacturer
As a rule, the products of famous manufacturers (Grundfos, Pedrolo, Wilo and so on) last longer and create much less problems for the owners. In case of equipment failure, companies have developed service network.
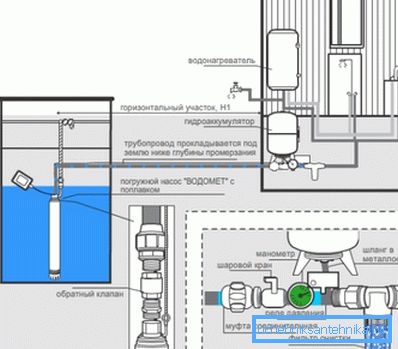
Installation
The actual installation of the submersible pump in the well looks like this:
- The well is pumped, clearing sand and silt. Of course, if possible.
- At the outlet of the pump clamp is attached plastic pipe for transporting water. In addition, the device is suspended on a steel cable with anti-corrosion protection.
- Then the unit is lowered into the wellbore. Recall: the distance to the bottom should not be less than a meter, otherwise the probability of capture of silt and sand is high.

- The cable is securely fixed on the tip. Pipe for water and cable are put in the house.
Attention: the pipe is laid below the ground freezing level.
When connecting to the water supply, however, it is worth considering a number of nuances.
- If the check valve is not provided in the design of the pump itself, it is installed after it. Without a valve when the engine is stopped, water from the water supply system will flow into the well.
- Installation of the hydroaccumulator is extremely desirable. It will smooth out the peaks of water use; in addition, if it is available, the pump will stand idle for a substantial part of the time, which will save both electricity and its resource.
- High power devices require a starter that gradually increases the starting current.
Conclusion
We hope that the choice and installation will not cause the reader serious difficulties. The video in this article will provide additional useful information. Successes!