Water purification from the well: the main impurities and
Water purification from a well in a country house is a necessary procedure that provides users access to a source of clean drinking water. The current view that groundwater does not need to be cleaned is mistaken.
We will talk about what impurities are typical for wells, and how to deal with them.

Typical impurities and cleaning methods
Iron

Iron is the most common mineral in the earth's crust..
Especially often this element is found in such rocks as:
- hematite,
- magnetic iron ore,
- brown iron,
- and also in various iron ores and other compounds.
As a rule, iron is in water in a dissolved form, and it is oxidized to a bivalent state. The permissible concentration of this impurity is not more than 0.3 mg / l, and if it is exceeded even slightly, the water is considered unsuitable for use.
Ferrous iron does not stain water, and the newly extracted liquid retains its transparency during the first period of its presence on the surface.

Then, as a result of contact with oxygen, which saturates the deep water, which is poor with this gas, iron oxidizes and precipitates, painting the liquid in a characteristic red-brown color. In addition, the water gets the smell and unpleasant taste, familiar to us to taste the blood.
The harm from the presence of iron oxides is quite noticeable:
- Drinking water from a well becomes unpleasant: it has a characteristic taste of iron, similar to the taste of blood in the mouth, if you bite your lip;
- There is a danger of the spread of the so-called iron bacteria, which adversely affect the quality of water;
- Small particles of sediment are absorbed into the smallest pores on the surface of dishes, plumbing, sinks, baths and paint these surfaces in the color of rust;
- The color of the water is easily transferred to the tissues during washing, as a result of which it is possible to spoil clothes and underwear.

To purify water from iron, various methods are used:
- Catalytic oxidation with pre-aeration. For cleaning use a compressor that enriches water with oxygen in the aeration column, where the oxidation of iron to the trivalent form, which precipitates and is filtered using a catalytic filter;
- Ion exchange method. It uses a special ion exchange resin, which replaces iron ions with sodium ions, which do not contaminate water. In the process, some amount of ferrous iron can be oxidized to the trivalent state, while clogging the resin with sediment;
- Reverse osmosis method. Water under pressure passes through a special membrane, the pores of which are of such size that uncharged water molecules pass through them, and the larger molecules and charged particles are filtered out. One of the most effective methods for the removal of iron and manganese, as well as a number of other impurities, operating at high pH;
- Chemical cleaning with oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate, manganese dioxide, ozone cleaning and others;
- Redox environment using zinc and copper allows you to stop the growth of iron bacteria due to the weak electric field generated by electrochemical processes.

Note! When choosing a filtration system for cleaning well water from iron impurities, you should take into account such factors as the temperature of the treated water, its acidity, alkalinity, free dissolved oxygen content and a number of other parameters that will determine the ability of the normal operation of a particular cleaning method. Conditions for the use of the filter contains the manufacturer's instructions.
Magnesium and calcium salts
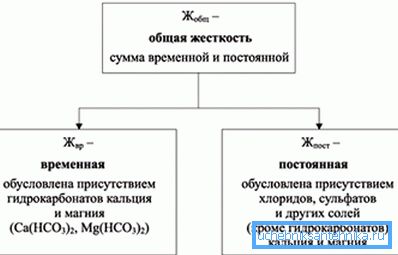
As can be seen from the diagram, the hardness of water causes an increased content of calcium and magnesium salts in it. The limit allowed for the drinking environment is 2–3 mg eq / l according to GOST and SanPiN. Also, the increase in hardness can cause sodium, barium, strontium and aluminum salts, but these impurities are usually insignificant and therefore are not taken into account when filtering.
A large number of these salts in water leads to a number of undesirable consequences:
- When boiling water, salt precipitate, which forms scale on the walls of dishes and heating elements of household appliances;
- In hard water, tea and coffee are badly brewed;
- In hard water soap is badly washed, forming soap slags that destroy the protective film of our skin;
- Water becomes bitter or tart to the taste;
- There is a danger of urolithiasis and salt deposits in the kidneys.
The salts of magnesium and calcium get into the water from lime, as well as upon contact with dolomite and gypsum.
Ways to reduce stiffness have been known for a long time: boiling, freezing, filtering, softening due to ion exchange and alkaline soda ash. Today at home most often use the method of reverse osmosis and softening.
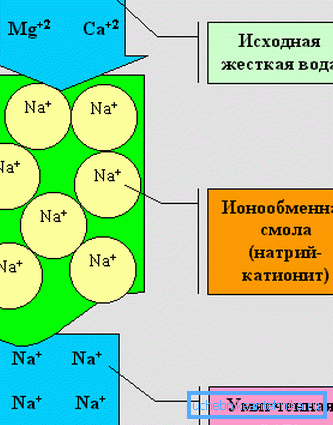
For softening, it is advisable to use high-quality monodisperse ion-exchange resin (German Lewatit S 1567 resin is suitable), which is regenerated with common salt. You will also need a cylinder for water purification and a salt tank for resin regeneration.
Do not forget that with an increased content of sodium and nitrates in water (more than 1000 mg eq / l) there is a danger of pressure increase in hypertensive patients and cores. The only way to get rid of molecules and sodium ions is reverse osmosis.
Note! When filtering hard water, reverse osmosis membranes are used as the only way to effectively eliminate salts. Such mechanical cleaning does not require reagents and their regeneration, and the filter is cleaned by back washing the membrane.
Hydrogen sulphide

The next undesirable chemical agent in water is hydrogen sulfide. Combining two hydrogen atoms with one sulfur atom is a toxic gas that dissolves in water and can be harmful to health if it is used without purification..
The source of this gas are most often sulfate-reducing bacteria, which release hydrogen sulfide in the process of life. The substance also enters the well from sulphide ores and as a result of the decomposition of high molecular weight organic impurities.
Note! The cost of drinking water with a high content of hydrogen sulfide can become too high and lead to serious poisoning.

Cleaning wells for water from hydrogen sulfide is possible by one of several methods:
- aeration;
- catalytic oxidation on ion exchangers;
- chemical oxidation with ozone, sodium hypochlorite or potassium permanganate;
- as well as by the method of biochemical purification and preliminary acidification followed by aeration.
Simple mechanical filtration with activated carbon is quite common.
Note! To use reverse osmosis for purifying drinking water from hydrogen sulphide is meaningless, since the molecules of this gas for the reverse osmosis membrane are indistinguishable from water molecules, and therefore they pass through it unhindered.

To determine the required method of water purification you must do a complete chemical analysis of water. To do this, you should contact the SES of your area, and her specialist will make a water intake, which will fall into the laboratory for study. The data of complete chemical analysis can be presented to any organization engaged in the purification of drinking water for the selection of a filtration system for a well.
Then you should buy a suitable filter, which you can then install by hand or with the help of professional installers. Usually installation does not cause problems and comes down to the implementation of the recommendations of the manufacturer, described in the instructions or the manual for assembly and installation of equipment.
Conclusion
Filtration of water extracted from a well of any depth is necessary and obligatory. There are many methods of cleaning liquids from impurities, when choosing the right method for you, you will have to do a complete chemical analysis of water. To better represent the work of water purification systems, we recommend watching the video in this article.