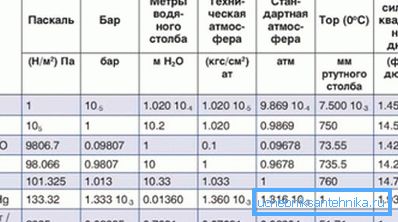
Water pressure in the water supply system: units of
What is the pressure of water in the cold or hot water supply? How are pressure measurements taken? Are there any regulatory limits of its value? In this article we will try to answer these questions, and at the same time learn how to calculate the pressure drop in a water supply system with known parameters.

Units
First, find out which units of water pressure in the water supply system are currently used.
Atmosphere
This unit corresponds to atmospheric pressure at sea level. Here, however, there is a small subtlety: it is about overpressure relative to atmospheric. Its value in a water pipe of 0.2 atmospheres, shown by a pressure gauge, corresponds to an absolute value of 1.2 atmospheres.
Useful: instead of the word atmosphere, an equivalent concept is often used - kgf / cm2. The physical meaning of the unit is the force with which the mass of 1 kg during the earth’s acceleration of gravity will press on an area of 1 cm2.
Bar
Obsolete unit of measure, borrowed from the GHS measurement system used before the SI. It is enough to know about it that the bar is approximately (with an accuracy of about 2%) equal to the atmosphere. Quite often, a pressure gauge for measuring the pressure of water in a water supply system has two scales - in bars and megapascals.
Megapascal
Pascal corresponds to one newton per square meter of surface. Since the mass of one kilogram presses on the base with a force of 9.8 Newtons, 1 megapascal approximately corresponds to 9.8 kgf / cm2. Sometimes this value is rounded to 10.
Head pressure
The concept of head, measured in meters, means the height of the water column corresponding to a certain overpressure. How to find out the pressure at the known indications of the manometer in kgf / cm2? It is enough to multiply them by 10: one excess atmosphere can raise a water column by 10 meters.
Measurements
A device for measuring the pressure of water in a water supply system is known as a pressure gauge. The price of the most affordable gauges starts from about 150-200 rubles; however, digital devices can cost in units and even tens of thousands.

The way to measure the parameter of interest to us with our own hands is extremely:
- A device coiled up with flax or other sealing material is screwed into the control valve..
- The valve opens, and then takes off.
Check valves for taking measurements are always present in the elevator assembly (flow, return and mixture after the elevator) and in the water meter (usually before and after the meter). If it is necessary to remove the measurement at an arbitrary point in the water supply system, this is easy to do by screwing the pressure gauge instead of the plug into one of the risers and launching it.
As always, there are a number of subtleties.
- In order to make a detailed picture of the work of the water supply system, measurements should be carried out at the peak of the water intake that falls on the evening hours.
- A device that is constantly connected to the water supply system often sticks: the arrow is stuck in one position. To prevent this from happening, instead of the control valve, a three-way valve with a drain hole is placed, which allows water to be dumped from its body after measurement.

- The brass pipe thread of a continuously removable device wears out quickly. A simple instruction will help to solve the problem: supply the manometer with a steel extension cord.
Regulations
Here are the norms of water pressure in the water supply system contained in the current SNiP 2.04.01-85.
| Location of the point of water pump | Pressure, MPa |
| Lower building | No more than 0.45 |
| Lower building erected in an area with old buildings | Not more than 0.6 |
| Upper in the building | Not less than 0.2 |
As it is easy to calculate, the water pressure in the city water supply can generally differ from its value on the upper floor by only 0.25 MPa, which corresponds to a head of 25 meters. With a higher building height, intermediate pumping should be installed on the middle floors.
However: in practice, all pumping stations familiar to the author are located in the basement of the house or in a separate building. When working on the first floors at the points of dismantling, it may well be 8 - 9 kgf / cm2.

In practice, typical pressure values in highways and highways are as follows:
- Cold Water - 3 - 4 kgf / cm2.
- DHW - 3.5 - 6.5 kgf / cm2.
Pressure drop
When water flows through the pipe, the pressure at the outlet will be less than at the inlet.
The fall is determined by several factors:
- The diameter of the pipe.
- Its length.
- The roughness of its walls.

- The flow rate in it.
For calculation, the formula H = iL (1 + K) is used.
In it:
- H - pressure drop in meters. To translate it into the atmosphere, it is enough to divide the resulting value by 10.
- i - hydraulic slope, determined by the diameter, the pipe material and the flow velocity in it.
- L is the length of the pipe in meters.
- K - coefficient for drinking water supply systems assumed to be 0.3.
Where to take the value of the hydraulic slope? In the so-called Shevelev tables. We give a fragment of one of them, relevant to the new steel pipe size D15.
| Water consumption, l / s | Flow rate, m / s | 1000i |
| 0.17 | 1.00 | 266.2 |
| 0.18 | 1.06 | 296.1 |
| 0.19 | 1.12 | 327.6 |
| 0.20 | 1.18 | 360.5 |
| 0.25 | 1.47 | 560.4 |
| 0.30 | 1.77 | 807.0 |
| 0.35 | 2.06 | 1098 |
The 1000i value is a hydraulic slope with a pipe length of 1 km. To calculate the value of i for a running meter, it is enough to divide it by 1000.
So, for steel pipe DU15 with a length of 25 meters and a water flow rate of 0.2 l / s through it, the pressure drop will be (360.5 / 1000) * 25 * (1 + 0.3) = 11.7 meters, which corresponds to the difference pressure of 1.17 kgf / cm2.

Conclusion
We hope that the proposed information will help the reader in the implementation of his own projects. To learn more about how much water pressure in the water supply is considered to be the norm, the video in this article will allow. Successes!