What to do if water leaves the well: diagnostics and repair
The well has been and remains the main source of drinking water for owners of country houses and country houses, as well as for residents of remote areas and the private sector of rural areas. But what to do if suddenly water left the well, or its level became catastrophically low? We will explain why the water leaves the well, and how you can solve this problem yourself.

Fault Diagnosis
Normal work

In order to establish the fact of disturbance of the source’s normal operation, it is first necessary to figure out how the well is arranged and what this norm is. To do this, let's say a few words about the device and design of the well structure.
Regardless of the type of construction, all the wells are a vertical shaft, which opens the aquifer and accumulates water in its trunk.
The shaft of the shaft is strengthened with a casing structure, which is constructed of durable, water-resistant materials:
- Some wood species - aspen, oak, larch, pine. It is the most environmentally friendly and proven technology for centuries, but lately the ever-increasing price of high-quality raw materials has become a serious problem;
- Natural stone and brick. One of the most reliable and durable casing techniques, which, however, requires the work of experienced craftsmen;
- Reinforced concrete rings or monolithic structures. RC rings are best suited for self-assembly, and the column itself is strong and durable, especially when using monolithic construction;
- Various polymers and plastics. These materials are airtight, water resistant and non-corrosive. The service life may be interrupted only due to an accident or other emergency.

The upper part of the casing comes to the surface and rises above the ground to a height of from meter to one and a half meters. This part is called the tip and is used for convenient access to the wellhead and extracting water to the surface. For this purpose, the end cap is provided with a lifting drum with a handle and a hanging chain, on which a bucket is hung.

The lower part of the casing is under water and is called the water receiving part. It has a bottom filter or perforation in the walls of the casing structure for the entry of water into the tank.
By the type of water intake part, wells are divided into three types:
- Imperfect (incomplete) - those in which the lower (receiving) part of the casing does not reach the bottom of the aquifer. Water enters the pipe through the bottom of the casing through a gravel filter;
- Perfect - those whose casing rests on the bottom of the impermeable formation. Water enters the pipe through the perforations on the bottom of the casing;
- Perfect with sump - those that have a dimple (sump) in waterproof rock for an additional volume of water.
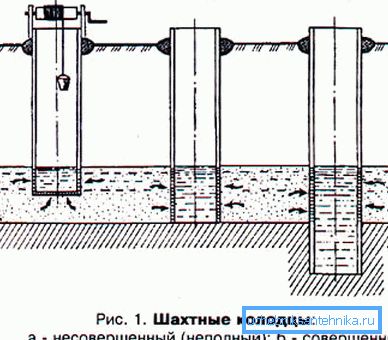
Note! Most often, in the case of independent construction, it is the imperfect type of well that is being built, since it is simpler, and the average family with a standard household farm usually has enough water in it.
So, we can distinguish three main functional areas of the well structure:
- Cap with a canopy, lifting device and lid;
- Casing shaft;
- Water receiving part with casing and filter.

In normal operation, the following process occurs: water that is infiltrated in the sand of an aquifer, seeps through a perforation or filter, and is collected inside the column. At the same time, sand and other particles practically do not penetrate into the column, and the liquid in it remains in its pure form.
Note! The water level in the water intake will be set at the height at which the fluid was inside the aquifer (the law of communicating vessels). Here we can note one important feature: the groundwater level may fluctuate due to changes in temperature and rainfall, which is observed when the seasons change.
We go further. As we have said, the level of fluid in the water intake remains the same as in the aquifer. But over time, the sand, however, falls into the well and settles at the bottom.
Because of this, the bottom level rises, and the liquid level remains the same: the volume of water in the column drops. This is also a normal mode of operation, and nothing can be done here except to eliminate the consequences.
In addition, over time, the aquifer is gradually depleted, the water lenses that feed it become shallow, and the water level in the wells decreases, and their flow rate decreases.

It is also possible to call the normal process of silting a well: over time, an ever increasing amount of the smallest suspension of mineral and organic particles settles in the filter, which clog pores and reduce the rate of fluid passing through the filter material. In the end, the rate of replenishment of the well drops to such an extent that water consumption exceeds its arrival, and the water intake becomes empty.
So, we have listed the normal modes of operation of wells and deviations within the normal range, which, if not properly taken care of, can lead to a decrease in the volume or disappearance of water.
Abnormality

As a result of normal operation, the water level decreases due to changes in the structural parameters of the well — depth, filling rate, filter permeability. You can also note the natural fluctuations in the level of fluid in the aquifer, which are not related to the operation of the structure.
Emergency changes may also concern the design of a well shaft or other parts. The most destructive changes and failures of the casing, which lead to its depressurization. As a result, fissures and fissures appear in the casing material, through which a stream of dirt and sand may rush inwards.

It is not difficult to diagnose such a process: unlike the natural settling of sand at the bottom of the face, in the event of an accident, the bottom is raised not sharply, but gradually. If during normal operation it takes at least 3 years, then in case of a breakdown it may take several days or even hours.
Fistula can also be determined by the fractional composition of penetrating sand and rock particles: they will be presented in the widest range, from the smallest to natural stones of small size. For comparison: particles of approximately the same fine fraction pass through the filter of the well construction.

In addition, emergency changes occur due to interference with the hydrogeology of the area as a result of human activity. It may be a quarry, deep well, artesian well, etc. Large-scale opening of the aquifer or a serious increase in consumption can lead to a drop in the general level of the fluid and even to its disappearance.

The hydrogeological picture sometimes changes due to natural causes: soil movements, landslides and landslides, overlap of channels of underground rivers, etc. If water left the well due to changes in hydrogeology, then it will most likely not be possible to repair it, and it will be easier and cheaper to dig up a new source.
Note! With catastrophic drops in the water level in the vein due to changes in the hydrogeological picture of the area, the only way to save the source is to go to the next stratum.
Repairs

If the fluid level in the water intake falls, but you cannot determine why the water left the well, a set of measures should be taken to diagnose and eliminate the causes of this phenomenon.
For those who are going to work with their own hands, our specialists have compiled a step-by-step instruction:
- The water from the well is pumped out by a pump. It is better to use an ordinary surface vortex unit of the “Kid” type;

- The walls of the casing are washed off from the plaque using a metal brush or strong water pressure, then leave them to dry;

- We inspect the bottom of the well, and if there is a layer of sand on it - we extract it with a shovel and give it to the buckets;

- We collect the gravel bedding (bottom filter) in a separate container and wash it with a solution of water and bleach, then rinse in clean water;

- If there is a lot of silt and fine sand under the filter, then knock a round shield out of the boards to the size of the casing and put it on the bottom (important for imperfect models), and pour washed gravel on top;

- Carefully by the light of the lantern, we inspect the casing walls for cracks, cracks, displacements of the rings relative to the central axis, drips and fistulas. We repair all found flaws with the help of a mixture of cement and liquid glass; you can use ready-made sealants suitable for use with drinking water;

- We strengthen the column with steel hinges and staples;

- We look forward to filling the water intake, while note the time set by the liquid of its normal level. If this time does not exceed 2 - 5 days (for the cumulative well), then we can assume that the event was successful.

Note! If these activities did not help, then it remains only to deepen the mine. This is done as in the construction of a well from rings, only rings for a well use a smaller diameter: the ring is lowered to the bottom and ground is dug under it until it drops, then the next ring is placed on it and the process is repeated until the desired depth is reached.
Conclusion
If you notice an unusual decrease in the water level in the well or a decrease in its performance, it is likely that the time has come for preventive maintenance and cleaning of the structure. This can be done independently with the help of our guide, and for clarity - the video in this article.