Why rusty water comes from the well: types of filters
If rusty water comes from a well, then this can be explained by nothing more than an increased iron content in the source, and this is a completely natural phenomenon, since such a metal is extremely common in the bowels of the Earth. Most often such a disease affects the artesian aquifer, where just the most often you can find deposits of iron ore. Below we will talk about this in more detail, consider ways to protect, and also see the thematic video in this article on this topic.

Water containing iron
Why is that bad

- If the ferrum is present in excess in drinking water, then this can be determined not only by color, but also by taste and smell during its use, which makes its ingestion at least unpleasant. A serious danger is that the content of only 0.3 g of Fe in one liter of liquid can cause allergic reactions on the skin, not to mention red drains on plumbing fixtures and problems in washing white linen.
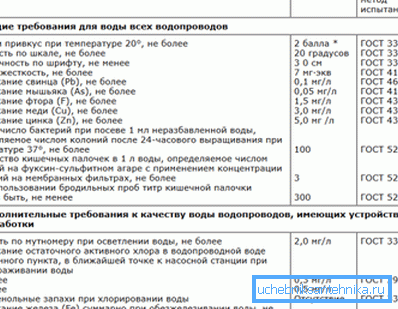
- But is it really dangerous for the iron content in water to be healthy, if such a liquid is ingested regularly? If we talk about the Russian Federation, then this indicator has a third degree of importance on sanitary standards. But according to the WHO (World Health Organization), iron-fortified water is absolutely not harmful to the body if the iron content is up to 0.8 mln per kilogram of body weight.
- Now you can make the simplest mathematical calculations - if you take the weight of a teenager, for example, 50kg, then the daily rate will be 40ml of ferrum per day. Can you imagine how much water you need to drink at least 5 liters for this! But note that we are talking about acceptable standards, whereas rusty water from a well needs special cleaning, that is, filters are needed here.
Note. As you understand, despite the existing opinion about the danger of iron, that is, its negative impact on the body, in fact, everything is not so scary. Just when it seems to you that the rate has been exceeded, you need to make a laboratory chemical analysis of the well.

- In the photo above you see the effects of flowing rusty water - pipes and fittings, in fact, have become unusable. The fact is that in the aquifer contains ferrous iron, but when the fluid is pumped up and into the pipes, it interacts with oxygen, resulting in oxidation. That is, now we are already dealing with trivalent Fe, or simply speaking - rust.
- From the point of view of the consumer, everything looks much more prosaic - trivalent iron (rust) does not dissolve in water, so it precipitates. The problem here is that it is not just red drains on the plumbing that can be washed, but deposits in the pipes that cause corrosion and destruction. In fact, such a state of things is unacceptable, as it can significantly hit the pocket (replacement of pipes often entails an overhaul).
Cleaning methods

Well, why rusty water in the well is now clear, and the fact that it is not particularly harmful to the body is also understandable, but, nevertheless, cleaning is needed at least to spare the entire system of water supply and sewerage.
There is more than one way to do this, but the principle always remains the same - first you need to oxidize the ferrum, that is, make it trivalent (the process is called aeration), and then collect the precipitate (suspension) through a filter. The difference lies only in the methods, or how they will oxidize, and then filter the water.
If you are looking for a simple method for carrying out the procedure described above, then it should be noted that simple solutions do not exist here in principle - for natural aeration (oxidation), certain equipment and time are needed. But aeration with the help of reagents (the initial substance that is involved in a chemical reaction) requires constant monitoring of the presence of chemicals and the reloading of filters.
In addition, there is increased sensitivity to the dosage - if there is an excess of chlorine, and with a deficiency - ferrum will remain.
Recommendation. In the case of a well design, you should take samples for water analysis from your neighbors in order to use the cleanest aquifer. At the same time, the price of drilling may, of course, increase, but you will save on further exploitation.
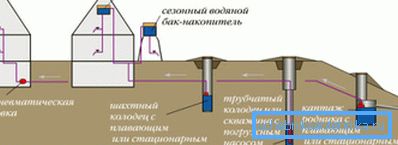
The easiest way to clean in a private house or in the country, when the water from the well rusts, is to install a large tank of stainless steel or food-grade plastic for sludge in the attic (the more - the better).
The method consists in oxidation and subsequent sludge, that is, water enters the pipes where it comes into contact with oxygen, then the iron becomes trivalent and after that it takes time, at least 4-6 hours, for it to precipitate to the bottom of the tank. The drain is installed in such cases a few centimeters above the bottom of the tank, thus creating a natural sump.
To increase the rate of oxidation in such a home-grown method, they resort to a little trick - they put a tank compressor in the tank, significantly speeding up the process of oxidation and removal of hydrogen sulfide. In cases where the capacity is large enough and this volume is enough for you for a day, your problem is almost solved - you just need to replenish the water supply in the reserve tank every evening.
Of course, at the summer cottage there may be a need for watering plants, but in such situations you can make a tie-in to the tank and watering with not filtered water - this will not hurt flora.
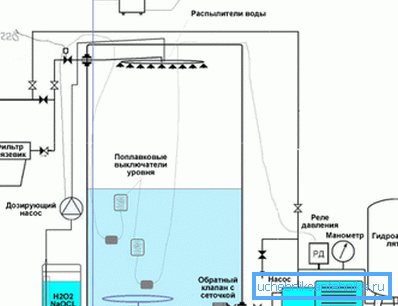
The aeration and metering free-flow system by the principle of the device practically does not differ from the above described attic device. Only here the free-flow adapter is a tank into which water enriched with oxygen from the compressor flows under pressure through nozzles, which speeds up the process. But if you want to make it even faster, then a reagent (hydrogen peroxide or sodium hydrochloride) is placed at the inlet.
Note. Industrial aerators do not make for long sludge and suspensions are removed using a filter located at the outlet of the tank. Such a tank is usually installed in the basement, therefore, in addition to the submersible pump in the well, an additional one is needed - to pump water from the tank.
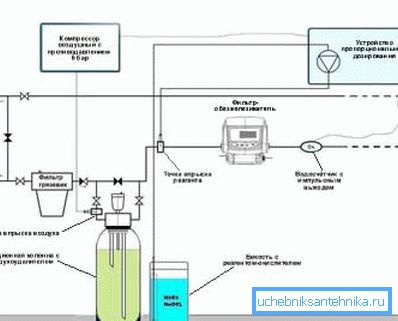
There are three types of pressure installations that neutralize iron in water; these are combined units, where reagents are combined with an aerator, as well as reagent (without an aerator) and non-reagent systems. The great advantage of such neutralizers is that they do not need an additional pumping station to supply water to the water distribution unit - a downhole submersible pump carrying water intake is sufficient.
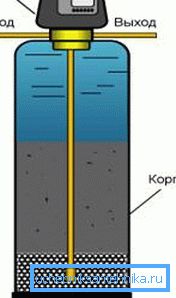
Whether you need to remove iron from water or not is up to you to decide yourself first, but if its composition exceeds 0.3mlg / l, then you can definitely say what you need. If such a question concerns a summer cottage, where you are extremely rare, and the water there is used purely for technical purposes, then you are unlikely to install such an installation with your own hands, but for a permanent place of residence you cannot do without it.
Conclusion
If you are still going to install a cleaning system, then you need to decide whether it will be a pressure or non-pressure unit. Despite the fact that the manufacturer’s instructions for pressure systems colorfully paint its advantages, practice shows that the non-pressure system is more reliable, which means its service life is longer.