Water well depth is a necessary parameter
Whatever is said, but to acquire its own source of drinking water at the dacha is the ideal option that everyone dreams of. Moreover, if you try a little, the source can be obtained without any problems, given that it is usually there and this will require drilling.
There is only a completely understandable question, and how deep is the reservoir to ensure sufficient pressure above. Without addressing this issue is not recommended to start work.

Depth: how important
But first, it is generally required to determine what types of formations exist..
There are actually four of them:
- 1 - topline - this is the top and simple, located at a depth of 4 meters; it feeds on precipitation, which is why it is very dirty or in the summer period is completely absent as a result of drying;
- 2 - groundwater - such up to 10 meters in clay or stony rocks as impermeable; this source is much cleaner vodovka;
- 3 - interstitial waters - from 10 to 100 meters; This horizon is often located between waterproof clay; the upper layer may be partially permeable, which provides the reservoir with groundwater;
- 4 - artesian water - more than 100 m (although sometimes it is already found at 40 m); the source here is the purest, although sometimes with impurities.
Helpful advice! We advise you to very accurately understand the terminology of the subject under discussion. So, often the first two layers, the upper layer and the ground layers, are very similar to each other and are combined under the same name “ground”. The first three layers are also called sandy, by the nature of the aquifers. And the fourth, for the same reason - limestone. Therefore, they say, "drilling in the sand" and "drilling in limestone."
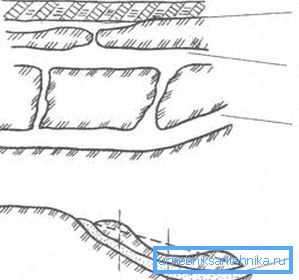
In fact, the situation with underground soils can be much more complicated. The most typical is shown in Figure "A".
Here:
- A - surface layer of soil;
- B - groundwater, we note, indicated the actual position of the reservoir, the height of which can change at different points of drilling;
- C - waterproof clay of the upper horizons;

- D is a layer of sand and gravel;
- E - rocky rocks, as waterproof for lower layers;
- F - deep water;
- G is the crack that can cause layer loss.
Depth determination
The depth of the well for drinking water can be determined in several ways.
The first is the simplest
The simplest, but quite accurate way is this everyday:
- you find a well already operating nearby;
- learn its depth;
- determine exactly what your aquifer is the same;
- his level of occurrence will be yours;
- for more accurate data, it would be nice to find a couple more wells of the same horizon to determine the nature of the horizontal layer;
- if others approximately have the same depth indicator as the first, then you can, with a high probability, attribute yours to the same one.
Second - by seam
But with a simple way to get lucky can not always.
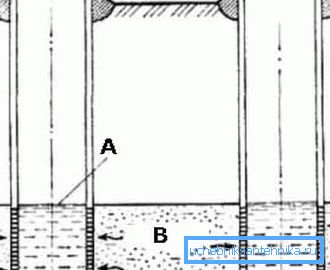
Then you have to focus on the levels of occurrence of the layers (figure "B"):
- A - river, as a zone of discharge of water layers;
- B - waterproof layers;
- C - interstitial waters, pressure; well for getting from here - no more than 50 m;
- D - flowing artesian water; as a rule - about 100 m, but if you're lucky, you can get a fountain from 40-50 m;
- E - interstratal, free-flow - from 10 to 30 m;
- F - topline - from 3-4 to 10 meters;
- G - the so-called groundwater feeding zone.
What does this mean
To know the depth of its layer is important, first of all, for two reasons:
- firstly, to determine the necessary labor costs;
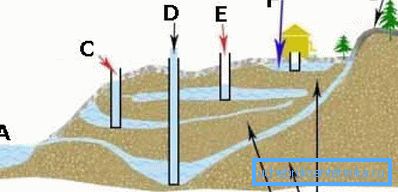
- and, secondly, to determine the specifics of the necessary equipment, which is clearly shown in Figure “C”:
- if “a well on sand” (A), that is, no more than 50 meters, then pipes of one diameter of 127 mm will be enough, but you will have to equip the entire system with a filter for the well, there is a high probability of excessive contamination;

- if the “well is limestone” (B), the occurrence is much deeper, therefore a whole cascade of pipes with a gradually decreasing diameter — from 133 to 117 and further to 95 mm — cannot be avoided; a so-called telescopic well is created; although it may be possible to do without a filter.

Helpful advice! The nominal permitted depth of artesian wells of 100 meters can vary significantly depending on the area of drilling. For example, in the Moscow region they can reach up to 250 meters with a minimum of 35 m. At the same time, one should not be surprised at their popularity, because their performance is significantly higher due to greater pressure from the inside. Productivity can reach up to 50 liters per minute, which is enough for 3-5 sites.
findings
The instruction and price of drilling a well directly depend on the depth of the formation. It is not always possible to determine the depth accurately, but it is not difficult to have a rough estimate. Be sure to check out the additional video in this article, it will once again allow you to systematize your knowledge regarding the possible depths of the moisture you need in the area.