What is well logging
The word logging comes from the French carottage, which, in turn, comes from carotte - carrots, which is very similar to the logging probe. This word is used for the general name of geophysical research of wells, which may differ from each other in the method of the procedure.
This is what will be discussed below, and in addition, you can watch the thematic video in this article as additional material.

About logging
General information
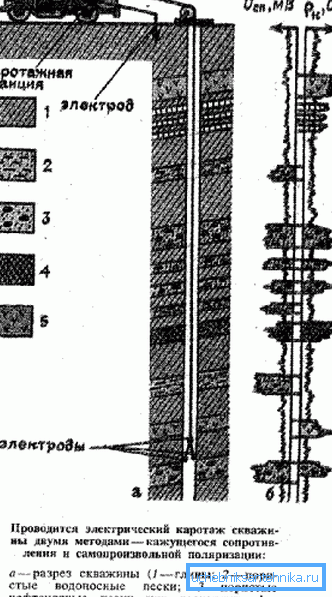
In order to carry out logging work, in the well, as required by the instructions, it is necessary to introduce a geophysical probe, which contains all the equipment necessary for the study.. The information received here, as a rule, is transmitted in two ways - one of the parts is immediately transmitted to the surface by means of a geophysical cable - it is also an electrical conductor, a carrier element, and a data transmission channel. Another part of the received information is written into the memory of the probe itself and can be obtained only after the latter is retrieved to the surface. (See also the article How to equip a well with your own hands.)
A number of technical reasons determine the receipt of information - it is collected at the time when the probe moves along the well from the bottom up at a low speed. This method allows the device to move evenly, while moving down it can simply get stuck in the well and the resulting information will be distorted.
Although, nevertheless, some parameters are recorded exactly when it is lowered, but in any case, the radius of the research zone remains small - from a few centimeters to several meters.

In those cases when the probe moves too quickly, and this, as a rule, occurs during its descent, it is unable to clearly register even large anomalies in the surrounding layers. But too little movement speed, which can occur during lifting, significantly increases the time of logging, which means that its price increases.
The problem with this method is that the well itself is never perfectly flat and its diameter is variable, so several methods are used to measure the current depth.
- With the help of the coupling locator (LM) it is possible to determine the number of connections, and hence the number of pipes lowered into the well. Therefore, by calculating their total length, you can determine the size of the depth.
- Also on the geophysical cable there are magnetic tags, which are located every 10 m and every tenth of them (after 100 m) is doubled. The number of tags is calculated by a special counter.
Note. At first glance, both methods are almost perfect, but practice shows that the locator can skip one or several marks, just like a meter misses magnetic marks. But when comparing data from two devices, the picture is more accurate.
As noted above, the readings of the probe, or more precisely, the well itself will affect their accuracy, and this:
- The walls of metal wells, therefore, magnetic measurements are distorted. Also, the metal, being an excellent conductor, makes electrical scanning difficult and prevents the annular space from being investigated.
- Since the drilling fluid, which remains in the well quite a lot, contains water, and there, respectively, there are chlorine and hydrogen atoms, this makes it difficult to check for the hydrogen content of the oil.

Note. Depending on the method and nature of the study, it may be necessary to either bring the probe closer to the wall of the well or place it in the center. This is quite possible with the help of springs, which the installers install with their own hands as needed. So, for the central location, four springs are needed, uniformly supporting the device from all sides, while only one spring is enough to press the probe against the wall.
Methods
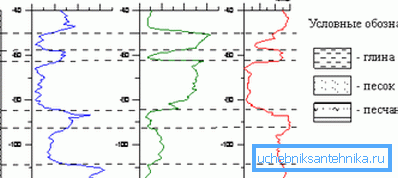
Now we will pay attention to some basic types of well logging, which are used in industry and construction. First of all, it is an electric way, which is divided into groups. (See also the article Types of water purification systems from a well.)
The most common can be called the method of KS (apparent resistance) - this is an analogue of electrical profiling in electrical prospecting. Micro-logging is very similar to it, where small probes are tightly pressed against the borehole wall.
The resistivity method can measure the electrical resistivity of the fluid that is in the well at the moment. This could be oil, formation fluids, drilling fluids, and groundwater.
For vertical electrical reconnaissance, lateral logging is used. There is also a side and microborne logging - BK and MBK, respectively.
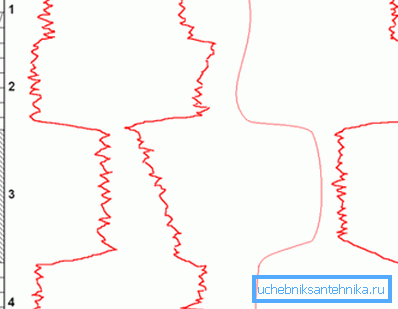
I would like to draw attention to the methods of nuclear research, the names of which, as a rule, consist of three letters. The first one indicates the type of radiation used in this situation (G is gamma and H is neutron), the second indicates the type of response radiation, therefore the letter is preserved and the third classifies the scope (A - analysis, K - logging, M - general method, About - testing). In cases where there is a fourth letter, it already indicates a modification. (See also the article Borehole adapter: how to choose and install.)
Conclusion
Any video logging of wells is divided into two ways - surface and underground, and both studies always complement each other, but still, among them are the main methods - electrical and nuclear. This allows you to set not only the depth of the reservoir up to a centimeter, but also the nature of its change.